multiple七七seo
七七seo 时间:2021-03-25 阅读:()
IndexAcetylcholine(ACh),efferents,350ffmodulationofouterhaircell,169Actinmonomers,outerhaircell,147–148Actin-spectrincorticallattice,154Activeamplification,andmechanosensorytransducers,79ffDrosophila,199–201tympanalears,201–203ultrasonichearing,201–203Activebandwidth,amplification,69frequencyselectivity,69Activecochlearmechanics,history,39ffActivehairbundle,mechanics,127–129movements,112–114oscillations,122ffActivehairbundleresponse,bullfrogsaccule,124Activemodels,nonlinearityandphysiologicalvulnerability,382–383Activemotormodel,mechanismsofadaptation,107ffActiveoscillators,physicalrealizations,75ffActiveprocessesandhaircells,Tiliquarugosa,54Activeprocesses,7–8,53–55andautocorrelationfunction,73criteriafor,195evolution,204futureresearchdirections,461ffhairbundle,53–55hair-cellbundlesinmammals,464historicalantecedents,10ff,39ff,461ffinallanimaltaxa,463–464insecthearing,191,194ff,203–204insectsvs.
vertebrates,204mosquitoes,196ffnonmammalianspecies,249,337–338outerhaircells,55Ranacatesbeiana,54Trachemisscriptaelegans,54–55Activetravelingwaves,criticaloscillators,83ffAdaptationkinetics,hairbundle,104–105Adaptationmotor,relaxationelement,122haircells,465Adaptation,haircell,102ffmechanicalcorrelates,112–114mechanisms,107ffsustainedstimuli,102ffAgerelatedhearingloss,andOAE,293AgerelatedOAE,432,435ffAllen-Faheyparadigm,324Aminoglycosideantibiotics,andOAE,286–287Amphibian,seealsoBufo,Hyla,Hylids,Rana,Ranids,Xenopusamphibianpapilla,214ffauditorynerve,215–217basilarpapilla,214ffcharacteristicfrequencyofear,215–217click-evokedemissions,224–225DPOAE,222–224evokedemissions,220fffirstmeasureofSOAE,213haircells,215innerear,214ffmiddleear,214noise-evokedemissions,224–225OAEs,211ffsaccule,215SFOAE,217,ff,220–222tectorialmembrane,215Amphipaths,modulationofouterhaircell,170Amplification,andOAE,328–329criticaloscillators,63ffAnguillaanguilla(eel),ampullahaircells,115Anoxia,OAE,285Antennalears,insect,191–192,197–199Antennalreceptor,Drosophila,199–201Archosaur,definition,212evokedemissions,245ffOAEsvs.
mammals,249ffOAEs,211ff,241ffseealsobird,avianAspirin,cochlearamplifiergain,398–399Auditoryfovea,barnowl,245473474IndexAuditorymicrostructure,cuestoOAEs,16ffAuditorynerveresponse,amphibian,215–217Tytoalba,242vs.
DPOAE,235–236Auditorypapilla,seealsoBasilarpapillaAuditorypapillaeinlizards,seeBasilarpapillaAuditoryresearch,OAEsrolein,31–32Auditorysystemfunctions,andcriticaloscillators,79ffAvian,seealsoArchosaurs,birdsAxialstiffness,outerhaircell,167ffBarnowl,seeTytoalbaBasilarmembranedisplacements,modulationbyACh,353Basilarmembranefrequencyselectivity,384ffBasilarmembranemotion,measurements,51–53Basilarmembranestiffness,349Basilarmembrane,motionmeasurements,46–47non-linearity,47ffobservationsofactivebehavior,381outerhaircell,347–348tuning,47,50Basilarpapilla,amphibian,214ffbird,241fffrequencymap,228–229,243lizard,225–226micromechanics,242–243tonotopy,241–242Tytoalba,241Békésy,seevonBékésyBiasingprocess,hairbundle,104Bicuculine,modulationofOAEs,363Bird,seealsoArchosaurs,Avian,Dromaiusnovaehollandiae,Gallusgallus,Sturnusvulgaris,Tytoalbabasilarpapilla,241ffcomparativeSEOAE,245–246DPOAE,247–249efferentmodulationofhaircells,346evokedemissions,245ffhaircells,241ffinnerear,241ffSOAE,244–245stereocilia,242Bobtailskink,see,Lizards,TiliquarugosaBrownianmotion,fluctuation-dissipationfunction,72Bufo,seealsoAmphibianBullfrogsaccule,activehairbundleresponse,124spontaneoushairbundleoscillations,116–117activehairbundlemovements,113hairbundleadaptation,110–111hairbundlemovements,115Ca2+reclosuremodel,hairbundleadaptation,111–112Ca2+,effectonspontaneoushairbundleoscillations,117–118Caimancrocodilus(Caiman),DPOAE,247–249SEOAE,245–246Calcium,regulationofadaptation,105–106Calcium-inducedcalciumrelease,seealsoCICR,efferents,350cAMPsecond-messengerpathway,regulationofadaptation,107CEOAE,definition,33seealsoTEOAEChannelgating,hairbundle,118ffChaoticdynamics,mammaliancochlea,87Characteristicfrequency,amphibianear,215–217Chicken,seeGallusgallusChordotonalcells,evolution,204Chordotonalneurons,roleinhearing,201Chordotonalorgan,Drosophila,193function,194receptorpotential,194insect,192ffChordotonalsensilla,insect,193–194CICR,slowefferenteffects,352ffCiliamotionandouterhaircellmotility,171–172Clickevokedotoacousticemission,seeCEOAE,TEOAEClick-evokedemissions,amphibians,224–225Clinicalapplications,OAEs,437ffClinicaldiagnosis,OAEs,421ffCochlea,electromotility,11–12hairbundlemotility,93ffnonlinearity,49–50standingwave,27Cochlearamplifierdisorders,andOAEs,421ffCochlearamplifiergain,thresholdmicrostructure,398–399Cochlearamplifier,387andOAEs,262,335–336clinicalassessment,421ffearlyideas,50–51Index475outerhaircell,145vulnerability,177Cochleardysfunction,andOAEs,422ffCochlearfunction,andpsychophysics,395ffHelmholtzideas,39–40,41Cochlearmechanics,Gold,40–41nonlinearity,382–383vonBékésy,40,43–44Cochlearmechanism,OAEsproduction,7–8Cochlearmicrophonic,10electromotility173Cochlearmodels,activeprocesses,381ffneuralcontrol,382–383vulnerability,382–383Cochlearnonlinearities,efferentcontrol,343ffCochlearpartition,earlymeasurements,43–44rapidstiffnesschanges,358–359Cochlearreflector,OAEs,27–29Cochlearresonator,ThomasGold,10ffCochleartuning,10,47ffleveleffects,411Coherentoscillations,65–66Coherentreflectionfiltering,29andOAEs,388–389criticisms,336–337fromperturbations,316ffColumella,amphibian,214Comparativeactiveprocesses,249ffComparativeOAEs,249ffbirds,241ffComparativeSOAE,lizards,228–230Compartmentalization,outerhaircell,159Compressiongrowth,maskinggrowth,400ffCompressionofcochlearamplifier,salicylateoverdose,447–448Compression,andclinicaldiagnosis,421ffandOAEs,405ffandouterhaircell,347–348andsuppression,405cochlearamplifier,400ffcochlearmodels,389frequencyrangeof,406loudnessgrowth,407Compressivenonlinearity,63ffCortex-evoked,efferenteffects,368ffCorticallattice,outerhaircell,153Criticallayerabsorption,travelingwave,86Criticaloscillator,63ffandmultiplefrequencies,73ffdefinition,65Cytoskeleton,outerhaircell,147ffDefinition,CEOAE,33DPOAE,33–34,213–214EEOAE,214OAEstypes,33–34,213–214SOAE,3,213TEOAE,33Descartes,nervestimulation,39Diamide,modulationofouterhaircell,170Directionalityofsources,OAEs,315–316Discovery,OAEs,2ffDistortionemissions,264OAEs,29–30Distortionincochlea,OAEs,306DistortionproductOAEs,seealsoDPOAE,OAEs,29–31andtwotonesuppression,74–75atstapes,320ffcharacteristiccochlearplace,324–325inthetravelingwave,86–87Distortionsources,OAEs,320ffDistortion,contributionstoSFOAE,322ffDopplershift,mustachedbat,368,370DPfilter,OAEs,321DPOAEfinestructure,327–328DPOAEI/Ofunctions,clinicalapplications,448–449DPOAEphase,308ff,320ffDPOAEvs.
SOAE,lizards,234DPOAE,seealsoDistortionproductotoacousticemissions,29,383activeversuspassive,278–279adaptation,389–390amphibian,222–224andbehavioralmeasures,434ffandcompression,389,405anddiuretics,282–283andhearingloss,400andloudness,453andnoisedamageeffects,279andphase,263ffandprolongedacousticalstimulation,362ffandsimultaneouslymaskedPTC,409ffandSTC,408ffandsuppression,412andthresholdmicrostructure,399animalscomparedtohumans,277ffbird,247–249Caimancrocodilus,247–249cochlearamplifierassessment,423ffcontralateralstimulation,363–364contralateralsuppression,426definition,33–34,213–214frequencyselectivity,235Gallusgallus,247–249growthfunctionnotches,365ff476IndexDPOAE(Cont.
