efficient因特网是什么
因特网是什么 时间:2021-04-18 阅读:()
Internetpeering:WhatdoesitmeanfordevelopingcountriesTimKelly--ITUTheinternationaltelecommunicationsregimehastraditionallybeencharacterisedbybilateral,correspondentrelationsbetweencountries,operatingunderwhatisknownastheaccountingratesystem.
Thissystem,rootedintheprincipleofnationalsovereignty,hasoperatedinoneformoranotherformorethanonehundredyearsandisbasedaninternationaltreaty,theInternationalTelecommunicationRegulations(ITR),lastrevisedin1988.
Thissystemisbasedonrevenue-sharingratherthancost-orientationandisoftenblamedforkeepingthepriceofinternationaltelephonecallsattoohighalevel.
Whiletheaccountingratesystemisremarkableforitslongevity,itisnowwidelyperceivedtobeindangerofcollapse,underpressurefromcompetitivemarketentry,technologicalchangeandby-pass.
TheInternethasevolvedaverydifferentsystemofrelationsbetweennetworkswhichmightbroadlybedescribedaspeeringarrangements.
Trafficisexchangedbetweennetworksinamannerwhichisindependentofitsultimateoriginanddestination.
Whilepeeringbeganasaconvenientandnon-for-profitarrangementbetweenacademicnetworks,ithassubsequentlybecomemorecommercialwiththeprogressiveprivatisationoftheInternetbackbone.
Peeringarrangementsarenotcurrentlyregulatedandarenotsubjecttoanyinternationaltreaty.
ItiswidelybelievedthatnetworksrunningIPtrafficbecomethemajorbearerforbothvoiceanddatatrafficinthefuture.
Ifso,doesthismeanthatpeeringarrangementswillsteadilyreplacetheaccountingratesystemonthepublicnetworkInparticular,whataretheimplicationsofsuchashiftfordevelopingcountries,whoareamongthemajorbeneficiariesofpaymentsmadeundertheexistingregimeWillthetransitionfromahalf-circuittoawhole-circuitregimemeanthatdevelopingcountriesenduppaying,ratherthanreceivingmoney,toterminatetrafficWhatpotentialrolecouldinternationalorganisations,suchastheITU,playWhyistheInternetsocheapProbablythesinglemostimportantfactorinexplainingthephenomenalsuccessoftheInternetisthatitischeap,oratleastispopularlyperceivedtobecheap.
Ofcourse,whenoneremembersthatpossessionofaPersonalComputer,appropriatesoftware,amodemandatelephonelineareallfairlyessentialprerequisitesforInternetaccess,thenmaybeitisnotsocheap,especiallyfordevelopingcountrycitizens.
Andwhenoneaddstothattheconstantpressurefromthecomputerindustrytoupgradetothelatestmodels,touseahigherbandwidthconnection,ortostartpayingforinformationthatwaspreviouslyavailableforfree,thenInternetbeginstolookdistinctlylikealuxuryitem.
TheperceptionthatInternetischeapreallyrelatestotheusagecostsratherthanthefixedcosts.
Formanyusers,theirinitialcontactwiththeInternetwouldbeatschooloruniversity,orperhapsatwork,wherethefixedcostsofinstallationandmaintenancearelargelyhiddentothem.
Thustheyareawareprimarilyofthe"saving"theyaremaking,say,byplacingatelephonecallovertheInternetratherthanoverafixedlinenetwork,ratherthanthetotalpictureofwhatthatcallcosts.
Certainly,therateswhichareavailableforanInternettelephonycallareconsiderablycheaperthanforanequivalenttelephonycall,especiallywhenthecallcrossesinternationalborders.
WhyshouldperminuteusagecostsforinternationaltelephonecallsontheInternetbesomuchlowerthanonthepublicswitchedtelephonenetwork(PSTN)Afterall,theybothusethesamecablesandthesamecopper:ThestraightforwardansweristhattheInternetusestheavailablecapacityinamoretechnicallyefficientmanner.
AtypicalcallplacedoverthePSTNwouldoccupyaduplex(two-way)circuitfortheentiredurationofthecall,includingthepausesbetweenwordsorbetweenreplies.
AcallplacedovertheInternethowevercouldtheoreticallyberoutedoverseveraldifferentcircuits,eachofwhichwouldbeoccupiedforafewthousandthsofasecondatatime,aspacketsareroutedacrossthenetworktobereassembledatthedistantend.
ThePSTNisoptimisedforvoicetransmission,sampledin8bitbytes,8'000timesasecond,foranaggregaterateof64kbit/s.
TheInternet,bycontrast,isdesignedtobeplatformindependent,collectingandterminatingtrafficuptothemaximumspeedthattheweakestlinkonthenetworkwillbear.
