identifywle
wle 时间:2021-02-28 阅读:()
PoliticalBehavior,Vol.
19,No.
1,1997THEECONOMICSOFPOLITICSINCOMPARATIVEPERSPECTIVEREVISITED:AnIntroductionChristopherJ.
AndersonandChristopherWlezienStudentsofpoliticalbehaviorhavelongbeeninterestedinwhetherandhoweconomicsstructurespolitics.
Overthepasttwoandahalfdecades,muchefforthasbeendevotedtoinvestigatingtheinfluenceoftheeconomyonvotingbehavior,electionoutcomes,andgovernmentsupportindemocraticpolities.
AspecialissueofPoliticalBehaviorexplicitlyaddressedtheseissuessomethirteenyearsago.
Sincethepublicationofthatspecialissue,however,anumberofimportantdevelopmentshaveoccurred.
Clearly,wehavelearnedagreatdealabouttheinfluenceoftheeconomyonelections.
Wehavebeenabletoestablishthattherearepowerfuleffectsofeconomicconditionsandperceptionsatvariouslevelsofanalysis(seeNan-nestadandPaldam,1994,foranoverview).
Increasingly,attentionhascen-teredonidentifyinghowtheeconomyinfluencesvotechoice;thatis,researchhasfocusedonwhichofvoters'manyeconomicperceptionsaremostimpor-tant(seeespeciallyLewis-Beck,1988).
Thecumulativebodyofempiricalworknowsupportsasociotropicelectoratethatvotesonthebasisofthestateofthenationaleconomy.
Thebulkofthisworkfindsthatvotersevaluatepastperformance,althoughsomerecentresearchalsosuggeststhatvotersare"prospective,"basingtheirpoliticaljudgmentsonexpectationsoffutureeco-nomicperformance(Lewis-Beck,1988).
Regardlessoftheexactnatureoftheeffects,itisnowfairlyclearthatvotechoiceandelectionoutcomesaredrivenbythedirectionandmagnitudeofeconomicchange,whetherretrospectiveorprospectiveinnature.
ScholarlyinterestintherelationshipbetweentheeconomyandpoliticsChristopherJ.
Anderson,J.
L.
KelloggGraduateSchoolofManagement,NorthwesternUni-versity,Evanston,IL60208-2001,andDepartmentofPoliticalScience,RiceUniversity,Houston,TX77005-1892.
ChristopherWlezien,DepartmentofPoliticalScience,UniversityofHouston,Houston,TX77204-3474.
10190-9320/97/0300-0001SOJ2.
50/01997PlenumPublishingCorporationdoesnotendwithelections,however.
Recentresearchalsohasexaminedtheeffectsoftheeconomyonpublicsupportforvariouspoliticalactorsandinsti-tutions,suchaspoliticalparties,coalitiongovernments,Europeanintegration,anddemocraticsystems(see,e.
g.
,MacKuen,Erikson,andStimson,1989;EichenbergandDalton,1993;Duch,1993;Clarke,Dutt,andKornberg,1993;Anderson,1995a).
Otherrecentresearchhasexploredtheeffectsoftheeconomyonpolicyattitudesandpoliticalvalues(see,e.
g.
,Durr,1993;DuchandTaylor,1993;ClarkeandDutt,1991;AbramsonandInglehart,1995;Wlezien,1995).
Most,ifnotall,ofthisresearchrevealsimportanteconomiceffects.
Yetotherresearchhasfocusedonthecausesofeconomicperceptionsthemselves,bothcross-sectionallyandovertime(see,e.
g.
,Neumann,1986;Luskin,1987;Conover,Feldman,andKnight,1987;MacKuenandMouw,1995;WilcoxandWlezien,1996).
Itappearsthatperceptionsofeconomicperformancevaryacrossindividuals,dependingonsocioeconomicstatus,eco-nomicexperiences,cognitiveabilities,andpoliticalpreferences.
Italsoseemstobethecasethatperceptionsofeconomicperformancecanvaryovertimeindependentlyofactualeconomicconditions.
Overall,researchontheecon-omyandpoliticsismovinginmanydifferentdirections,reflectingamorediversesetoftheoreticalconcerns.
InApril1995,aworkshopwasheldatRiceUniversitytotakestockofthesedevelopmentsandtoidentifyandpursuethenextstageofresearchontheeconomicsofpoliticalbehaviorandattitudes.