)growthofmaskingandsuppression,401ffhaircells,343hearingassessment,424highfrequency,280–281I/Ofunctions,277–278,425,428,435,443ffinnewborns,435ffinvariousspecies,276ffipsilateraladaptation,425iso-suppressiontuningcurves,425,436–437latency,276–277lizards,234ffLocustamigratoria,202lowandhighlevel,223loweranduppersideband,281–282microstructure,399MOCefferents,361ffMOCexcitation,364ffmoth,202mustachedbat,370–371origins,422patientcaseexamples,440,444–445,452phase,223placeorigin,264properties,275ffschematicrepresentation,7slope,425sourcetypes,325–326suppressionandadaptation,433suppressiontuningcurves,405ffsuppression,279–280,282–283,400temperatureeffects,223thresholdestimates,425,435thresholdmicrostructure,397–398Tiliquarugosa,235–236twosources,265,431Tytoalba,247–249vs.
auditorynerveresponse,235–236Xenopus,222DPOAE-grams,423ffDromaiusnovaehollandiae(Emu),241ffDrosophilamelanogaster,activeamplification,199–201antennalreceptor,199–201chordotonalorgan,193geneticsofactiveamplification,199–201hearing,191–192,194prestinhomologs,166Ear,activesensoryprocesses,7–8amphibian,214ffbird,241ffInsects,191fflizards,225ffEardrum,creatingsoundwithOAEs,2–4Eel,seeAngulllaanguillaEEOAE,andouterhaircell,388definition,214entrainmentbyACcurrent,238ffgenerationbyhaircells,237fflizards,237ffsourceinTiliquarugosa,239source,237ffEfferentcontrol,cellularandmolecularmechanisms,343ff,468–469Efferenteffects,"slow"and"fast,"344ff,352ffEfferentmechanisms,andprestin,465Efferentreflexstrength,OAEs,450–451Efferentsloweffects,outerhaircellstiffness,354Efferent,cortex,368ffcorticofugaleffects,369phasechanges,348–349timecourseofeffects,349Electricallyevokedotoacousticemissions,seealsoEEOAE,261,388Electromechanicaltransducer,operatingpoint,358Electromotilitiy,prestin,160ffcochlea,11–12cochlearmicrophonic,173extracellularpotential,173outerhaircell,145ff,156ffEmu,seeDromaiusnovaehollandiaeEndolymphatichydrops,andOAEs,291–292EPSPsuppression,efferenteffects,350–351Equivalentrectangularbandwidth(ERB),408Evokedemissions,amphibians,220ffarchosaurs,245ffbirds,245fflizards,234ffEvolution,activeprocessesininsects,204chordotonalcells,204lizardbasilarpapilla,225ffExtracellularpotential,electromotility,173Facilitation,SOAE,231–233F-actin,lateralwall,153outerhaircell,153Fastadaptation,haircellbundle,465Fasteffect,MOC,364ffFastefferenteffects,small-conductance,calcium-activatedpotassiumchannels(SK),350ffFastelectromotility,156–158Feedbackmechanism,outerhaircell,175–176Feedbackregulation,andHopfbifurcation,78Index477Forwardmaskinggrowth,compressivenonlinearity,404–405Forwardmasking,frequencyselectivity,409ffFouriercomponents,66–67Fouriertransform,ofautocorrelationfunction,72Frequencymap,basilarpapilla,228–229Frequencyselectivity,basilarpapilla,243DPOAE,235Frequencytuning,OAEs,408ffsharpness,383–384Frog,seeAmphibianGallusgallus(chicken),DPOAE,247–249OAEs,241ffSOAE,244–245Gatingcompliance,81Gatingspringhypothesis,hairbundle,98–100mechanochemicaltransduction,98–100Gatingspring,tiplink,101–102Gating-compliance,negativestiffness,118ffGating-springmodel,112–114mechanismsofadaptation,107Gecko,seeGekkogecko,LizardsGekkogecko(gecko),SOAE,228ffGenderdifferences,SOAE,468Genetichearingloss,andOAEs,292Genetics,activeamplificationinDrosophila,199–201GLUT5,outerhaircell,176–177Glycogen,outerhaircellcytoplasm,155–156Gold,Thomas,cochlearmechanics,40–41cochlearresonator,10ffcontributionstoOAEs,10ffGrasshopper,seeLocustamigratoriaGrowthofmaskingslopes,400ffGTPases,modulationofouterhaircell,170–171Hairbundlemotion,Ranacatesbeiana,95Hairbundleadaptation,Ca2+reclosuremodel,111–112myosinmolecules,110–111turtle,103Hairbundlemechanics,127–129Hairbundlemotility,93ff,383cochlearmodels,390Hairbundlemovements,bullfrog,115electricallyevoked,114–116Hairbundleoscillation,myosin-basedadaptationmotors,126ffmechanicalamplification,122ffspontaneous,116–118Haircellbundle,seealsoStereociliaactivemotormodel,107ffactiveoscillations,53–55,79–80adaptationkinetics,104–105adaptation,models,107ff,111ffandnoisyactiveoscillator,80–81biasingprocess,104force-displacementrelation,118ffgating-springhypothesis,98–100,107maximumsensitivity,132mechanoelectricaltransduction,96ffmotion,95–96rapidchangesinmechanicalproperties,359–360regulationofadaptation,105–107responsetoincreasedstimulation,125–126stiffness,118ffstimulation,93structure,93–95transductionchannel,100–101twitch,132ffvertebrates,80ffHaircellmotility,55Haircellpattern,evolutioninlizards,227–228Haircellresonance,efferenteffects,356Haircells,seealsoOuterhaircellsadaptationmotors,465adaptation,102ffamphibian,215andcalciumdynamics,81bird,241ffEEOAE,237ffefferentsynapse,343ffionchannels,96–97lizard,225–226motors,211–212Tiliquarugosa,54Hearingimpairment,OAEs,421ffHearingloss,andOAEs,437DPOAE,278quantitativeevaluation,442ffHearingmechanism,7–8Hearingpathology,OAEs,283ffHearingscreening,OAE,422ffHearingthreshold,correlationwithOAE,8–9Hearing,Drosophila,191–192,194insects,191mosquitoes,197Ormiaochracea,192Pseudemysscripta,212–213roleofchordotonalneurons,201roleofprestin,166–167ultrasonicininsects,201–203478IndexHearingaidfitting,andOAE,450ffHelmholtz,cochlearfunction,39–40,41History,activecochlearmechanics,39ffactiveprocessesininsects,195–196activeprocesses,10ffcochlearamplifier,50–51contributionspsychoacousticstodiscoveryOAE,13ffdiscoveryofactiveprocesses,39ffdiscoveryofOAEs,6,9ff,19ff,24ff,42–43KempdiscoveryofOAEs,1ffmeasuresofneuralactivity,44–45secondfilterdemise,49–50standing-wavetheory,40ThomasGold,10ffHopfbifurcation,66ff,129ffcochlearmodels,387Hopfoscillator,activeprocesses,466Hormones,SOAE,468Horseshoebat,efferentinnervation,368ffHumans,OAEscomparedtootheranimals,4,249ffHyla,auditorynerveresponse,216OAEs,214seealsoAmphibianHylidsHylids,DFOAE,222–224seealsoHylaSOAE,217fftemperatureeffectsonSOAE,220Hypoxia,OAEs,285Iguanidae,innerear,226IHCefferents,development,352IHCpotentials,effectsofcurrentinjection,357–358Inertialoscillator,withnegativedamping,75–76Innerear,amphibian,214ffbird,241fflizards,225ffInnerhaircells,262–263,343–344activeamplifiers,79–80structure,146–147Insecthearing,activeprocesses,191evidenceforactiveprocesses,194ffInsects,seealsoDrosophila,Mosquitoesactiveprocessesmechanisms,80,203–204antennalears,191–192chordotonalneuronsandhearing,201chordotonalorgan,192ffchordotonalsensilla,193–194DPOAE,202ears,191ffevolutionofactiveprocesses,204hearing,191mechanoreceptorcells,192–193nonlinearities,196fftympanalears,191–192ultrasonichearing,201–203Instability,characteristicofactivemodels,381ffIntermediatefilaments,outerhaircell,150Ionchannels,mechanochemicaltransduction,96–97transduction,100–101IPSC,efferent,345Ischemia,OAE,285Johnston'sorgan,mosquitoes,197–199Kemp,demonstrationofactivemechanismsincochlea,49discoveryofOAEs,1ff,42–43Kinetics,mechanochemcialtransduction,97LaserDopplervibrometry,mosquitoes,197Laserinterferometry,51–52Laseroscillator,OAEmodel,333–334Laterallinesystem,efferentcontrol,345Lateralwallstructure,outerhaircell,150ffputativecomponents,153–154subsurfacecisternae,154–155Lepidosaurs,OAEs,211ff,225ffseealsolizardsLimit-cycleoscillators,cochlearmodels,387Limit-cyclesolution,70Linearreflectionemissions,264Lizardbasilarpapilla,SOAE,468Lizards,seealsoGekko,Lepidosaurs.