ThequalityoftheInternetconnectionmaybelower,butit'sefficiencywillinvariablybehigher.
AfurtherelementisthegreatercapacityutilisationachievedforInternetuse.
TheInternetisengineeredtomeetaverageloads,andthetypicalutilisationoveranextendedtimeperiodisaround60-70percent.
Bycontrast,thePublicSwitchedTelephoneNetworkisengineeredtomeetthebusinesspeakhourandthusutilisationistypicallybelow20percent.
Athirdfactoriseconomiesofscale.
IfyoucoulddrawthePSTN,itwouldlooklikeadensemeshofconnectionsinthatmostofthenodesinthenetworkareconnectedtoeveryothernodeor,iftheylackadirectconnection,couldbeconnectedbyjustoneintermediary.
Bycontrast,apictureoftheInternetwouldlookmuchmorelikeanairlineroutemapinwhichasmallnumberofhubsareconnectedtoeachotherandareeachsurroundedbyastar-shapednetworkoflocalpeeringarrangements.
Atypicalinternationalvoicetelephonycallwouldpassbetweenthehandsortwoorperhapsthreecarriers;atypicalInternettelephonycallwouldpassthroughanaverageof15hopsandmultipledifferentcarriers.
Thelogicoftheroutingisunrelatedtogeographyandinsteadrelatedtothevolumeoftrafficflows.
Trafficgravitatestothickroutes,thatisthosecableswhichhavethehighest(available)capacity.
TheseareinvariablytheoneswithintheUnitedStates,orwhichlinktheUnitedStatestoothercountries.
Whattheseexamplesillustrateisthatthe"cheapness"oftheInternetdependsonone'sviewpoint.
Internetappearcheapifoneconsidersusagecostsonlyratherthanthecompletepictureofusageandfixedcharges.
Similarly,Internetappearscheapwhencomparedtocomparableinternationalcallsbutlesssowhencomparedtolocalcalls.
TheInternetisalsocheapertheclosertheuseristoahighbandwidthpipe.
ThatmeansthatittendstobemoreexpensiveforusersoutsidetheUnitedStates.
WhyareinternationaltelephonecallssoexpensiveThecorollarytothequestion"WhyistheInternetsocheap"is"Whyisthetelephonenetworksoexpensive",particularlyforinternationalcalls.
Typically,auserin,say,sub-SaharanAfrica,wouldpaymanytimesmoreforathreeminuteinternationaltelephonecalltotheUnitedStatesthantheywouldtobeloggedonforanhourorsotoawebsitelocatedintheUnitedStates.
Andyet,thefacilitiesusedinthetwocallswouldbesimilar.
Indeed,thetwomessageswouldprobablypassundertheAtlanticonthesamecable,albeitondifferentfibrestrands,withthetelephonemessagebringingperhapsahundredtimesmorerevenuetothecarriersinvolvedthanthewebbrowsingsession.
Thesimple,thoughnotentirelyconvincinganswertothequestionisthatinternationaltelephonecallsareexpensivebecausetheyhavealwaysbeenexpensive.
Originally,internationaltelephonecallswerepricedasaluxurycommoditybecausethebandwidththatconveyedthem—initiallyHFradio,latersatellitesandunderseacables—wasinshortsupply.
Themostsignificantpricereductionsininternationalservicewereachievedinthe1960sand1970s.
Sincetheearly1980sthepricehasbeenrelativelystable(albeitdecreasingrelativetoinflation).
Ontheotherhand,thecostsofterminatingthecall,asshownbythesettlementrate,havefallensubstantiallyonalmostallroutes.
Since1995,theaveragerateofreductioninsettlementratesgloballyhasbeenoftheorderof12percentperyear,andin1998thereductionislikelytoexceed20percent.
Thishasbeenmuchfasterthantherateofreductioninprices,hencecreatingscopeforserviceswhicharbitragethedifferencebetweenthepriceoforiginatingacallandterminatingit,suchascall-back.
Furthermore,theunderlyinginfrastructurecostsfortransmissionofinternationalcallshavebeenfallingevenfaster.
Onthetrans-Atlanticroute,forinstance,thecostoftheAC-1cable,completedin1998,isjustoverUS$300per64kbit/scircuitperyear,whereastheTAT-8cable,completedadecadeearlier,costmorethanUS$10'000percircuitperyear.
Tothispriceerosioncanbeaddedthefactthatthepossibilitiesfordatacompressionhavealsoincreasedsignificantlyduringthatperiod.
Theoverallconclusionthereforemustbethatthecostreductionsbeingachievedthroughtechnologicalchangeandsettlementratereformarenotbeingpassedoninfulltotelephonyconsumers.