Theworkshopbroughttogetheranumberofscholarswithdifferentperspectivesonthesubject.
Asubsetofthepaperspresentedattheworkshophasbeencompiledforthisvolume.
1Eachofthearticlescontainedhereinbuildsonthebodyofpreviousworkandseekstoadvanceourunderstandingofthenexusbetweeneconomicsandpoliticsinimportantways.
Indeed,eachofthearticlesformspartofthenewagendaoutlinedabove.
Tobeginwith,Wlezien,Franklin,andTwiggsreconsidertheeffectsofeco-nomicperceptionsonvotingbehavior,focusingonLewis-Beck's(1988)semi-nalwork.
Buildingonthegrowingliteraturethatexaminesthedeterminantsofeconomicperceptions,theauthorstreatperceptionsasadependentvari-ableandaskwhethertheyaretrulyexogenous,asmostresearchersassume.
Theiranalysesshowthatindividuals'economicperceptions,particularlypro-spectiveones,arestructuredbyvotechoiceitself.
Moreover,whenthisendo-geneityistakenintoaccount,theeffectsofeconomicperceptionsonvotechoicearesubstantiallyreduced.
Thenexttwoarticlesaddressmaterialistandpostmaterialistvalueorienta-tions.
IntheirstudyofvaluechangeinWesternEurope,Clarke,Dutt,andRapkinchallengeAbramsonandInglehart's(1995)pathbreakingresearchonthesubject.
Clarkeetal.
findthattheobservedtrendtowardpostmaterialism2ANDERSONANDWLEZIENlargelyreflectsmacroeconomicconditions.
Basedontheseanalysestheycon-cludethatthetrendisameasurementartifact.
Inresponse,Abramson,Ellis,andInglehartprovidetheirownanalysesandarguethatClarkeetal.
'sconclu-sionsareunfounded.
Inabriefpostscript,Clarkeetal.
offeranassessmentofwhatwehavelearnedabouttheeconomicsofvaluechange.
ThefinaltwoarticlesaddressattitudestowardEuropeanintegration,whichalsohaveonlyrecentlybeenanalyzedfromaneconomicperspective.
Build-ingontheevolvingliteratureonthesubject,DuchandTaylorexaminetheinfluenceofobjectiveeconomicconditionsonpublicsupportforEuropeanintegration.
Incontrast,GabelandWhittenexaminetheinfluenceofeco-nomicperceptions.
Theirfindingsdiffer:whileDuchandTaylorshowthatsupportforEuropeanintegrationislargelyunrelatedtoeconomicperfor-mance,GabelandWhittenfindthatsupportforintegrationiscloselylinkedtoeconomicperceptionsattheindividuallevel.
Inonesense,thesefindingsalsosuggestthatpeoplesperceptionsoftheeconomydonotneatlyreflectobjectiveeconomicconditionsthemselves.
Allofthearticlesinthisissuedoshareoneimportantfeature:theyallareexplicitlycomparativeandcross-nationalinapproach.
Suchcomparativere-searchoffersobviousadvantages.
Perhapsmostimportantly,itallowsustoassesswhetherrelationshipsholdinageneralwayacrosspoliticalcontexts.
Ofcourse,itmaybethatthepoliticalsystemstructurestheeffectsofeconomicconditionsandperceptionsinpredictableways(see,e.
g.
,PowellandWhitten,1993;Remmer,1993;PacekandRadcliff,1995;Anderson,1995b).
Italsomaybethatthepoliticalsystemeffectivelystructureseconomicperceptionsthemselves.
Theseissueswarranttheongoingattentionofpoliticalscientists.
Itisasimportanttotakestockofwherewehavebeenasitisusefultoplotwherewearegoing,particularlywhereresearchhasevolved(andisevolving)invariousdirections.
Judgingfromourexperienceattheworkshop,researchontheeconomyandpoliticalbehavior—whilemovingindifferentdirec-tions—ismovingforwardinsystematicways.
InresponsetoMichaelLewis-Beck'sintroductiontothepreviousspecialissueofPoliticalBehavior,wecansaythatwehavemovedbeyondouroriginalpreoccupationwithwhethertheeconomyinfluencesbehaviortofocusonhowtheeconomyinfluencesbehav-ior.
Moreover,wehavemovedbeyondourpreoccupationwithelectionout-comesandvotingbehaviorinahandfulofcountriestofocusonarangeofsubstantiveconcernsinanumberofregionsoftheworld.