Tiliquaadaptiveradiation,227–228basilarpapilla,225–226comparativeSOAE,228–230definition,212DPOAE,234ffEEOAE,237ffevokedacousticemissions,234ffevolutionbasilarpapilla,225ffhaircells,225–226innerear,225ffOAEs,228ffSOAE,217,228ffLizards,suppressiontuningcurves,230ffLocalsuppression,SOAE,231Locust,ultrasonichearing,201–203Index479Locustamigratoria(grasshopper),DPOAE,202Loopdiuretics,andOAE,285–286Loudnessgrowth,andcochlearamplifier,400ffOAE,407Macacamulatta(macaquemonkey),SOAE,269–270Mammalmodels,otoacousticemissions,261ffMammaliancochlea,activeamplification,81ffMammalianOAE,comparisontononmammals,249ffMaskinggrowth,DPOAEgrowth,400ffMasking,SOAE,398–399Mechanicalamplification,activehairbundleoscillations,122ffMechanicalnonlinearity,49–50Mechanismsofadaptation,hairbundle,107ffMechanochemicaltransduction,gating-springhypothesis,98–100hairbundle,96ffionicbasis,96–97kinetics,97operatingpoint,355ffMechanoreceptorcells,insect,192–193Medialolivocochlearefferentsystem,seealsoMOC,344ffMeniere'sdisease,andOAE,291–292Microfilaments,outerhaircell,147–148Microimpedancespectroscopy,outerhaircell,466Micromechanicalperturbations,generationofOAE,306,316ff,334Micromechanicalroughness,319Microtubules,outerhaircell,148–150Middleear,amphibian,214influenceonOAE,433–434MOCefferents,cochleargain,344fastandslow,351IHCresponse,352MOC,adaptation,389–390andhaircelltuning,355andouterhaircellelectromotility,359–360extracellularpotentialeffects,360–361frequency-dependentsuppression,346ffshuntingconductance,354–355stiffnessofouterhaircell,358–359voltage-dependentmotilityofouterhaircell,358Model,mechanismsofadaptation,107ffstanding-wave,18ffModelofcochlea,inversesolutionsandnegativedamping,384lumpedelements,381ffractivecochlea,381ffMorphologicalspecializations,outerhaircell,146ffMorphology,outerhaircellandelectromotility,145ffMosquitoes,activeprocesses,196ffantennalhearingorgan,197–199hearing,197Johnston'sorgan,197–199Mssbauertechnique,46Moth,DPOAE,202ultrasonichearing,201–203Motility,acousticallyevoked,160haircells,55haircellbundles,94ff.
lateralwall,150ffMotorproteins,diversity,81Motors,mammalianhaircells,211–212Mouse,DPOAEandthresholdshift,290Multimerization,prestin,164–165Mustachedbat,seePteronotusparnelliMyosinadaption,stereocilia,81Myosinmolecules,hairbundleadaptation,110–111Myosin-basedadaptationmotors,spontaneoushairbundleoscillation,126ffNegativedamping,andactivemodels,381ffincochlearmodels,384ffNegativestiffness,77Newbornhearingscreening,OAEs,437ffvalidity,438Newton'slaws,OAEmodels,337Noisedamage,andDPOAE,265Noiseeffects,DPOAE,279Noise,andHopfbifurcation,71Noise-evokedemissions,amphibians,224–225Nonlinearcapacitance,prestin,158–159Nonlinearcompliance,prestin,163–164Nonlinearities,efferentcontrol,343ffessential,64ff,69insects,196ffbasilarmembrane,47ffcochlea,49–50OAEs,28–29Nonmammalianspecies,OAEmechanisms,249ff480IndexOAEssuppression,andmasking,401ffOAEs,4–5,seealsoOtoacousticemissionsabsenceintheear,8agerelatedchanges,432agerelatedhearingloss,293amphibians,211ff,214ffanesthesia,268archosaurs,211ff,241ffassessmentofcochlearvulnerability,449–450auditorymicrostructure,16ffbasicprinciples,2–4behavioralthresholds,395ffcause,5ffcharacteristics,431–432classification,263ffclinicalapplications,283ff,421ff,469,437ffcochlearmechanism,7–8cochlearmodels,381cochlearreflector,27–29comparativeinbirds,241ffcomparative,211–213,249ffcorrelationwithhearingthreshold,8–9delay,28discovery,2ff,42–43distortionemissions,29–30distortionproduction,29–31Dromaiusnovaehollandiae,241ffearcanalvolume,431earlyhistory,1ff,6,9ff,17,19ff,24ffefferent-dependentmechanicalchangesincochlea,361fffinestructure,31–32,389frequencyrangeofprimariesformammals,266fffrequencyselectivity,408fffunction,5fffutureresearchapplications,461ffGallusgallus,241ffgenetichearingloss,292hearingpathologies,283ff,291–292human,249ffHyla,214hypoxia,anoxia,andischemia,285inauditoryresearch,31–32inmonitoringcochlearfunction,446ffinfluenceofmiddleear,433–434initiallabstudies,2Lepidosaurs,211ff,225fflevelinhumans,4lizards,228ffloudnessgrowth,407mammalvs.
non-mammal,211–213,249ffmeasurement,266ffmechanismsinnonmammalianspecies,249ffmechanismsofgeneration,305ffmicrostructure,399–400middleear,284modeling,336–337,387ffmonkey,269–270nonlinearactivemodels,382nonlinearfeedback,387–388nonlinearity,28–29nonmotorsystem,211–212ototoxicdrugs,285ff,288overview,1ffphasegradient,28propagationtoearcanal,266psychoacousticcluestodiscovery,13ffpsychophysics,395ffquantitativeevaluationofhearingimpairment,442ffquinine,cisplatin,andtoluene,287–288Rana,214recordingtechnologies,2–4,429ffretrocochlearhearingloss,284–285reversewaves,305ffrodents,269roleofeardrumincreatingsound,2–4sourceofemissions,8,26ffsourcetypemixing,325ffstimuluscalibration,426–427suppressiontuningcurves,405fftemperatureeffectsinbirds,245thresholdmicrostructure,395fftinnitus,9–10transmissionlinemodel,310fftravelingwaveasasource,27Tytoalba,241ffuse,1Olivocochlearefferents,horseshoebat,371Ormiaoncracea(parasitoidfly),hearing,192Oscillators,activeversuspassive,64ffOscillatoryinstability,64Otoacousticemissions,seeOAEmammals,261ffOtotoxicity,andOAEs,446–447Outerhaircellcapacitance,voltagedependence,358Outerhaircellelectromotility,andDPOAE,279problems,172ffOuterhaircellimpairment,OAEs,423ffOuterhaircelllateralwall,pillars,153–154Index481Outerhaircellmotility,andciliamotion,171–172membranepotential,358Outerhaircellpotentials,effectsofcurrentinjection,357–358Outerhaircellsomaticmotility,hairbundlemotility,464–465uniquelymammalian,464Outerhaircell,acousticallyevokedmotility,160actinmonomers,147–148activeprocess,55anatomicaldistinctiveness,146–147andOAEs,262andspontaneousoscillations,82axialstiffness,167ffcochlearamplification,347–348cochlearamplifier,145comparedtoothertypesofhaircells,146–147corticallattice,153cytoskeleton,147ffefferentmodulationofreversetransduction,346ffefferentmodulation,346ffelectromotilitiy,79,145ff,156ff,344feedbackmechanism,175–176,387feed-forward,387functionalcompartmentalization,159GLUT5,176–177glycogenincytoplasm,155–156hairbundlestiffness,347ffintermediatefilaments,150lateralwallstructure,150fflocalizationofprestin,165mechanicallyactivatedchloridechannel,175microfilaments,147–148microtubules,148–150modulationbyacetylcholine,169modulationbyamphipaths,170modulationbydiamide,170modulationbyGTPases,170–171morphologicalspecializationsforelectromotility,145ffmultiplemotilities,390nonlinearcapacitance,158–159OAE,421ffplasmamembrane,150–152prestin,151,160ffreversetransductionandOAEs,306roleofelectromotility,177slowmotility,159–160somaticmotility,347ffstructuralproteins,147ffsubsurfacecisternae,154–155tubulin,148–150voltage-dependentstiffness,171Parasatoidfly,seeOrmiaoncraceaPermanentthresholdshift,andOAEs,289ffPhasecoherence,OAEs,313ffPhasegradient,OAEs,28Phase,DPOAE,223OAEs,307ffPhase-locking,auditorynerve,71Pillars,outerhaircelllateralwall,153–154Place-fixedOAEs,264Plasmamembrane,outerhaircell,150–152prestin,151Positivefeedback,64Prestinexpression,control,165Prestin,383,464asatransportermolecule,167electromotility,160ffhomologs,166localizationincell,165multimerization,164–165nonlinearcapacitance,158–159outerhaircellstiffness,354outerhaircell,151,160ffroleinhearing,165–166sequence,161–163structuralfeatures,164Prestin-associatednonlinearcompliance,163–164Prestin-associatedproteins,167Pseudemysscripta(turtle,hearing),SOAE,212–213Pteronotusparnelli(mustachedbat),efferenteffects,308ffCF-FMcalls,368efferentcontroloffinetuning,370innervationofOuterhaircell,368Psychoacoustics,cluestodiscoveryofOAEs,13ffPsychophysicaltuningcurve(PTC),OAEs,408ffPsychophysics,andcochlearfunction,395ffandOAE,395ffRanacatesbeiana(frog),stereocilia,54hairbundlemotion,95auditorynerveresponse,216OAEs,214seealsoAmphibianRanidsSFOAE,220–222482IndexRanids,DPOAE,222–224seealsoRanaSOAE,217fftemperatureeffectsonSOAE,220Rapidchannelreclosure,andcalcium,466Receptorpotential,chordotonalorgan,194augmentationbyefferents,345–346Recording,OAEs,2–4Recruitment,andouterhaircells,389quantitativeevaluation,442ffReflectioninthecochlea,OAEs,264–265Reflection,cochlearroughness,398OAEs,329ffRegulationofadaptation,calcium,105–106cAMPsecondmessengerpathway,107hairbundle105–107turtle,106Relaxationelement,adaptationmotor,122Reptiles,taxonomicnames,212Reversewaves,OAEs,305ffRubeGoldbergian,gearwhirlingandtwirling,335Ryanodine,fastefferenteffect,350Saccule,amphibian,215haircellfunction,54Salicylateoverdose,andOAEs,447Salicylate,andOAEs,286Scatteringincochlea,OAEs,306,316ffScolopidia,seeChordotonalorganSecondfilterhypothesis,383–384Secondfilter,39ff,47ffdemise,49–50Selfadjustment,andHopfbifurcation,77–78SEOAE,Caimancrocodiles,245–246comparativeinbirds,245–246SFOAEphase,308ffSFOAE,seealsoStimulus-frequencyotoacousticemissionsamphibian,220–222andcompression,405anddistortion,322ffandforwardmasking,410–411coherentreflection,316ffdefinition,33,213groupdelay,410–411invariousspecies,274ffmustachedbat,370–371properties,273ffsourcetypes,325–326suppressiontuningcurves,405ffthresholdmicrostructure,397–398Shorthaircells,bird,241Slowmotility,outerhaircell,159–160Small-conductance,calcium-activatedpotassiumchannels,seealsoSKSOAE(Spontaneousotoacousticemission)amphibianfrequencyrange,218amphibian,213,217ffandmasking,398–399asemergentproperties,336–336aspirin,398–399bird,244–245coupledoscillators,388definition,3,213dropouts,333energyrequirements,262entrainmentbyACcurrent,238fffacilitation,231–233frequencyandamplitude,230,467Gallusgallus,244–245Gekkogecko,228ffgenderdifferences,468globalstandingwavemodels,467innonmammals,467interactionswithexternaltones,230ffinternalreflection,329fflizard,217,228fflocaloscillatormodel,335–336localsuppression,231minimumfrequencyspacing,332–333MOCefferents,361multiple,332–333mustachedbat,368pointsourceexplanations,467properties,268–269Pseudemysscripta,212relationtocochlearmodels,388shiftsinfrequency,233standing-waveresonance,331ffSturnusvulgaris,245–246suppressiontuningcurves,230ffsuppression,219temperateeffectsinlizards,233–234temperaturedependence,219,245thresholdmicrostructure,397–398Tiliquarugosa,228ff,232Xenopus,218Somaticelectromotility,problems,172ffSomaticmotility,cochlearmodels,390outerhaircell,383Sourcemixing,OAE,325ffSource,OAEsemission,8,26ffSpaceconstant,cochlea,319Spectrin,outerhaircell,153Spontaneousbundleoscillations,andOAE,466myosin-basedadaptationmotors,126ffIndex483Spontaneoushairbundleoscillations,116–118bullfrogsaccule,116–117effectofCa2+,117–118turtle,116Spontaneousoscillation,entrainment,123–125Standingwavequantizationcondition,332Standingwave,cochlea,27,330ff,467Standing-wavemodelofauditorymicrostructure,16ffStanding-wavemodel,18ffStanding-waveresonance,OAE,330–331Standing-wavetheory,history,40Starling,seeSturnusvulgarisStereocilia,activeprocess,53–55birdhaircells,242aRanacatesbeiana,54seealsoHairbundleStereovilli,seeStereocilia,Hairbundle,HaircellbundleStiffness,hairbundle,118ffStimulusfrequencyOAE,seeSFOAEStretch-activation,inmuscle,77Structuralproteins,outerhaircell,147ffSturnusvulgaris(starling),SEOAE,245–246Subsurfacecisternae,outerhaircell,154–155Suppressiongrowth,maskinggrowth,400ffSuppressionofafferentactivity,mechanisms,360–361Suppressiontuningcurve,OAEs,405ffSOAE,230ff,408ffSuppression,andOAEs,328–329Suppression,ofbasilarmembraneresponse,348Synapticcistern,efferenteffects,350Tallhaircells,bird,241Tectorialmembrane,amphibian,215roleinthecochlearamplifier,469–470roleincouplinghaircells,230Temperateeffects,DPOAE,223Temperatureeffects,OAEs,245Temperature,effectsonSOAEinlizards,233–234effectsonSOAE,219–220Temporarythresholdshift(TTS),andOAE,288SOAE,398thresholdmicrostructure,398TEOAE,seealsoTransientevokedotoacousticemissionscompressivenon-linearity,431–432definition,33gallimaufry,334–335growthwithprimarylevels,271innewborns,432invariousspecies,272–273monkeys,271–272origins,422patientcaseexamples,439,444properties,269ffreliabilityandcalibrationerrors,427Tetrodotoxin,seeTTXThresholdfinestructure,andOAEs,395ffThresholdmicrostructure,395ffmechanisms,398ffperiodicity,396ffThyroidhormone,prestinexpression,165Tiliquarugosa(Bobtailskink),seealsoLizardsactiveprocessesandhaircells,54DPOAE,235–236EEOAEsource,239effectsonSOAEofexternaltones,232SOAE,228fftemperatureeffectsonSOAE,234Time-delayedfeedback,activeundamping,76–77Tinnitus,andOAEs,9–10andsalicylateoverdose,447Tiplink,gatingspring,101–102transduction,80Tonotopy,birdbasilarpapilla,241–242Toxorhynchitesbrevipalpis,seemosquitoesTrachemisscriptaelegans(turtle),activeprocess,54–55Transductionchannel,100–101Transductionmolecules,100–101Transduction,seealsoMechanochemicaltransductionmechanoelectrical,96ffTransientevokedOAEs,seeTEOAETransientevokedotoacousticemission,seeTEOAE,CEOAETransientreceptorpotential(TRP),101channels,463Translationinvariance,travelingwave,307–308Transmissionlinemodel,OAE,310ffTravelingwave"reflections,"assourceofOAE,27Travelingwavemodels,82–83Travelingwave,andregenerationbyactiveprocesses,83–84Travelingwave,OAEs,39ff,318fftwo-toneinterference,86–87TTX,modulationofOAE,363Tubulin,outerhaircell,148–150Tuningsharpness,OAE,408ffTuning,basilarmembrane,47,50cochlea,10,47ff484IndexTurtle,seealsoPseudemysscripta,Trachemisscriptaeleganshairbundleadaptation,103regulationofadaptation,106spontaneoushairbundleoscillations,116Twitch,132ffTwo-tonesuppression,74–75travelingwave,86–87Tympanalears,activeamplification,201–203insect,191–192Tympanicmiddleear,amphibian,214Tytoalba(barnowl),basilarpapilla,241auditorynerveresponse,242DPOAE,247–249OAEs,241ffUltrasonichearing,activeamplification,201–203insects,201–203Upwardspreadofexcitation,andOAEs,412ffUpwardspreadofsuppression,412ffVanderPoloscillators,cochlearmodels,76,387Vestibularreceptors,hairbundlemotility,93ffViscousdamping,383–384necessityforactiveprocesses,462–463Voltage-dependentstiffness,outerhaircell,171vonBékésy,cochlearmotion,40cochleartuning,10earlystudies,43–44Vulnerability,physiological,63ffWavenumber,SFOAE,321Wave-fixedOAEs,264Wave-inducedperturbations,OAEs,306,334Waveletsummation,OAEs,310ffXenopus,amphibianpapilla,215DPOAE,222SOAE,218Zebrafish,prestinhomologs,166
vertebrates,204mosquitoes,196ffnonmammalianspecies,249,337–338outerhaircells,55Ranacatesbeiana,54Trachemisscriptaelegans,54–55Activetravelingwaves,criticaloscillators,83ffAdaptationkinetics,hairbundle,104–105Adaptationmotor,relaxationelement,122haircells,465Adaptation,haircell,102ffmechanicalcorrelates,112–114mechanisms,107ffsustainedstimuli,102ffAgerelatedhearingloss,andOAE,293AgerelatedOAE,432,435ffAllen-Faheyparadigm,324Aminoglycosideantibiotics,andOAE,286–287Amphibian,seealsoBufo,Hyla,Hylids,Rana,Ranids,Xenopusamphibianpapilla,214ffauditorynerve,215–217basilarpapilla,214ffcharacteristicfrequencyofear,215–217click-evokedemissions,224–225DPOAE,222–224evokedemissions,220fffirstmeasureofSOAE,213haircells,215innerear,214ffmiddleear,214noise-evokedemissions,224–225OAEs,211ffsaccule,215SFOAE,217,ff,220–222tectorialmembrane,215Amphipaths,modulationofouterhaircell,170Amplification,andOAE,328–329criticaloscillators,63ffAnguillaanguilla(eel),ampullahaircells,115Anoxia,OAE,285Antennalears,insect,191–192,197–199Antennalreceptor,Drosophila,199–201Archosaur,definition,212evokedemissions,245ffOAEsvs.
mammals,249ffOAEs,211ff,241ffseealsobird,avianAspirin,cochlearamplifiergain,398–399Auditoryfovea,barnowl,245473474IndexAuditorymicrostructure,cuestoOAEs,16ffAuditorynerveresponse,amphibian,215–217Tytoalba,242vs.