Itisthusnotsurprisingthatthereisconsiderablyinterest,indevelopingcountriesaswellasdevelopedones,inthepotentialforInternetTelephony,tobringlowerpricesforconsumers.
Settlementsandpeering:What'sthedifferenceFordevelopingcountries,theimplicationsofashiftawayfromsettlementstowardsapeeringregimearemixed.
Ontheonehand,itcouldmeanareductioninpriceforoutgoinginternationalcallsifthepromiseofInternetTelephonyisembraced.
Ontheotherhand,itcouldmeanthatinpaymentsreceivedforterminatinginternationalcallsaresubstantiallyreduced.
DevelopingcountriesareestimatedtogainsomeUS$7-10billionperyearinnetsettlements,muchofwhichcomesfromtheUnitedStates.
Asthesepaymentsaremadeintheformofregularmonthlycheques,cashedinhardcurrency,theyformaninvaluablesupportforadevelopingcountry'sbalanceofpayments,aswellastheirtelecommunicationinfrastructureinvestmentprogramme.
Anincominginternationaltelephoneorfaxcallwouldbringwithitasettlementpaymentofuptoacoupleofdollarsperminute.
Bycontrast,anincomingInternetcallwhichispatchedtothePSTNmightbringonlysufficientrevenuetocoverthecostofalocalcall,whichwouldamount,atmost,toafewUScentsperminute.
Indeed,inthecasewherethedevelopingcountryInternetServiceProvider(ISP)paysforthewholecircuitwhichconnectsittotheInternetbackbonenetwork,sayintheUnitedStates,thenitmayfindthatitactuallylosesmoneyonthetransactionaswellasthelostsettlementpayment.
ThedifferencebetweenthetreatmentofanincomingPSTNcallandanInternetTelephonycallisillustratedinFigure1.
Intheleftchart,thedevelopedcountrypublictelecommunicationoperator(PTOA)whichdeliversaPSTNcalltothedevelopingcountry(PTOB),alsomakesasettlementpayment,inlinewithitscorrespondentrelationshipwithPTOB.
Thiswouldnormallybehalfoftheaccountingratenegotiatedbetweenthetwo.
Intherightchart,anInternetServiceProviderinadevelopedcountry(ISPA)picksupacallwhichitpassesontoitslocalInternetExchangePoint(IXPX).
ThisisthendeliveredtoanIXPwithpeeringarrangementswiththedestinationcountry(IXPY).
ItisthendeliveredoveraleasedlinetoISPBinthedevelopingcountry(presumingISPBhasnodirectpeeringarrangementswithIXPX)whereitispatchedontothePSTNanddeliveredtotheuser.
ThereisnofinancialpaymentwhatsoeverbetweenISPAandISPB,exceptinsofarasISPBisabletorecoverthecostofalocaltelephonecall(thoughtheprocessofbillingthiscallfromISPAmayprovetobemoreexpensivethanthecallitself!
).
FurthermoreISPBmayactuallybecross-subsidisingthecallinthatitispayingforthewholecircuitleasedlinetoIXPYinaforeigncountry.
ItisrequiredtopayforthecostsbecauseISPB'suserswishtobrowsecontentonwebsitesintheforeigncountry(invariablytheUnitedStates).
ThustheincomingInternetTelephonycalliseffectivelyfreeridingthenetwork.
Figure1:EquityandinequityContrastbetweenaccountingandsettlementarrangementsfromdevelopedcountryAtodevelopingcountryB,viathePublicTelephoneNetworkandtheInternetSource:ITU"ChallengestotheNetwork:Internetfordevelopment",1998.
StrategiesfordevelopingcountriesDevelopingcountriesuptonowhavebeenmuchmorefocusedontheimplicationsofaccountingratereformthanonanypossibleimplicationsofInternetpeeringarrangements.
Forinstance,whentheFCC,theUSregulator,launcheditsNoticeofProposedRulemakinglatein1997ontheso-called"benchmarking"ofsettlementrates,itdrewcomplaintsfromsome90countries,manyofthemdeveloping.
Ontheotherhand,littleattentionhasbeenpaidtoInternetPeering.
FewdevelopingcountrieshavedevelopedpoliciesforInternettelephonyandfewerstillhavequestionedexistingpeeringarrangements.
Itmaywellbethatdevelopingcountrieshavebeenfightingyesterday'sbattlesratherthantomorrow'swars.
Settlementratesareundoubtedlytrendingtowardscosts,albeitmoreslowlythanmostconsumerswouldlike.
Developingcountriesmayconceivablybeabletoslowthisprocessdown,butonlyatthecostofseeinglargetrafficstreamsleavingtheaccountingratesystemaltogether.