Thesedevelop-mentscauseustobesanguineabouttheenterprise.
NOTE1.
WealsohaveincludedanarticlebyAbramson,Ellis,andInglehartthatwasnotpresentedattheworkshopheldApril22-23,1995.
Asidefromtheindividualscontainedherein,severalECONOMICSOFPOLITICS3othersparticipatedintheworkshop:RobertErikson,CarolynFunk,PatriciaGarci'a-Monet,JanLeighley,MichaelMacKuen,CalvinMouw,HelmutNorpoth,DavidSanders,MarianneStewart,andDanielS.
Ward.
WearegratefultotheCenterfortheStudyofInstitutionsandValuesatRiceUniversityaswellastheCollegeofSocialSciencesandtheCenterforPublicPolicyattheUniversityofHoustonfortheirsponsorship.
WealsothankAnneCooney-Smith,ChristineGuillory,JuanCarlosHuerta,M.
ShawnReichert,RichardRozelle,RobertStein,RichardStoll,KentTedin,andGregoryWeiher.
REFERENCESAbramson,PaulR.
,andRonaldInglehart(1995).
ValueChangeinGlobalPerspective.
AnnArbor:UniversityofMichiganPress.
Anderson,ChristopherJ.
(1995a).
Thedynamicsofpublicsupportforcoalitiongov-ernments.
ComparativePoliticalStudies28(3):350-383.
Anderson,ChristopherJ.
(1995b).
Partysystemsandthedynamicsofgovernmentsupport:BritainandGermany,1960-1990.
EuropeanJournalofPoliticalResearch27(1):93-118.
Clarke,HaroldD.
,andNitishDutt(1991).
Measuringvaluechangeinwesternindus-trializedsocieties:Theimpactofunemployment.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview85:905-920.
Clarke,HaroldD.
,NitishDutt,andAllanKornberg(1993).
ThepoliticaleconomyofattitudestowardpolityandsocietyinwesternEuropeandemocracies.
JournalofPolitics55(4):998-1021.
Clarke,Harold,andMarianneStewart(1994).
Prospections,retrospections,andratio-nality:The"bankers"modelofpresidentialapprovalreconsidered.
AmericanJour-nalofPoliticalScience38(4):1104-1123.
Conover,Pamela,StanleyFeldman,andKathleenKnight(1987).
Thepersonalandpoliticalunderpinningsofeconomicforecasts.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience31.
559-583.
Duch,RaymondM.
(1993).
Toleratingeconomicreform:Popularsupportfortransi-tiontoafreemarketinrepublicsoftheformerSovietUnion.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview87:590-608.
Duch,RaymondM.
,andMichaellTaylor(1993).
Postmaterialismandtheeconomiccondition.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience37:747-778.
Durr,RobertH.
(1993).
WhatmovespolicysentimentAmericanPoliticalScienceReview87(1):158-170.
Eichenberg,Richard,andRussellDalton(1993).
EuropeansandtheEuropeanCom-munity:ThedynamicsofpublicsupportforEuropeanintegration.
InternationalOrganization47:507-534.
Goodhart,C.
A.
E.
andR.
J.
Bhansali(1970).
Politicaleconomy.
PoliticalStudies18:43-106.
Kramer,Gerald(1971).
Short-termfluctuationsinU.
S.
votingbehavior,1896-1964.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview65:131-143.
Lewis-Beck,Michael(1988).
EconomicsandElections:TheMajorDemocracies.
AnnArbor:UniversityofMichiganPress.
Luskin,Robert(1987).
Measuringpoliticalsophistication.
AmericanJournalofPoliti-calScience31:856-899.
MacKuen,MichaelB.
,RobertS.
Erikson,andJamesA.
Stimson(1989).
Macropar-tisanship.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview83(4):1125-1142.
4ANDERSONANDWLEZIENMacKuen,MichaelB.
,andCalvinMouw(1995).
SocialClassandEconomicJudg-ments.
PaperpresentedattheWorkshopontheEconomyandPoliticalBehavior,RiceUniversity,Houston,TX,April22-23,1995.
Nannestad,Peter,andMartinPaldam(1994).
TheVP-function:Asurveyofthelitera-tureonvoteandpopularityfunctionsafter25years.
PublicChoice79:213-245.
Neumann,W.
Russell(1986).
TheParadoxofMassPolitics:KnowledgeandOpinionintheAmericanElectorate.
Cambridge,MA:HarvardUniversityPress.