DPOAE,235–236Auditorypapilla,seealsoBasilarpapillaAuditorypapillaeinlizards,seeBasilarpapillaAuditoryresearch,OAEsrolein,31–32Auditorysystemfunctions,andcriticaloscillators,79ffAvian,seealsoArchosaurs,birdsAxialstiffness,outerhaircell,167ffBarnowl,seeTytoalbaBasilarmembranedisplacements,modulationbyACh,353Basilarmembranefrequencyselectivity,384ffBasilarmembranemotion,measurements,51–53Basilarmembranestiffness,349Basilarmembrane,motionmeasurements,46–47non-linearity,47ffobservationsofactivebehavior,381outerhaircell,347–348tuning,47,50Basilarpapilla,amphibian,214ffbird,241fffrequencymap,228–229,243lizard,225–226micromechanics,242–243tonotopy,241–242Tytoalba,241Békésy,seevonBékésyBiasingprocess,hairbundle,104Bicuculine,modulationofOAEs,363Bird,seealsoArchosaurs,Avian,Dromaiusnovaehollandiae,Gallusgallus,Sturnusvulgaris,Tytoalbabasilarpapilla,241ffcomparativeSEOAE,245–246DPOAE,247–249efferentmodulationofhaircells,346evokedemissions,245ffhaircells,241ffinnerear,241ffSOAE,244–245stereocilia,242Bobtailskink,see,Lizards,TiliquarugosaBrownianmotion,fluctuation-dissipationfunction,72Bufo,seealsoAmphibianBullfrogsaccule,activehairbundleresponse,124spontaneoushairbundleoscillations,116–117activehairbundlemovements,113hairbundleadaptation,110–111hairbundlemovements,115Ca2+reclosuremodel,hairbundleadaptation,111–112Ca2+,effectonspontaneoushairbundleoscillations,117–118Caimancrocodilus(Caiman),DPOAE,247–249SEOAE,245–246Calcium,regulationofadaptation,105–106Calcium-inducedcalciumrelease,seealsoCICR,efferents,350cAMPsecond-messengerpathway,regulationofadaptation,107CEOAE,definition,33seealsoTEOAEChannelgating,hairbundle,118ffChaoticdynamics,mammaliancochlea,87Characteristicfrequency,amphibianear,215–217Chicken,seeGallusgallusChordotonalcells,evolution,204Chordotonalneurons,roleinhearing,201Chordotonalorgan,Drosophila,193function,194receptorpotential,194insect,192ffChordotonalsensilla,insect,193–194CICR,slowefferenteffects,352ffCiliamotionandouterhaircellmotility,171–172Clickevokedotoacousticemission,seeCEOAE,TEOAEClick-evokedemissions,amphibians,224–225Clinicalapplications,OAEs,437ffClinicaldiagnosis,OAEs,421ffCochlea,electromotility,11–12hairbundlemotility,93ffnonlinearity,49–50standingwave,27Cochlearamplifierdisorders,andOAEs,421ffCochlearamplifiergain,thresholdmicrostructure,398–399Cochlearamplifier,387andOAEs,262,335–336clinicalassessment,421ffearlyideas,50–51Index475outerhaircell,145vulnerability,177Cochleardysfunction,andOAEs,422ffCochlearfunction,andpsychophysics,395ffHelmholtzideas,39–40,41Cochlearmechanics,Gold,40–41nonlinearity,382–383vonBékésy,40,43–44Cochlearmechanism,OAEsproduction,7–8Cochlearmicrophonic,10electromotility173Cochlearmodels,activeprocesses,381ffneuralcontrol,382–383vulnerability,382–383Cochlearnonlinearities,efferentcontrol,343ffCochlearpartition,earlymeasurements,43–44rapidstiffnesschanges,358–359Cochlearreflector,OAEs,27–29Cochlearresonator,ThomasGold,10ffCochleartuning,10,47ffleveleffects,411Coherentoscillations,65–66Coherentreflectionfiltering,29andOAEs,388–389criticisms,336–337fromperturbations,316ffColumella,amphibian,214Comparativeactiveprocesses,249ffComparativeOAEs,249ffbirds,241ffComparativeSOAE,lizards,228–230Compartmentalization,outerhaircell,159Compressiongrowth,maskinggrowth,400ffCompressionofcochlearamplifier,salicylateoverdose,447–448Compression,andclinicaldiagnosis,421ffandOAEs,405ffandouterhaircell,347–348andsuppression,405cochlearamplifier,400ffcochlearmodels,389frequencyrangeof,406loudnessgrowth,407Compressivenonlinearity,63ffCortex-evoked,efferenteffects,368ffCorticallattice,outerhaircell,153Criticallayerabsorption,travelingwave,86Criticaloscillator,63ffandmultiplefrequencies,73ffdefinition,65Cytoskeleton,outerhaircell,147ffDefinition,CEOAE,33DPOAE,33–34,213–214EEOAE,214OAEstypes,33–34,213–214SOAE,3,213TEOAE,33Descartes,nervestimulation,39Diamide,modulationofouterhaircell,170Directionalityofsources,OAEs,315–316Discovery,OAEs,2ffDistortionemissions,264OAEs,29–30Distortionincochlea,OAEs,306DistortionproductOAEs,seealsoDPOAE,OAEs,29–31andtwotonesuppression,74–75atstapes,320ffcharacteristiccochlearplace,324–325inthetravelingwave,86–87Distortionsources,OAEs,320ffDistortion,contributionstoSFOAE,322ffDopplershift,mustachedbat,368,370DPfilter,OAEs,321DPOAEfinestructure,327–328DPOAEI/Ofunctions,clinicalapplications,448–449DPOAEphase,308ff,320ffDPOAEvs.
SOAE,lizards,234DPOAE,seealsoDistortionproductotoacousticemissions,29,383activeversuspassive,278–279adaptation,389–390amphibian,222–224andbehavioralmeasures,434ffandcompression,389,405anddiuretics,282–283andhearingloss,400andloudness,453andnoisedamageeffects,279andphase,263ffandprolongedacousticalstimulation,362ffandsimultaneouslymaskedPTC,409ffandSTC,408ffandsuppression,412andthresholdmicrostructure,399animalscomparedtohumans,277ffbird,247–249Caimancrocodilus,247–249cochlearamplifierassessment,423ffcontralateralstimulation,363–364contralateralsuppression,426definition,33–34,213–214frequencyselectivity,235Gallusgallus,247–249growthfunctionnotches,365ff476IndexDPOAE(Cont.
)growthofmaskingandsuppression,401ffhaircells,343hearingassessment,424highfrequency,280–281I/Ofunctions,277–278,425,428,435,443ffinnewborns,435ffinvariousspecies,276ffipsilateraladaptation,425iso-suppressiontuningcurves,425,436–437latency,276–277lizards,234ffLocustamigratoria,202lowandhighlevel,223loweranduppersideband,281–282microstructure,399MOCefferents,361ffMOCexcitation,364ffmoth,202mustachedbat,370–371origins,422patientcaseexamples,440,444–445,452phase,223placeorigin,264properties,275ffschematicrepresentation,7slope,425sourcetypes,325–326suppressionandadaptation,433suppressiontuningcurves,405ffsuppression,279–280,282–283,400temperatureeffects,223thresholdestimates,425,435thresholdmicrostructure,397–398Tiliquarugosa,235–236twosources,265,431Tytoalba,247–249vs.