Ontheotherhand,pricesforinternationalleasedlinesremainstubbornlyhigh,bothforhalfcircuitsfromtheUnitedStatesandforhalfcircuitsfromdevelopingcountries.
DevelopingcountrieswantingtoconnecttotheInternethavetopayforboth.
Whatthismeansisthat,asmoretrafficshiftsoffpublicswitchednetworksandontotheInternetwhichoperatesoverleasedlines,thenitwillbethepriceoftheleasedlineswhichwillbecomethemajordeterminantofservicecosts.
Furthermore,thetraditionalsystemofcostandrevenue-sharingforinternationalservicesislikelytobeeclipsedbyanewparadigmofdevelopingcountrieshavingtopaythefullcostsofbothhalfcircuits,aswellaspayingforpeering,iftheywanttoconnecttotheInternetbackbone.
Thereisaveryrealdangerthandevelopingcountriesmayhavetopayalotmorethandevelopedcountriesiftheywanttoavoidbeingbypassedbytheglobalinformationsuperhighway.
TheITUistryingtobringtheattentionofpolicy-makersindevelopingcountriestothisissue.
AccountingratereformdiscussionsarecurrentlybeingdebatedonafasttrackbasisthroughaFocusGroup,setupinMarch1998andduetoreporton6thNovember1998.
Also,aRapporteur'sGrouphasbeenestablishedtoexaminetheinternationalcostcomponentsoftheInternet.
BothGroupsareduetoreporttoITU-TStudyGroup3atitsDecember1998meeting.
Thusthe300orsoexpertsfromaroundtheworldwhoattendthemeetingwillhavethechancetodebatethelinkagebetweenaccountingratereformandInternetpeeringarrangementsinthesameforum.
Inalllikelihood,itistheaccountingratereformissuethatwilldominatethemeetingandgraballtheheadlines.
ButitislikelytobeInternet-stylepeeringarrangementswhichwilldominatethepublicnetworkinthecomingdecade.
[2'500words]
Thissystem,rootedintheprincipleofnationalsovereignty,hasoperatedinoneformoranotherformorethanonehundredyearsandisbasedaninternationaltreaty,theInternationalTelecommunicationRegulations(ITR),lastrevisedin1988.
Thissystemisbasedonrevenue-sharingratherthancost-orientationandisoftenblamedforkeepingthepriceofinternationaltelephonecallsattoohighalevel.
Whiletheaccountingratesystemisremarkableforitslongevity,itisnowwidelyperceivedtobeindangerofcollapse,underpressurefromcompetitivemarketentry,technologicalchangeandby-pass.
TheInternethasevolvedaverydifferentsystemofrelationsbetweennetworkswhichmightbroadlybedescribedaspeeringarrangements.
Trafficisexchangedbetweennetworksinamannerwhichisindependentofitsultimateoriginanddestination.
Whilepeeringbeganasaconvenientandnon-for-profitarrangementbetweenacademicnetworks,ithassubsequentlybecomemorecommercialwiththeprogressiveprivatisationoftheInternetbackbone.
Peeringarrangementsarenotcurrentlyregulatedandarenotsubjecttoanyinternationaltreaty.
ItiswidelybelievedthatnetworksrunningIPtrafficbecomethemajorbearerforbothvoiceanddatatrafficinthefuture.
Ifso,doesthismeanthatpeeringarrangementswillsteadilyreplacetheaccountingratesystemonthepublicnetworkInparticular,whataretheimplicationsofsuchashiftfordevelopingcountries,whoareamongthemajorbeneficiariesofpaymentsmadeundertheexistingregimeWillthetransitionfromahalf-circuittoawhole-circuitregimemeanthatdevelopingcountriesenduppaying,ratherthanreceivingmoney,toterminatetrafficWhatpotentialrolecouldinternationalorganisations,suchastheITU,playWhyistheInternetsocheapProbablythesinglemostimportantfactorinexplainingthephenomenalsuccessoftheInternetisthatitischeap,oratleastispopularlyperceivedtobecheap.
Ofcourse,whenoneremembersthatpossessionofaPersonalComputer,appropriatesoftware,amodemandatelephonelineareallfairlyessentialprerequisitesforInternetaccess,thenmaybeitisnotsocheap,especiallyfordevelopingcountrycitizens.
Andwhenoneaddstothattheconstantpressurefromthecomputerindustrytoupgradetothelatestmodels,touseahigherbandwidthconnection,ortostartpayingforinformationthatwaspreviouslyavailableforfree,thenInternetbeginstolookdistinctlylikealuxuryitem.
TheperceptionthatInternetischeapreallyrelatestotheusagecostsratherthanthefixedcosts.
Formanyusers,theirinitialcontactwiththeInternetwouldbeatschooloruniversity,orperhapsatwork,wherethefixedcostsofinstallationandmaintenancearelargelyhiddentothem.