Pacek,AlexanderC.
,andBenjaminRadcliff(1995).
Economicvotingandthewelfarestate:Across-nationalanalysis.
JournalofPolitics57(1):44-61.
Powell,G.
Bingham,andGuyWhitten(1993).
Across-nationalanalysisofeconomicvoting:Takingaccountofthepoliticalcontext.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience37:391-414.
Remmer,KarenL.
(1993).
ThepoliticaleconomyofelectionsinLatinAmerica,1980-1991.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview87(2):393-407.
Wilcox,NathanielT,andChristopherWlezien(1996).
Thecontaminationofresponsestosurveyitems:Economicperceptionsandpoliticaljudgments.
PoliticalAnalysis5:181-213.
Wlezien,Christopher(1995).
Thepublicasthermostat:Dynamicsofpreferencesforspending.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience39:981-1000.
ECONOMICSOFPOLITICS5CopyrightofPoliticalBehavioristhepropertyofSpringerScience&BusinessMediaB.
V.
anditscontentmaynotbecopiedoremailedtomultiplesitesorpostedtoalistservwithoutthecopyrightholder'sexpresswrittenpermission.
However,usersmayprint,download,oremailarticlesforindividualuse.
19,No.
1,1997THEECONOMICSOFPOLITICSINCOMPARATIVEPERSPECTIVEREVISITED:AnIntroductionChristopherJ.
AndersonandChristopherWlezienStudentsofpoliticalbehaviorhavelongbeeninterestedinwhetherandhoweconomicsstructurespolitics.
Overthepasttwoandahalfdecades,muchefforthasbeendevotedtoinvestigatingtheinfluenceoftheeconomyonvotingbehavior,electionoutcomes,andgovernmentsupportindemocraticpolities.
AspecialissueofPoliticalBehaviorexplicitlyaddressedtheseissuessomethirteenyearsago.
Sincethepublicationofthatspecialissue,however,anumberofimportantdevelopmentshaveoccurred.
Clearly,wehavelearnedagreatdealabouttheinfluenceoftheeconomyonelections.
Wehavebeenabletoestablishthattherearepowerfuleffectsofeconomicconditionsandperceptionsatvariouslevelsofanalysis(seeNan-nestadandPaldam,1994,foranoverview).
Increasingly,attentionhascen-teredonidentifyinghowtheeconomyinfluencesvotechoice;thatis,researchhasfocusedonwhichofvoters'manyeconomicperceptionsaremostimpor-tant(seeespeciallyLewis-Beck,1988).
Thecumulativebodyofempiricalworknowsupportsasociotropicelectoratethatvotesonthebasisofthestateofthenationaleconomy.
Thebulkofthisworkfindsthatvotersevaluatepastperformance,althoughsomerecentresearchalsosuggeststhatvotersare"prospective,"basingtheirpoliticaljudgmentsonexpectationsoffutureeco-nomicperformance(Lewis-Beck,1988).
Regardlessoftheexactnatureoftheeffects,itisnowfairlyclearthatvotechoiceandelectionoutcomesaredrivenbythedirectionandmagnitudeofeconomicchange,whetherretrospectiveorprospectiveinnature.
ScholarlyinterestintherelationshipbetweentheeconomyandpoliticsChristopherJ.
Anderson,J.
L.
KelloggGraduateSchoolofManagement,NorthwesternUni-versity,Evanston,IL60208-2001,andDepartmentofPoliticalScience,RiceUniversity,Houston,TX77005-1892.
ChristopherWlezien,DepartmentofPoliticalScience,UniversityofHouston,Houston,TX77204-3474.
10190-9320/97/0300-0001SOJ2.
50/01997PlenumPublishingCorporationdoesnotendwithelections,however.
Recentresearchalsohasexaminedtheeffectsoftheeconomyonpublicsupportforvariouspoliticalactorsandinsti-tutions,suchaspoliticalparties,coalitiongovernments,Europeanintegration,anddemocraticsystems(see,e.
g.
,MacKuen,Erikson,andStimson,1989;EichenbergandDalton,1993;Duch,1993;Clarke,Dutt,andKornberg,1993;Anderson,1995a).
Otherrecentresearchhasexploredtheeffectsoftheeconomyonpolicyattitudesandpoliticalvalues(see,e.
g.
,Durr,1993;DuchandTaylor,1993;ClarkeandDutt,1991;AbramsonandInglehart,1995;Wlezien,1995).