auditorynerveresponse,235–236Xenopus,222DPOAE-grams,423ffDromaiusnovaehollandiae(Emu),241ffDrosophilamelanogaster,activeamplification,199–201antennalreceptor,199–201chordotonalorgan,193geneticsofactiveamplification,199–201hearing,191–192,194prestinhomologs,166Ear,activesensoryprocesses,7–8amphibian,214ffbird,241ffInsects,191fflizards,225ffEardrum,creatingsoundwithOAEs,2–4Eel,seeAngulllaanguillaEEOAE,andouterhaircell,388definition,214entrainmentbyACcurrent,238ffgenerationbyhaircells,237fflizards,237ffsourceinTiliquarugosa,239source,237ffEfferentcontrol,cellularandmolecularmechanisms,343ff,468–469Efferenteffects,"slow"and"fast,"344ff,352ffEfferentmechanisms,andprestin,465Efferentreflexstrength,OAEs,450–451Efferentsloweffects,outerhaircellstiffness,354Efferent,cortex,368ffcorticofugaleffects,369phasechanges,348–349timecourseofeffects,349Electricallyevokedotoacousticemissions,seealsoEEOAE,261,388Electromechanicaltransducer,operatingpoint,358Electromotilitiy,prestin,160ffcochlea,11–12cochlearmicrophonic,173extracellularpotential,173outerhaircell,145ff,156ffEmu,seeDromaiusnovaehollandiaeEndolymphatichydrops,andOAEs,291–292EPSPsuppression,efferenteffects,350–351Equivalentrectangularbandwidth(ERB),408Evokedemissions,amphibians,220ffarchosaurs,245ffbirds,245fflizards,234ffEvolution,activeprocessesininsects,204chordotonalcells,204lizardbasilarpapilla,225ffExtracellularpotential,electromotility,173Facilitation,SOAE,231–233F-actin,lateralwall,153outerhaircell,153Fastadaptation,haircellbundle,465Fasteffect,MOC,364ffFastefferenteffects,small-conductance,calcium-activatedpotassiumchannels(SK),350ffFastelectromotility,156–158Feedbackmechanism,outerhaircell,175–176Feedbackregulation,andHopfbifurcation,78Index477Forwardmaskinggrowth,compressivenonlinearity,404–405Forwardmasking,frequencyselectivity,409ffFouriercomponents,66–67Fouriertransform,ofautocorrelationfunction,72Frequencymap,basilarpapilla,228–229Frequencyselectivity,basilarpapilla,243DPOAE,235Frequencytuning,OAEs,408ffsharpness,383–384Frog,seeAmphibianGallusgallus(chicken),DPOAE,247–249OAEs,241ffSOAE,244–245Gatingcompliance,81Gatingspringhypothesis,hairbundle,98–100mechanochemicaltransduction,98–100Gatingspring,tiplink,101–102Gating-compliance,negativestiffness,118ffGating-springmodel,112–114mechanismsofadaptation,107Gecko,seeGekkogecko,LizardsGekkogecko(gecko),SOAE,228ffGenderdifferences,SOAE,468Genetichearingloss,andOAEs,292Genetics,activeamplificationinDrosophila,199–201GLUT5,outerhaircell,176–177Glycogen,outerhaircellcytoplasm,155–156Gold,Thomas,cochlearmechanics,40–41cochlearresonator,10ffcontributionstoOAEs,10ffGrasshopper,seeLocustamigratoriaGrowthofmaskingslopes,400ffGTPases,modulationofouterhaircell,170–171Hairbundlemotion,Ranacatesbeiana,95Hairbundleadaptation,Ca2+reclosuremodel,111–112myosinmolecules,110–111turtle,103Hairbundlemechanics,127–129Hairbundlemotility,93ff,383cochlearmodels,390Hairbundlemovements,bullfrog,115electricallyevoked,114–116Hairbundleoscillation,myosin-basedadaptationmotors,126ffmechanicalamplification,122ffspontaneous,116–118Haircellbundle,seealsoStereociliaactivemotormodel,107ffactiveoscillations,53–55,79–80adaptationkinetics,104–105adaptation,models,107ff,111ffandnoisyactiveoscillator,80–81biasingprocess,104force-displacementrelation,118ffgating-springhypothesis,98–100,107maximumsensitivity,132mechanoelectricaltransduction,96ffmotion,95–96rapidchangesinmechanicalproperties,359–360regulationofadaptation,105–107responsetoincreasedstimulation,125–126stiffness,118ffstimulation,93structure,93–95transductionchannel,100–101twitch,132ffvertebrates,80ffHaircellmotility,55Haircellpattern,evolutioninlizards,227–228Haircellresonance,efferenteffects,356Haircells,seealsoOuterhaircellsadaptationmotors,465adaptation,102ffamphibian,215andcalciumdynamics,81bird,241ffEEOAE,237ffefferentsynapse,343ffionchannels,96–97lizard,225–226motors,211–212Tiliquarugosa,54Hearingimpairment,OAEs,421ffHearingloss,andOAEs,437DPOAE,278quantitativeevaluation,442ffHearingmechanism,7–8Hearingpathology,OAEs,283ffHearingscreening,OAE,422ffHearingthreshold,correlationwithOAE,8–9Hearing,Drosophila,191–192,194insects,191mosquitoes,197Ormiaochracea,192Pseudemysscripta,212–213roleofchordotonalneurons,201roleofprestin,166–167ultrasonicininsects,201–203478IndexHearingaidfitting,andOAE,450ffHelmholtz,cochlearfunction,39–40,41History,activecochlearmechanics,39ffactiveprocessesininsects,195–196activeprocesses,10ffcochlearamplifier,50–51contributionspsychoacousticstodiscoveryOAE,13ffdiscoveryofactiveprocesses,39ffdiscoveryofOAEs,6,9ff,19ff,24ff,42–43KempdiscoveryofOAEs,1ffmeasuresofneuralactivity,44–45secondfilterdemise,49–50standing-wavetheory,40ThomasGold,10ffHopfbifurcation,66ff,129ffcochlearmodels,387Hopfoscillator,activeprocesses,466Hormones,SOAE,468Horseshoebat,efferentinnervation,368ffHumans,OAEscomparedtootheranimals,4,249ffHyla,auditorynerveresponse,216OAEs,214seealsoAmphibianHylidsHylids,DFOAE,222–224seealsoHylaSOAE,217fftemperatureeffectsonSOAE,220Hypoxia,OAEs,285Iguanidae,innerear,226IHCefferents,development,352IHCpotentials,effectsofcurrentinjection,357–358Inertialoscillator,withnegativedamping,75–76Innerear,amphibian,214ffbird,241fflizards,225ffInnerhaircells,262–263,343–344activeamplifiers,79–80structure,146–147Insecthearing,activeprocesses,191evidenceforactiveprocesses,194ffInsects,seealsoDrosophila,Mosquitoesactiveprocessesmechanisms,80,203–204antennalears,191–192chordotonalneuronsandhearing,201chordotonalorgan,192ffchordotonalsensilla,193–194DPOAE,202ears,191ffevolutionofactiveprocesses,204hearing,191mechanoreceptorcells,192–193nonlinearities,196fftympanalears,191–192ultrasonichearing,201–203Instability,characteristicofactivemodels,381ffIntermediatefilaments,outerhaircell,150Ionchannels,mechanochemicaltransduction,96–97transduction,100–101IPSC,efferent,345Ischemia,OAE,285Johnston'sorgan,mosquitoes,197–199Kemp,demonstrationofactivemechanismsincochlea,49discoveryofOAEs,1ff,42–43Kinetics,mechanochemcialtransduction,97LaserDopplervibrometry,mosquitoes,197Laserinterferometry,51–52Laseroscillator,OAEmodel,333–334Laterallinesystem,efferentcontrol,345Lateralwallstructure,outerhaircell,150ffputativecomponents,153–154subsurfacecisternae,154–155Lepidosaurs,OAEs,211ff,225ffseealsolizardsLimit-cycleoscillators,cochlearmodels,387Limit-cyclesolution,70Linearreflectionemissions,264Lizardbasilarpapilla,SOAE,468Lizards,seealsoGekko,Lepidosaurs.
Tiliquaadaptiveradiation,227–228basilarpapilla,225–226comparativeSOAE,228–230definition,212DPOAE,234ffEEOAE,237ffevokedacousticemissions,234ffevolutionbasilarpapilla,225ffhaircells,225–226innerear,225ffOAEs,228ffSOAE,217,228ffLizards,suppressiontuningcurves,230ffLocalsuppression,SOAE,231Locust,ultrasonichearing,201–203Index479Locustamigratoria(grasshopper),DPOAE,202Loopdiuretics,andOAE,285–286Loudnessgrowth,andcochlearamplifier,400ffOAE,407Macacamulatta(macaquemonkey),SOAE,269–270Mammalmodels,otoacousticemissions,261ffMammaliancochlea,activeamplification,81ffMammalianOAE,comparisontononmammals,249ffMaskinggrowth,DPOAEgrowth,400ffMasking,SOAE,398–399Mechanicalamplification,activehairbundleoscillations,122ffMechanicalnonlinearity,49–50Mechanismsofadaptation,hairbundle,107ffMechanochemicaltransduction,gating-springhypothesis,98–100hairbundle,96ffionicbasis,96–97kinetics,97operatingpoint,355ffMechanoreceptorcells,insect,192–193Medialolivocochlearefferentsystem,seealsoMOC,344ffMeniere'sdisease,andOAE,291–292Microfilaments,outerhaircell,147–148Microimpedancespectroscopy,outerhaircell,466Micromechanicalperturbations,generationofOAE,306,316ff,334Micromechanicalroughness,319Microtubules,outerhaircell,148–150Middleear,amphibian,214influenceonOAE,433–434MOCefferents,cochleargain,344fastandslow,351IHCresponse,352MOC,adaptation,389–390andhaircelltuning,355andouterhaircellelectromotility,359–360extracellularpotentialeffects,360–361frequency-dependentsuppression,346ffshuntingconductance,354–355stiffnessofouterhaircell,358–359voltage-dependentmotilityofouterhaircell,358Model,mechanismsofadaptation,107ffstanding-wave,18ffModelofcochlea,inversesolutionsandnegativedamping,384lumpedelements,381ffractivecochlea,381ffMorphologicalspecializations,outerhaircell,146ffMorphology,outerhaircellandelectromotility,145ffMosquitoes,activeprocesses,196ffantennalhearingorgan,197–199hearing,197Johnston'sorgan,197–199Mssbauertechnique,46Moth,DPOAE,202ultrasonichearing,201–203Motility,acousticallyevoked,160haircells,55haircellbundles,94ff.