Thustheyareawareprimarilyofthe"saving"theyaremaking,say,byplacingatelephonecallovertheInternetratherthanoverafixedlinenetwork,ratherthanthetotalpictureofwhatthatcallcosts.
Certainly,therateswhichareavailableforanInternettelephonycallareconsiderablycheaperthanforanequivalenttelephonycall,especiallywhenthecallcrossesinternationalborders.
WhyshouldperminuteusagecostsforinternationaltelephonecallsontheInternetbesomuchlowerthanonthepublicswitchedtelephonenetwork(PSTN)Afterall,theybothusethesamecablesandthesamecopper:ThestraightforwardansweristhattheInternetusestheavailablecapacityinamoretechnicallyefficientmanner.
AtypicalcallplacedoverthePSTNwouldoccupyaduplex(two-way)circuitfortheentiredurationofthecall,includingthepausesbetweenwordsorbetweenreplies.
AcallplacedovertheInternethowevercouldtheoreticallyberoutedoverseveraldifferentcircuits,eachofwhichwouldbeoccupiedforafewthousandthsofasecondatatime,aspacketsareroutedacrossthenetworktobereassembledatthedistantend.
ThePSTNisoptimisedforvoicetransmission,sampledin8bitbytes,8'000timesasecond,foranaggregaterateof64kbit/s.
TheInternet,bycontrast,isdesignedtobeplatformindependent,collectingandterminatingtrafficuptothemaximumspeedthattheweakestlinkonthenetworkwillbear.
ThequalityoftheInternetconnectionmaybelower,butit'sefficiencywillinvariablybehigher.
AfurtherelementisthegreatercapacityutilisationachievedforInternetuse.
TheInternetisengineeredtomeetaverageloads,andthetypicalutilisationoveranextendedtimeperiodisaround60-70percent.
Bycontrast,thePublicSwitchedTelephoneNetworkisengineeredtomeetthebusinesspeakhourandthusutilisationistypicallybelow20percent.
Athirdfactoriseconomiesofscale.
IfyoucoulddrawthePSTN,itwouldlooklikeadensemeshofconnectionsinthatmostofthenodesinthenetworkareconnectedtoeveryothernodeor,iftheylackadirectconnection,couldbeconnectedbyjustoneintermediary.
Bycontrast,apictureoftheInternetwouldlookmuchmorelikeanairlineroutemapinwhichasmallnumberofhubsareconnectedtoeachotherandareeachsurroundedbyastar-shapednetworkoflocalpeeringarrangements.
Atypicalinternationalvoicetelephonycallwouldpassbetweenthehandsortwoorperhapsthreecarriers;atypicalInternettelephonycallwouldpassthroughanaverageof15hopsandmultipledifferentcarriers.
Thelogicoftheroutingisunrelatedtogeographyandinsteadrelatedtothevolumeoftrafficflows.
Trafficgravitatestothickroutes,thatisthosecableswhichhavethehighest(available)capacity.
TheseareinvariablytheoneswithintheUnitedStates,orwhichlinktheUnitedStatestoothercountries.
Whattheseexamplesillustrateisthatthe"cheapness"oftheInternetdependsonone'sviewpoint.
Internetappearcheapifoneconsidersusagecostsonlyratherthanthecompletepictureofusageandfixedcharges.
Similarly,Internetappearscheapwhencomparedtocomparableinternationalcallsbutlesssowhencomparedtolocalcalls.
TheInternetisalsocheapertheclosertheuseristoahighbandwidthpipe.
ThatmeansthatittendstobemoreexpensiveforusersoutsidetheUnitedStates.
WhyareinternationaltelephonecallssoexpensiveThecorollarytothequestion"WhyistheInternetsocheap"is"Whyisthetelephonenetworksoexpensive",particularlyforinternationalcalls.
Typically,auserin,say,sub-SaharanAfrica,wouldpaymanytimesmoreforathreeminuteinternationaltelephonecalltotheUnitedStatesthantheywouldtobeloggedonforanhourorsotoawebsitelocatedintheUnitedStates.
Andyet,thefacilitiesusedinthetwocallswouldbesimilar.
Indeed,thetwomessageswouldprobablypassundertheAtlanticonthesamecable,albeitondifferentfibrestrands,withthetelephonemessagebringingperhapsahundredtimesmorerevenuetothecarriersinvolvedthanthewebbrowsingsession.
Thesimple,thoughnotentirelyconvincinganswertothequestionisthatinternationaltelephonecallsareexpensivebecausetheyhavealwaysbeenexpensive.
Originally,internationaltelephonecallswerepricedasaluxurycommoditybecausethebandwidththatconveyedthem—initiallyHFradio,latersatellitesandunderseacables—wasinshortsupply.