Most,ifnotall,ofthisresearchrevealsimportanteconomiceffects.
Yetotherresearchhasfocusedonthecausesofeconomicperceptionsthemselves,bothcross-sectionallyandovertime(see,e.
g.
,Neumann,1986;Luskin,1987;Conover,Feldman,andKnight,1987;MacKuenandMouw,1995;WilcoxandWlezien,1996).
Itappearsthatperceptionsofeconomicperformancevaryacrossindividuals,dependingonsocioeconomicstatus,eco-nomicexperiences,cognitiveabilities,andpoliticalpreferences.
Italsoseemstobethecasethatperceptionsofeconomicperformancecanvaryovertimeindependentlyofactualeconomicconditions.
Overall,researchontheecon-omyandpoliticsismovinginmanydifferentdirections,reflectingamorediversesetoftheoreticalconcerns.
InApril1995,aworkshopwasheldatRiceUniversitytotakestockofthesedevelopmentsandtoidentifyandpursuethenextstageofresearchontheeconomicsofpoliticalbehaviorandattitudes.
Theworkshopbroughttogetheranumberofscholarswithdifferentperspectivesonthesubject.
Asubsetofthepaperspresentedattheworkshophasbeencompiledforthisvolume.
1Eachofthearticlescontainedhereinbuildsonthebodyofpreviousworkandseekstoadvanceourunderstandingofthenexusbetweeneconomicsandpoliticsinimportantways.
Indeed,eachofthearticlesformspartofthenewagendaoutlinedabove.
Tobeginwith,Wlezien,Franklin,andTwiggsreconsidertheeffectsofeco-nomicperceptionsonvotingbehavior,focusingonLewis-Beck's(1988)semi-nalwork.
Buildingonthegrowingliteraturethatexaminesthedeterminantsofeconomicperceptions,theauthorstreatperceptionsasadependentvari-ableandaskwhethertheyaretrulyexogenous,asmostresearchersassume.
Theiranalysesshowthatindividuals'economicperceptions,particularlypro-spectiveones,arestructuredbyvotechoiceitself.
Moreover,whenthisendo-geneityistakenintoaccount,theeffectsofeconomicperceptionsonvotechoicearesubstantiallyreduced.
Thenexttwoarticlesaddressmaterialistandpostmaterialistvalueorienta-tions.
IntheirstudyofvaluechangeinWesternEurope,Clarke,Dutt,andRapkinchallengeAbramsonandInglehart's(1995)pathbreakingresearchonthesubject.
Clarkeetal.
findthattheobservedtrendtowardpostmaterialism2ANDERSONANDWLEZIENlargelyreflectsmacroeconomicconditions.
Basedontheseanalysestheycon-cludethatthetrendisameasurementartifact.
Inresponse,Abramson,Ellis,andInglehartprovidetheirownanalysesandarguethatClarkeetal.
'sconclu-sionsareunfounded.
Inabriefpostscript,Clarkeetal.
offeranassessmentofwhatwehavelearnedabouttheeconomicsofvaluechange.
ThefinaltwoarticlesaddressattitudestowardEuropeanintegration,whichalsohaveonlyrecentlybeenanalyzedfromaneconomicperspective.
Build-ingontheevolvingliteratureonthesubject,DuchandTaylorexaminetheinfluenceofobjectiveeconomicconditionsonpublicsupportforEuropeanintegration.
Incontrast,GabelandWhittenexaminetheinfluenceofeco-nomicperceptions.
Theirfindingsdiffer:whileDuchandTaylorshowthatsupportforEuropeanintegrationislargelyunrelatedtoeconomicperfor-mance,GabelandWhittenfindthatsupportforintegrationiscloselylinkedtoeconomicperceptionsattheindividuallevel.
Inonesense,thesefindingsalsosuggestthatpeoplesperceptionsoftheeconomydonotneatlyreflectobjectiveeconomicconditionsthemselves.
Allofthearticlesinthisissuedoshareoneimportantfeature:theyallareexplicitlycomparativeandcross-nationalinapproach.
Suchcomparativere-searchoffersobviousadvantages.
Perhapsmostimportantly,itallowsustoassesswhetherrelationshipsholdinageneralwayacrosspoliticalcontexts.
Ofcourse,itmaybethatthepoliticalsystemstructurestheeffectsofeconomicconditionsandperceptionsinpredictableways(see,e.
g.