lateralwall,150ffMotorproteins,diversity,81Motors,mammalianhaircells,211–212Mouse,DPOAEandthresholdshift,290Multimerization,prestin,164–165Mustachedbat,seePteronotusparnelliMyosinadaption,stereocilia,81Myosinmolecules,hairbundleadaptation,110–111Myosin-basedadaptationmotors,spontaneoushairbundleoscillation,126ffNegativedamping,andactivemodels,381ffincochlearmodels,384ffNegativestiffness,77Newbornhearingscreening,OAEs,437ffvalidity,438Newton'slaws,OAEmodels,337Noisedamage,andDPOAE,265Noiseeffects,DPOAE,279Noise,andHopfbifurcation,71Noise-evokedemissions,amphibians,224–225Nonlinearcapacitance,prestin,158–159Nonlinearcompliance,prestin,163–164Nonlinearities,efferentcontrol,343ffessential,64ff,69insects,196ffbasilarmembrane,47ffcochlea,49–50OAEs,28–29Nonmammalianspecies,OAEmechanisms,249ff480IndexOAEssuppression,andmasking,401ffOAEs,4–5,seealsoOtoacousticemissionsabsenceintheear,8agerelatedchanges,432agerelatedhearingloss,293amphibians,211ff,214ffanesthesia,268archosaurs,211ff,241ffassessmentofcochlearvulnerability,449–450auditorymicrostructure,16ffbasicprinciples,2–4behavioralthresholds,395ffcause,5ffcharacteristics,431–432classification,263ffclinicalapplications,283ff,421ff,469,437ffcochlearmechanism,7–8cochlearmodels,381cochlearreflector,27–29comparativeinbirds,241ffcomparative,211–213,249ffcorrelationwithhearingthreshold,8–9delay,28discovery,2ff,42–43distortionemissions,29–30distortionproduction,29–31Dromaiusnovaehollandiae,241ffearcanalvolume,431earlyhistory,1ff,6,9ff,17,19ff,24ffefferent-dependentmechanicalchangesincochlea,361fffinestructure,31–32,389frequencyrangeofprimariesformammals,266fffrequencyselectivity,408fffunction,5fffutureresearchapplications,461ffGallusgallus,241ffgenetichearingloss,292hearingpathologies,283ff,291–292human,249ffHyla,214hypoxia,anoxia,andischemia,285inauditoryresearch,31–32inmonitoringcochlearfunction,446ffinfluenceofmiddleear,433–434initiallabstudies,2Lepidosaurs,211ff,225fflevelinhumans,4lizards,228ffloudnessgrowth,407mammalvs.
non-mammal,211–213,249ffmeasurement,266ffmechanismsinnonmammalianspecies,249ffmechanismsofgeneration,305ffmicrostructure,399–400middleear,284modeling,336–337,387ffmonkey,269–270nonlinearactivemodels,382nonlinearfeedback,387–388nonlinearity,28–29nonmotorsystem,211–212ototoxicdrugs,285ff,288overview,1ffphasegradient,28propagationtoearcanal,266psychoacousticcluestodiscovery,13ffpsychophysics,395ffquantitativeevaluationofhearingimpairment,442ffquinine,cisplatin,andtoluene,287–288Rana,214recordingtechnologies,2–4,429ffretrocochlearhearingloss,284–285reversewaves,305ffrodents,269roleofeardrumincreatingsound,2–4sourceofemissions,8,26ffsourcetypemixing,325ffstimuluscalibration,426–427suppressiontuningcurves,405fftemperatureeffectsinbirds,245thresholdmicrostructure,395fftinnitus,9–10transmissionlinemodel,310fftravelingwaveasasource,27Tytoalba,241ffuse,1Olivocochlearefferents,horseshoebat,371Ormiaoncracea(parasitoidfly),hearing,192Oscillators,activeversuspassive,64ffOscillatoryinstability,64Otoacousticemissions,seeOAEmammals,261ffOtotoxicity,andOAEs,446–447Outerhaircellcapacitance,voltagedependence,358Outerhaircellelectromotility,andDPOAE,279problems,172ffOuterhaircellimpairment,OAEs,423ffOuterhaircelllateralwall,pillars,153–154Index481Outerhaircellmotility,andciliamotion,171–172membranepotential,358Outerhaircellpotentials,effectsofcurrentinjection,357–358Outerhaircellsomaticmotility,hairbundlemotility,464–465uniquelymammalian,464Outerhaircell,acousticallyevokedmotility,160actinmonomers,147–148activeprocess,55anatomicaldistinctiveness,146–147andOAEs,262andspontaneousoscillations,82axialstiffness,167ffcochlearamplification,347–348cochlearamplifier,145comparedtoothertypesofhaircells,146–147corticallattice,153cytoskeleton,147ffefferentmodulationofreversetransduction,346ffefferentmodulation,346ffelectromotilitiy,79,145ff,156ff,344feedbackmechanism,175–176,387feed-forward,387functionalcompartmentalization,159GLUT5,176–177glycogenincytoplasm,155–156hairbundlestiffness,347ffintermediatefilaments,150lateralwallstructure,150fflocalizationofprestin,165mechanicallyactivatedchloridechannel,175microfilaments,147–148microtubules,148–150modulationbyacetylcholine,169modulationbyamphipaths,170modulationbydiamide,170modulationbyGTPases,170–171morphologicalspecializationsforelectromotility,145ffmultiplemotilities,390nonlinearcapacitance,158–159OAE,421ffplasmamembrane,150–152prestin,151,160ffreversetransductionandOAEs,306roleofelectromotility,177slowmotility,159–160somaticmotility,347ffstructuralproteins,147ffsubsurfacecisternae,154–155tubulin,148–150voltage-dependentstiffness,171Parasatoidfly,seeOrmiaoncraceaPermanentthresholdshift,andOAEs,289ffPhasecoherence,OAEs,313ffPhasegradient,OAEs,28Phase,DPOAE,223OAEs,307ffPhase-locking,auditorynerve,71Pillars,outerhaircelllateralwall,153–154Place-fixedOAEs,264Plasmamembrane,outerhaircell,150–152prestin,151Positivefeedback,64Prestinexpression,control,165Prestin,383,464asatransportermolecule,167electromotility,160ffhomologs,166localizationincell,165multimerization,164–165nonlinearcapacitance,158–159outerhaircellstiffness,354outerhaircell,151,160ffroleinhearing,165–166sequence,161–163structuralfeatures,164Prestin-associatednonlinearcompliance,163–164Prestin-associatedproteins,167Pseudemysscripta(turtle,hearing),SOAE,212–213Pteronotusparnelli(mustachedbat),efferenteffects,308ffCF-FMcalls,368efferentcontroloffinetuning,370innervationofOuterhaircell,368Psychoacoustics,cluestodiscoveryofOAEs,13ffPsychophysicaltuningcurve(PTC),OAEs,408ffPsychophysics,andcochlearfunction,395ffandOAE,395ffRanacatesbeiana(frog),stereocilia,54hairbundlemotion,95auditorynerveresponse,216OAEs,214seealsoAmphibianRanidsSFOAE,220–222482IndexRanids,DPOAE,222–224seealsoRanaSOAE,217fftemperatureeffectsonSOAE,220Rapidchannelreclosure,andcalcium,466Receptorpotential,chordotonalorgan,194augmentationbyefferents,345–346Recording,OAEs,2–4Recruitment,andouterhaircells,389quantitativeevaluation,442ffReflectioninthecochlea,OAEs,264–265Reflection,cochlearroughness,398OAEs,329ffRegulationofadaptation,calcium,105–106cAMPsecondmessengerpathway,107hairbundle105–107turtle,106Relaxationelement,adaptationmotor,122Reptiles,taxonomicnames,212Reversewaves,OAEs,305ffRubeGoldbergian,gearwhirlingandtwirling,335Ryanodine,fastefferenteffect,350Saccule,amphibian,215haircellfunction,54Salicylateoverdose,andOAEs,447Salicylate,andOAEs,286Scatteringincochlea,OAEs,306,316ffScolopidia,seeChordotonalorganSecondfilterhypothesis,383–384Secondfilter,39ff,47ffdemise,49–50Selfadjustment,andHopfbifurcation,77–78