Themostsignificantpricereductionsininternationalservicewereachievedinthe1960sand1970s.
Sincetheearly1980sthepricehasbeenrelativelystable(albeitdecreasingrelativetoinflation).
Ontheotherhand,thecostsofterminatingthecall,asshownbythesettlementrate,havefallensubstantiallyonalmostallroutes.
Since1995,theaveragerateofreductioninsettlementratesgloballyhasbeenoftheorderof12percentperyear,andin1998thereductionislikelytoexceed20percent.
Thishasbeenmuchfasterthantherateofreductioninprices,hencecreatingscopeforserviceswhicharbitragethedifferencebetweenthepriceoforiginatingacallandterminatingit,suchascall-back.
Furthermore,theunderlyinginfrastructurecostsfortransmissionofinternationalcallshavebeenfallingevenfaster.
Onthetrans-Atlanticroute,forinstance,thecostoftheAC-1cable,completedin1998,isjustoverUS$300per64kbit/scircuitperyear,whereastheTAT-8cable,completedadecadeearlier,costmorethanUS$10'000percircuitperyear.
Tothispriceerosioncanbeaddedthefactthatthepossibilitiesfordatacompressionhavealsoincreasedsignificantlyduringthatperiod.
Theoverallconclusionthereforemustbethatthecostreductionsbeingachievedthroughtechnologicalchangeandsettlementratereformarenotbeingpassedoninfulltotelephonyconsumers.
Itisthusnotsurprisingthatthereisconsiderablyinterest,indevelopingcountriesaswellasdevelopedones,inthepotentialforInternetTelephony,tobringlowerpricesforconsumers.
Settlementsandpeering:What'sthedifferenceFordevelopingcountries,theimplicationsofashiftawayfromsettlementstowardsapeeringregimearemixed.
Ontheonehand,itcouldmeanareductioninpriceforoutgoinginternationalcallsifthepromiseofInternetTelephonyisembraced.
Ontheotherhand,itcouldmeanthatinpaymentsreceivedforterminatinginternationalcallsaresubstantiallyreduced.
DevelopingcountriesareestimatedtogainsomeUS$7-10billionperyearinnetsettlements,muchofwhichcomesfromtheUnitedStates.
Asthesepaymentsaremadeintheformofregularmonthlycheques,cashedinhardcurrency,theyformaninvaluablesupportforadevelopingcountry'sbalanceofpayments,aswellastheirtelecommunicationinfrastructureinvestmentprogramme.
Anincominginternationaltelephoneorfaxcallwouldbringwithitasettlementpaymentofuptoacoupleofdollarsperminute.
Bycontrast,anincomingInternetcallwhichispatchedtothePSTNmightbringonlysufficientrevenuetocoverthecostofalocalcall,whichwouldamount,atmost,toafewUScentsperminute.
Indeed,inthecasewherethedevelopingcountryInternetServiceProvider(ISP)paysforthewholecircuitwhichconnectsittotheInternetbackbonenetwork,sayintheUnitedStates,thenitmayfindthatitactuallylosesmoneyonthetransactionaswellasthelostsettlementpayment.
ThedifferencebetweenthetreatmentofanincomingPSTNcallandanInternetTelephonycallisillustratedinFigure1.
Intheleftchart,thedevelopedcountrypublictelecommunicationoperator(PTOA)whichdeliversaPSTNcalltothedevelopingcountry(PTOB),alsomakesasettlementpayment,inlinewithitscorrespondentrelationshipwithPTOB.
Thiswouldnormallybehalfoftheaccountingratenegotiatedbetweenthetwo.
Intherightchart,anInternetServiceProviderinadevelopedcountry(ISPA)picksupacallwhichitpassesontoitslocalInternetExchangePoint(IXPX).
ThisisthendeliveredtoanIXPwithpeeringarrangementswiththedestinationcountry(IXPY).
ItisthendeliveredoveraleasedlinetoISPBinthedevelopingcountry(presumingISPBhasnodirectpeeringarrangementswithIXPX)whereitispatchedontothePSTNanddeliveredtotheuser.
ThereisnofinancialpaymentwhatsoeverbetweenISPAandISPB,exceptinsofarasISPBisabletorecoverthecostofalocaltelephonecall(thoughtheprocessofbillingthiscallfromISPAmayprovetobemoreexpensivethanthecallitself!
).
FurthermoreISPBmayactuallybecross-subsidisingthecallinthatitispayingforthewholecircuitleasedlinetoIXPYinaforeigncountry.
ItisrequiredtopayforthecostsbecauseISPB'suserswishtobrowsecontentonwebsitesintheforeigncountry(invariablytheUnitedStates).