,PowellandWhitten,1993;Remmer,1993;PacekandRadcliff,1995;Anderson,1995b).
Italsomaybethatthepoliticalsystemeffectivelystructureseconomicperceptionsthemselves.
Theseissueswarranttheongoingattentionofpoliticalscientists.
Itisasimportanttotakestockofwherewehavebeenasitisusefultoplotwherewearegoing,particularlywhereresearchhasevolved(andisevolving)invariousdirections.
Judgingfromourexperienceattheworkshop,researchontheeconomyandpoliticalbehavior—whilemovingindifferentdirec-tions—ismovingforwardinsystematicways.
InresponsetoMichaelLewis-Beck'sintroductiontothepreviousspecialissueofPoliticalBehavior,wecansaythatwehavemovedbeyondouroriginalpreoccupationwithwhethertheeconomyinfluencesbehaviortofocusonhowtheeconomyinfluencesbehav-ior.
Moreover,wehavemovedbeyondourpreoccupationwithelectionout-comesandvotingbehaviorinahandfulofcountriestofocusonarangeofsubstantiveconcernsinanumberofregionsoftheworld.
Thesedevelop-mentscauseustobesanguineabouttheenterprise.
NOTE1.
WealsohaveincludedanarticlebyAbramson,Ellis,andInglehartthatwasnotpresentedattheworkshopheldApril22-23,1995.
Asidefromtheindividualscontainedherein,severalECONOMICSOFPOLITICS3othersparticipatedintheworkshop:RobertErikson,CarolynFunk,PatriciaGarci'a-Monet,JanLeighley,MichaelMacKuen,CalvinMouw,HelmutNorpoth,DavidSanders,MarianneStewart,andDanielS.
Ward.
WearegratefultotheCenterfortheStudyofInstitutionsandValuesatRiceUniversityaswellastheCollegeofSocialSciencesandtheCenterforPublicPolicyattheUniversityofHoustonfortheirsponsorship.
WealsothankAnneCooney-Smith,ChristineGuillory,JuanCarlosHuerta,M.
ShawnReichert,RichardRozelle,RobertStein,RichardStoll,KentTedin,andGregoryWeiher.
REFERENCESAbramson,PaulR.
,andRonaldInglehart(1995).
ValueChangeinGlobalPerspective.
AnnArbor:UniversityofMichiganPress.
Anderson,ChristopherJ.
(1995a).
Thedynamicsofpublicsupportforcoalitiongov-ernments.
ComparativePoliticalStudies28(3):350-383.
Anderson,ChristopherJ.
(1995b).
Partysystemsandthedynamicsofgovernmentsupport:BritainandGermany,1960-1990.
EuropeanJournalofPoliticalResearch27(1):93-118.
Clarke,HaroldD.
,andNitishDutt(1991).
Measuringvaluechangeinwesternindus-trializedsocieties:Theimpactofunemployment.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview85:905-920.
Clarke,HaroldD.
,NitishDutt,andAllanKornberg(1993).
ThepoliticaleconomyofattitudestowardpolityandsocietyinwesternEuropeandemocracies.
JournalofPolitics55(4):998-1021.
Clarke,Harold,andMarianneStewart(1994).
Prospections,retrospections,andratio-nality:The"bankers"modelofpresidentialapprovalreconsidered.
AmericanJour-nalofPoliticalScience38(4):1104-1123.
Conover,Pamela,StanleyFeldman,andKathleenKnight(1987).
Thepersonalandpoliticalunderpinningsofeconomicforecasts.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience31.
559-583.
Duch,RaymondM.
(1993).
Toleratingeconomicreform:Popularsupportfortransi-tiontoafreemarketinrepublicsoftheformerSovietUnion.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview87:590-608.
Duch,RaymondM.
,andMichaellTaylor(1993).
Postmaterialismandtheeconomiccondition.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience37:747-778.
Durr,RobertH.
(1993).
WhatmovespolicysentimentAmericanPoliticalScienceReview87(1):158-170.
Eichenberg,Richard,andRussellDalton(1993).
EuropeansandtheEuropeanCom-munity:ThedynamicsofpublicsupportforEuropeanintegration.
InternationalOrganization47:507-534.
Goodhart,C.
A.
E.
andR.
J.
Bhansali(1970).
Politicaleconomy.
PoliticalStudies18:43-106.
Kramer,Gerald(1971).
Short-termfluctuationsinU.
S.
votingbehavior,1896-1964.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview65:131-143.