SEOAE,Caimancrocodiles,245–246comparativeinbirds,245–246SFOAEphase,308ffSFOAE,seealsoStimulus-frequencyotoacousticemissionsamphibian,220–222andcompression,405anddistortion,322ffandforwardmasking,410–411coherentreflection,316ffdefinition,33,213groupdelay,410–411invariousspecies,274ffmustachedbat,370–371properties,273ffsourcetypes,325–326suppressiontuningcurves,405ffthresholdmicrostructure,397–398Shorthaircells,bird,241Slowmotility,outerhaircell,159–160Small-conductance,calcium-activatedpotassiumchannels,seealsoSKSOAE(Spontaneousotoacousticemission)amphibianfrequencyrange,218amphibian,213,217ffandmasking,398–399asemergentproperties,336–336aspirin,398–399bird,244–245coupledoscillators,388definition,3,213dropouts,333energyrequirements,262entrainmentbyACcurrent,238fffacilitation,231–233frequencyandamplitude,230,467Gallusgallus,244–245Gekkogecko,228ffgenderdifferences,468globalstandingwavemodels,467innonmammals,467interactionswithexternaltones,230ffinternalreflection,329fflizard,217,228fflocaloscillatormodel,335–336localsuppression,231minimumfrequencyspacing,332–333MOCefferents,361multiple,332–333mustachedbat,368pointsourceexplanations,467properties,268–269Pseudemysscripta,212relationtocochlearmodels,388shiftsinfrequency,233standing-waveresonance,331ffSturnusvulgaris,245–246suppressiontuningcurves,230ffsuppression,219temperateeffectsinlizards,233–234temperaturedependence,219,245thresholdmicrostructure,397–398Tiliquarugosa,228ff,232Xenopus,218Somaticelectromotility,problems,172ffSomaticmotility,cochlearmodels,390outerhaircell,383Sourcemixing,OAE,325ffSource,OAEsemission,8,26ffSpaceconstant,cochlea,319Spectrin,outerhaircell,153Spontaneousbundleoscillations,andOAE,466myosin-basedadaptationmotors,126ffIndex483Spontaneoushairbundleoscillations,116–118bullfrogsaccule,116–117effectofCa2+,117–118turtle,116Spontaneousoscillation,entrainment,123–125Standingwavequantizationcondition,332Standingwave,cochlea,27,330ff,467Standing-wavemodelofauditorymicrostructure,16ffStanding-wavemodel,18ffStanding-waveresonance,OAE,330–331Standing-wavetheory,history,40Starling,seeSturnusvulgarisStereocilia,activeprocess,53–55birdhaircells,242aRanacatesbeiana,54seealsoHairbundleStereovilli,seeStereocilia,Hairbundle,HaircellbundleStiffness,hairbundle,118ffStimulusfrequencyOAE,seeSFOAEStretch-activation,inmuscle,77Structuralproteins,outerhaircell,147ffSturnusvulgaris(starling),SEOAE,245–246Subsurfacecisternae,outerhaircell,154–155Suppressiongrowth,maskinggrowth,400ffSuppressionofafferentactivity,mechanisms,360–361Suppressiontuningcurve,OAEs,405ffSOAE,230ff,408ffSuppression,andOAEs,328–329Suppression,ofbasilarmembraneresponse,348Synapticcistern,efferenteffects,350Tallhaircells,bird,241Tectorialmembrane,amphibian,215roleinthecochlearamplifier,469–470roleincouplinghaircells,230Temperateeffects,DPOAE,223Temperatureeffects,OAEs,245Temperature,effectsonSOAEinlizards,233–234effectsonSOAE,219–220Temporarythresholdshift(TTS),andOAE,288SOAE,398thresholdmicrostructure,398TEOAE,seealsoTransientevokedotoacousticemissionscompressivenon-linearity,431–432definition,33gallimaufry,334–335growthwithprimarylevels,271innewborns,432invariousspecies,272–273monkeys,271–272origins,422patientcaseexamples,439,444properties,269ffreliabilityandcalibrationerrors,427Tetrodotoxin,seeTTXThresholdfinestructure,andOAEs,395ffThresholdmicrostructure,395ffmechanisms,398ffperiodicity,396ffThyroidhormone,prestinexpression,165Tiliquarugosa(Bobtailskink),seealsoLizardsactiveprocessesandhaircells,54DPOAE,235–236EEOAEsource,239effectsonSOAEofexternaltones,232SOAE,228fftemperatureeffectsonSOAE,234Time-delayedfeedback,activeundamping,76–77Tinnitus,andOAEs,9–10andsalicylateoverdose,447Tiplink,gatingspring,101–102transduction,80Tonotopy,birdbasilarpapilla,241–242Toxorhynchitesbrevipalpis,seemosquitoesTrachemisscriptaelegans(turtle),activeprocess,54–55Transductionchannel,100–101Transductionmolecules,100–101Transduction,seealsoMechanochemicaltransductionmechanoelectrical,96ffTransientevokedOAEs,seeTEOAETransientevokedotoacousticemission,seeTEOAE,CEOAETransientreceptorpotential(TRP),101channels,463Translationinvariance,travelingwave,307–308Transmissionlinemodel,OAE,310ffTravelingwave"reflections,"assourceofOAE,27Travelingwavemodels,82–83Travelingwave,andregenerationbyactiveprocesses,83–84Travelingwave,OAEs,39ff,318fftwo-toneinterference,86–87TTX,modulationofOAE,363Tubulin,outerhaircell,148–150Tuningsharpness,OAE,408ffTuning,basilarmembrane,47,50cochlea,10,47ff484IndexTurtle,seealsoPseudemysscripta,Trachemisscriptaeleganshairbundleadaptation,103regulationofadaptation,106spontaneoushairbundleoscillations,116Twitch,132ffTwo-tonesuppression,74–75travelingwave,86–87Tympanalears,activeamplification,201–203insect,191–192Tympanicmiddleear,amphibian,214Tytoalba(barnowl),basilarpapilla,241auditorynerveresponse,242DPOAE,247–249OAEs,241ffUltrasonichearing,activeamplification,201–203insects,201–203Upwardspreadofexcitation,andOAEs,412ffUpwardspreadofsuppression,412ffVanderPoloscillators,cochlearmodels,76,387Vestibularreceptors,hairbundlemotility,93ffViscousdamping,383–384necessityforactiveprocesses,462–463Voltage-dependentstiffness,outerhaircell,171vonBékésy,cochlearmotion,40cochleartuning,10earlystudies,43–44Vulnerability,physiological,63ffWavenumber,SFOAE,321Wave-fixedOAEs,264Wave-inducedperturbations,OAEs,306,334Waveletsummation,OAEs,310ffXenopus,amphibianpapilla,215DPOAE,222SOAE,218Zebrafish,prestinhomologs,166
Gcore(gcorelabs)俄罗斯海参崴VPS简单测试
有一段时间没有分享Gcore(gcorelabs)的信息了,这是一家成立于2011年的国外主机商,总部位于卢森堡,主要提供VPS主机和独立服务器租用等,数据中心包括俄罗斯、美国、日本、韩国、新加坡、荷兰、中国(香港)等多个国家和地区的十几个机房,商家针对不同系列的产品分为不同管理系统,比如VPS(Hosting)、Cloud等都是独立的用户中心体系,部落分享的主要是商家的Hosting(Virtu...
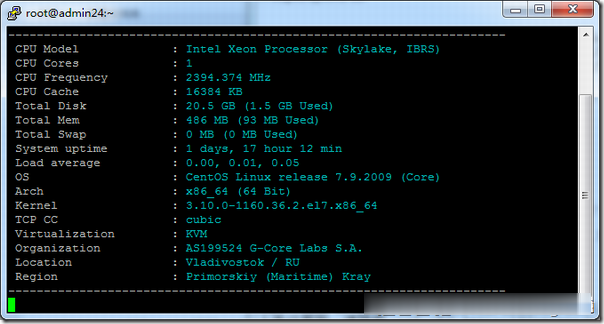
ParkinHost:俄罗斯离岸主机,抗投诉VPS,200Mbps带宽/莫斯科CN2线路/不限流量/无视DMCA/55折促销26.4欧元 /年起
外贸主机哪家好?抗投诉VPS哪家好?无视DMCA。ParkinHost今年还没有搞过促销,这次parkinhost俄罗斯机房上新服务器,母机采用2个E5-2680v3处理器、128G内存、RAID10硬盘、2Gbps上行线路。具体到VPS全部200Mbps带宽,除了最便宜的套餐限制流量之外,其他的全部是无限流量VPS。ParkinHost,成立于 2013 年,印度主机商,隶属于 DiggDigi...
6元虚拟主机是否值得购买
6元虚拟主机是否值得购买?近期各商家都纷纷推出了优质便宜的虚拟主机产品,其中不少6元的虚拟主机,这种主机是否值得购买,下面我们一起来看看。1、百度云6元体验三个月(活动时间有限抓紧体验)体验地址:https://cloud.baidu.com/campaign/experience/index.html?from=bchPromotion20182、Ucloud 10元云主机体验地址:https:...

七七seo为你推荐
-
.cn域名cn域名和com域名有什么不同?哪个更好?好在哪里?insomniac英文歌中有一句歌词是这样的:“here tonight”,谁知道这首歌曲叫什么名?咏春大师被ko大师:咏春是不会败的 教练:能不偷袭吗,咏春拳教练广东GDP破10万亿中国GDP10万亿,广东3万亿多。占了中国三分之一的经纪。如果,我是说如果。广东独立了。中国会有什www.jjwxc.net晋江文学网 的网址是什么?同ip站点同IP网站具体是什么意思,能换独立的吗www.e12.com.cn有什么好的高中学习网?www.zjs.com.cn请问宅急送客服电话号码是多少?se95se.comwww.sea8.com这个网站是用什么做的 需要多少钱javbibi日文里的bibi是什么意思