ThustheincomingInternetTelephonycalliseffectivelyfreeridingthenetwork.
Figure1:EquityandinequityContrastbetweenaccountingandsettlementarrangementsfromdevelopedcountryAtodevelopingcountryB,viathePublicTelephoneNetworkandtheInternetSource:ITU"ChallengestotheNetwork:Internetfordevelopment",1998.
StrategiesfordevelopingcountriesDevelopingcountriesuptonowhavebeenmuchmorefocusedontheimplicationsofaccountingratereformthanonanypossibleimplicationsofInternetpeeringarrangements.
Forinstance,whentheFCC,theUSregulator,launcheditsNoticeofProposedRulemakinglatein1997ontheso-called"benchmarking"ofsettlementrates,itdrewcomplaintsfromsome90countries,manyofthemdeveloping.
Ontheotherhand,littleattentionhasbeenpaidtoInternetPeering.
FewdevelopingcountrieshavedevelopedpoliciesforInternettelephonyandfewerstillhavequestionedexistingpeeringarrangements.
Itmaywellbethatdevelopingcountrieshavebeenfightingyesterday'sbattlesratherthantomorrow'swars.
Settlementratesareundoubtedlytrendingtowardscosts,albeitmoreslowlythanmostconsumerswouldlike.
Developingcountriesmayconceivablybeabletoslowthisprocessdown,butonlyatthecostofseeinglargetrafficstreamsleavingtheaccountingratesystemaltogether.
Ontheotherhand,pricesforinternationalleasedlinesremainstubbornlyhigh,bothforhalfcircuitsfromtheUnitedStatesandforhalfcircuitsfromdevelopingcountries.
DevelopingcountrieswantingtoconnecttotheInternethavetopayforboth.
Whatthismeansisthat,asmoretrafficshiftsoffpublicswitchednetworksandontotheInternetwhichoperatesoverleasedlines,thenitwillbethepriceoftheleasedlineswhichwillbecomethemajordeterminantofservicecosts.
Furthermore,thetraditionalsystemofcostandrevenue-sharingforinternationalservicesislikelytobeeclipsedbyanewparadigmofdevelopingcountrieshavingtopaythefullcostsofbothhalfcircuits,aswellaspayingforpeering,iftheywanttoconnecttotheInternetbackbone.
Thereisaveryrealdangerthandevelopingcountriesmayhavetopayalotmorethandevelopedcountriesiftheywanttoavoidbeingbypassedbytheglobalinformationsuperhighway.
TheITUistryingtobringtheattentionofpolicy-makersindevelopingcountriestothisissue.
AccountingratereformdiscussionsarecurrentlybeingdebatedonafasttrackbasisthroughaFocusGroup,setupinMarch1998andduetoreporton6thNovember1998.
Also,aRapporteur'sGrouphasbeenestablishedtoexaminetheinternationalcostcomponentsoftheInternet.
BothGroupsareduetoreporttoITU-TStudyGroup3atitsDecember1998meeting.
Thusthe300orsoexpertsfromaroundtheworldwhoattendthemeetingwillhavethechancetodebatethelinkagebetweenaccountingratereformandInternetpeeringarrangementsinthesameforum.
Inalllikelihood,itistheaccountingratereformissuethatwilldominatethemeetingandgraballtheheadlines.
ButitislikelytobeInternet-stylepeeringarrangementswhichwilldominatethepublicnetworkinthecomingdecade.