Lewis-Beck,Michael(1988).
EconomicsandElections:TheMajorDemocracies.
AnnArbor:UniversityofMichiganPress.
Luskin,Robert(1987).
Measuringpoliticalsophistication.
AmericanJournalofPoliti-calScience31:856-899.
MacKuen,MichaelB.
,RobertS.
Erikson,andJamesA.
Stimson(1989).
Macropar-tisanship.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview83(4):1125-1142.
4ANDERSONANDWLEZIENMacKuen,MichaelB.
,andCalvinMouw(1995).
SocialClassandEconomicJudg-ments.
PaperpresentedattheWorkshopontheEconomyandPoliticalBehavior,RiceUniversity,Houston,TX,April22-23,1995.
Nannestad,Peter,andMartinPaldam(1994).
TheVP-function:Asurveyofthelitera-tureonvoteandpopularityfunctionsafter25years.
PublicChoice79:213-245.
Neumann,W.
Russell(1986).
TheParadoxofMassPolitics:KnowledgeandOpinionintheAmericanElectorate.
Cambridge,MA:HarvardUniversityPress.
Pacek,AlexanderC.
,andBenjaminRadcliff(1995).
Economicvotingandthewelfarestate:Across-nationalanalysis.
JournalofPolitics57(1):44-61.
Powell,G.
Bingham,andGuyWhitten(1993).
Across-nationalanalysisofeconomicvoting:Takingaccountofthepoliticalcontext.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience37:391-414.
Remmer,KarenL.
(1993).
ThepoliticaleconomyofelectionsinLatinAmerica,1980-1991.
AmericanPoliticalScienceReview87(2):393-407.
Wilcox,NathanielT,andChristopherWlezien(1996).
Thecontaminationofresponsestosurveyitems:Economicperceptionsandpoliticaljudgments.
PoliticalAnalysis5:181-213.
Wlezien,Christopher(1995).
Thepublicasthermostat:Dynamicsofpreferencesforspending.
AmericanJournalofPoliticalScience39:981-1000.
ECONOMICSOFPOLITICS5CopyrightofPoliticalBehavioristhepropertyofSpringerScience&BusinessMediaB.
V.
anditscontentmaynotbecopiedoremailedtomultiplesitesorpostedtoalistservwithoutthecopyrightholder'sexpresswrittenpermission.
However,usersmayprint,download,oremailarticlesforindividualuse.
- identifywle相关文档
- 温江wle
- describewle
- Moldedwle
- 固定器wle
- 2.wle
- agreementwle
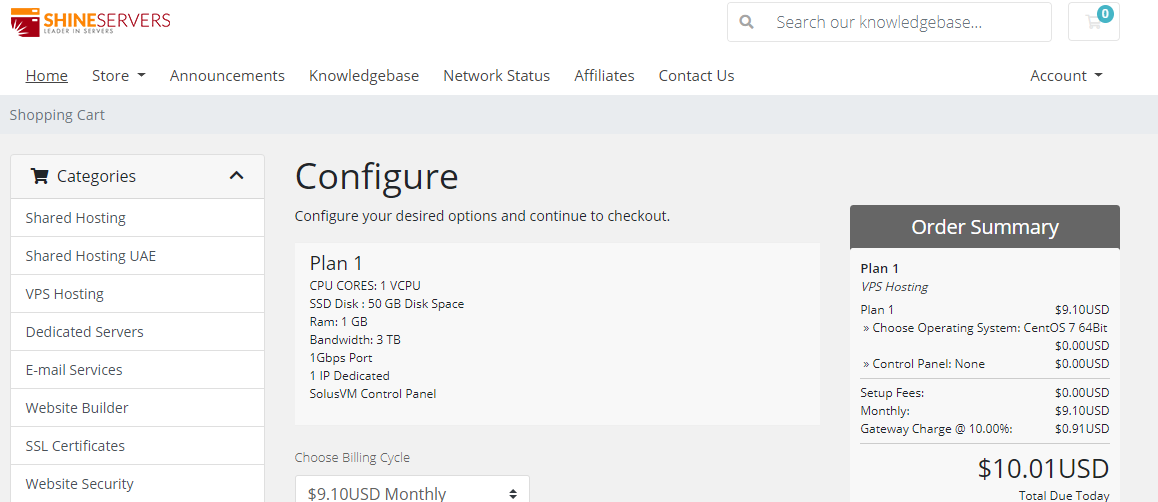
ShineServers(5美元/月)荷兰VPS、阿联酋VPS首月五折/1核1G/50GB硬盘/3TB流量/1Gbps带宽
优惠码50SSDOFF 首月5折50WHTSSD 年付5折15OFF 85折优惠,可循环使用荷兰VPSCPU内存SSD带宽IPv4价格购买1核1G50G1Gbps/3TB1个$ 9.10/月链接2核2G80G1Gbps/5TB1个$ 12.70/月链接2核3G100G1Gbps/7TB1个$ 16.30/月链接3核4G150G1Gbps/10TB1个$ 18.10/月链接阿联酋VPSCPU内存SS...
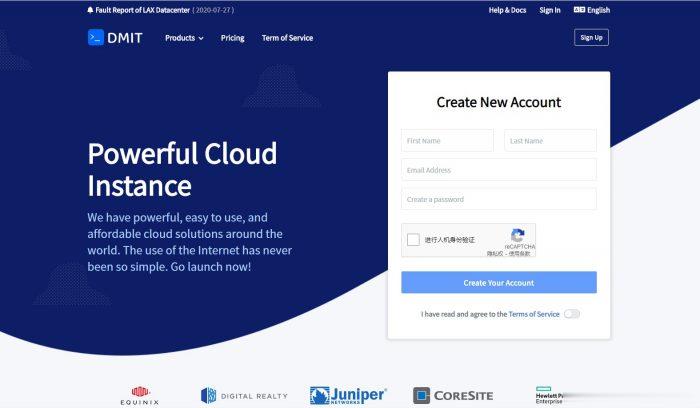
DMIT:香港国际线路vps,1.5GB内存/20GB SSD空间/4TB流量/1Gbps/KVM,$9.81/月
DMIT怎么样?DMIT是一家美国主机商,主要提供KVM VPS、独立服务器等,主要提供香港CN2、洛杉矶CN2 GIA等KVM VPS,稳定性、网络都很不错。支持中文客服,可Paypal、支付宝付款。2020年推出的香港国际线路的KVM VPS,大带宽,适合中转落地使用。现在有永久9折优惠码:July-4-Lite-10OFF,季付及以上还有折扣,非 中国路由优化;AS4134,AS4837 均...
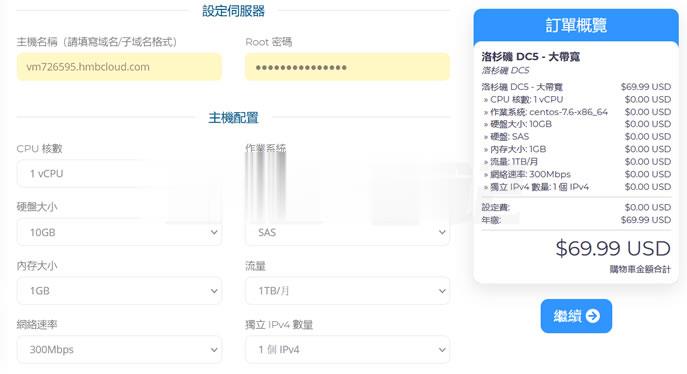
半月湾hmbcloud升级500Mbps带宽,原生VPS,$4.99/月
关于半月湾HMBCloud商家之前也有几篇那文章介绍过这个商家的产品,对于他们家的其他产品我都没有多加留意,而是对他们家的DC5机房很多人还是比较喜欢的,这个比我们有些比较熟悉的某商家DC6 DC9机房限时,而且半月湾HMBCloud商家是相对便宜的。关于半月湾DC5机房的方案选择和介绍:1、半月湾三网洛杉矶DC5 CN2 GIA同款DC6 DC9 1G内存 1TB流量 月$4.992、亲测选择半...
wle为你推荐
-
godaddy美国GODADDY 域名支持域名别名解析吗?godaddyGodaddy域名怎么接受神雕侠侣礼包大全神雕侠侣手游每天送的元宝买什么合适怎么升级ios6苹果iPhone6怎么升级系统mate8价格华为mate8 128g售价多少钱宕机宕机是什么意思云挂机快手极速版后台云挂机辅?助各位用了吗?在哪找的?什么是云平台什么是云平台管理软件,一个云平台软件应该具有哪些基本功能gbk编码表GB GBK utf8码的区别网站排名靠前网站排名靠前是否就意味着运营成功?阐述原因