[2'500words]
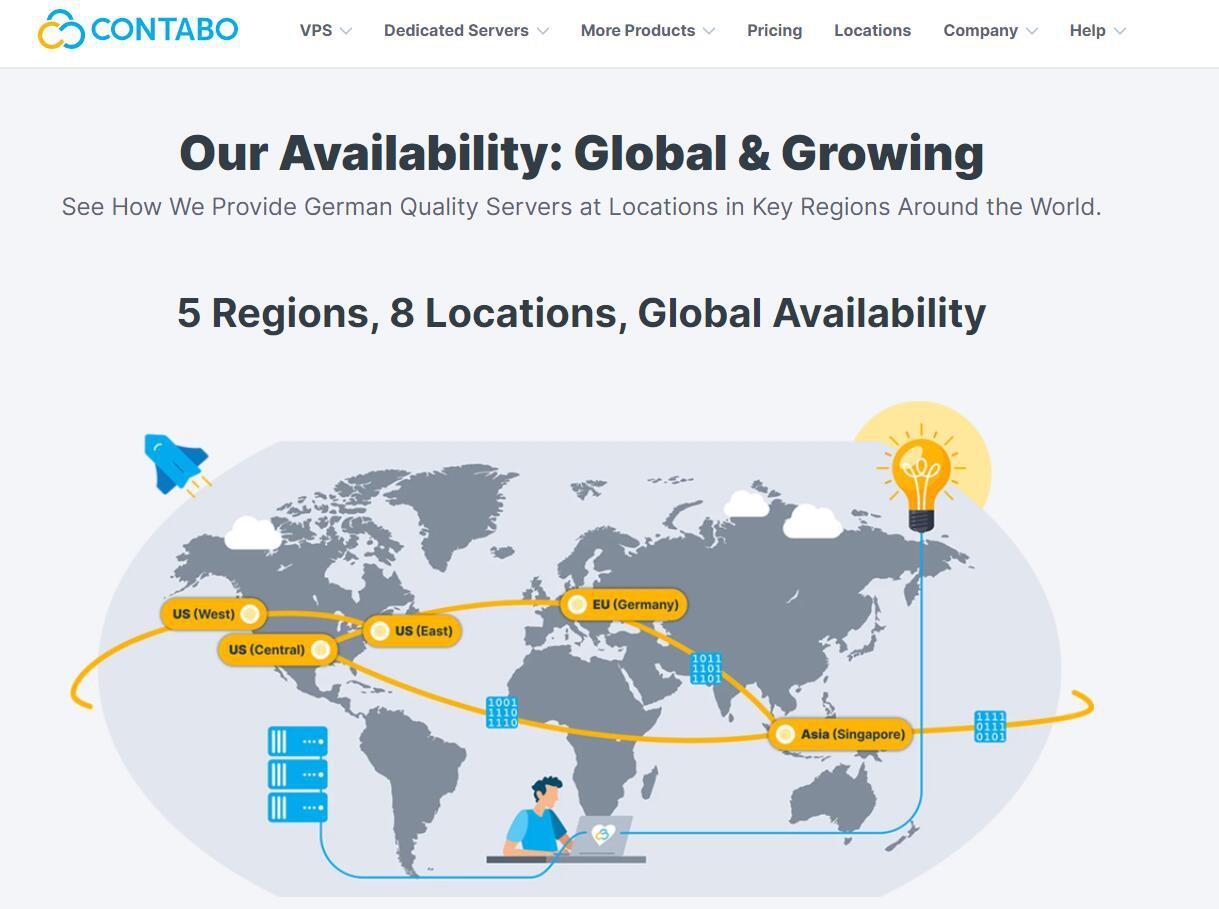
€4.99/月Contabo云服务器,美国高性价比VPS/4核8G内存200G SSD存储
Contabo是一家运营了20多年的欧洲老牌主机商,之前主要是运营德国数据中心,Contabo在今年4月份增设新加坡数据中心,近期同时新增了美国纽约和西雅图数据中心。全球布局基本完成,目前可选的数据中心包括:德国本土、美国东部(纽约)、美国西部(西雅图)、美国中部(圣路易斯)和亚洲的新加坡数据中心。Contabo的之前国外主机测评网站有多次介绍,他们家的特点就是性价比高,而且这个高不是一般的高,是...
香港最便宜的vps要多少钱?最便宜的香港vps能用吗?
香港最便宜的vps要多少钱?最便宜的香港vps能用吗?香港vps无需备案,整体性能好,而且租用价格便宜,使用灵活,因为备受站长喜爱。无论是个人还是企业建站,都比较倾向于选择香港VPS。最便宜的香港vps能用吗?正因为有着诸多租用优势,香港VPS在业内颇受欢迎,租用需求量也在日益攀升。那么,对于新手用户来说,香港最便宜的vps租用有四大要点是务必要注意的,还有易探云香港vps租用最便宜的月付仅18元...

乌云数据(10/月),香港cera 1核1G 10M带宽/美国cera 8核8G10M
乌云数据主营高性价比国内外云服务器,物理机,本着机器为主服务为辅的运营理念,将客户的体验放在第一位,提供性价比最高的云服务器,帮助各位站长上云,同时我们深知新人站长的不易,特此提供永久免费虚拟主机,已提供两年之久,帮助了上万名站长从零上云官网:https://wuvps.cn迎国庆豪礼一多款机型史上最低价,续费不加价 尽在wuvps.cn香港cera机房,香港沙田机房,超低延迟CN2线路地区CPU...
因特网是什么为你推荐
-
企业邮局系统企业邮件系统用什么软件好?特朗普吐槽iPhone为什么那么多人吐槽iphoneasp.net网页制作ASP.NET设计网页的方法?支付宝注册网站在哪里注册支付宝更新internal加多宝和王老吉王老吉和加多宝的关系?小型汽车网上自主编号申请请问各位大虾,如何在网上选车牌号?瑞东集团中粮集团主要生产什么的?是国企么powerbydedecms如何去掉底部的 powered by dedecmsjoomla安装下载app并安装