Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci
www.299pp.com 时间:2021-03-19 阅读:()
(2014)3(1):299-308299OriginalResearchArticleDetectionofheavymetals(Pb,Sb,Al,As)throughatomicabsorptionspectroscopyfromdrinkingwaterofDistrictPishin,Balochistan,PakistanAfrasiabKhanTareen1*,ImranaNiazSultan1,PramukParakulsuksatid2,MohammadShafi2,AshrafKhan2,MohammadWaseemKhan2andSadatHussain21BalochistanUniversityofInformationTechnologyEngineeringandManagementSciencesBalochistan,Pakistan2KasetsartUniversityBangkok,Thailand*CorrespondingauthorABSTRACTIntroductionAreadescriptionDistrictPishinissituatedintheNorthWestBalochistanprovince(Pakistan)nearAfghanistanborder.
TheSurroundingareasofPishinareBarshore,Milkyar,Nowabad,SarananandYaro;thisdistrictliesbetween30-04to31-17northlatitudesand66-13to67-50eastlongitudes.
GenerallydistrictPishinismountainousanditsnorthernhalfiscoveredbyTobaPlateau.
Themountainsarefairlyuniform,ISSN:2319-7706Volume3Number1(2014)pp.
299-308http://www.
ijcmas.
comKeywordsHeavyMetal;AtomicabsorptionSpectroscopy;Antimony;Aluminum.
ThisstudywasdesignedtodetectheavymetaltracessuchasAntimony,Arsenic,Lead,andAluminuminwatersamplesobtainedfromtubewellshavingdifferentdepthsindistrictPishin,Baluchistan,Pakistan.
Analysisof50freshwatersampleswasdonethroughAtomicabsorptionspectroscopyinordertocomparevariousparameterssuchasageoftubewell,EC,Area,pH,depthoftubewell,populationburdenanduseoffertilizersintheselectedareas.
Thestudyrevealedthatageoftubewellhadnoimpactonquantitiesofstudiedheavymetals,however,significantimpactoftubewellsdepthwasobservedindecreasingdepthorder.
AntimonyandAluminumvalueswerefoundinhigherquantitiesthanstandardrecommendedvaluesintubewellsoflowerdepth.
Arsenicandleadwerefoundinbelowrecommendedvaluesalltubewellwatersamples.
Thearsenicpresenceinthesamplesmaybeattributedtothepopulationburdenandtheuseofchemicalfertilizersinthesurroundingareaoftubewellsrespectively,thequantityofAluminumandAntimonywerefoundhigherthansafelevelswhichisanalarmingindicationforthedrinkingwaterforpublicuse.
TheconductivityandpHwerefoundhigherinshallowdepthsoftubewells.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308300withlongcentralridgesfromwhichfrequentspursdescend.
Theclimateofthisregioniscoldanddry,minimumtemperatureinwinterreachesbelowfreezingpointwhileinsummeritcanreachashighas400Pishinissituatedatanelevationof5104feetabovesealevel.
Pishindistrictisfamousforitsagricultureproducts,mostnotablyfruitorchardsincludingapples,grapes,somecropsandvegetables.
Theartificialirrigationchannelsinthearea,madebyboringholesintorockstobringwatertothesurfaceforagriculturaluseandhumanconsumption.
Karezandmodernagriculturalmethodshavedonewondersinthearea.
ThegroundwaterresourcesofdistrictPishinmostlydependsontubewells,riversandKarezsystem.
WaterandHeavymetalsSafeandgoodqualitydrinkingwateristhebasisforgoodhumanhealth.
Waterprovidessomeelements,butwhenpolluteditmaybecomethesourceofundesirablesubstances,dangeroustohumanhealthandcausediseasesuchas,variouscancers,adversereproductiveoutcomes,cardiovasculardisease,teethdecayandneurologicaldiseases.
Theinfantsandyoungerpopulationaremorepronetothetoxiceffectsofheavymetals,astherapidlydevelopingbodysystemsinthefetus,infantsandyoungchildrenarefarmoresensitive(JohnsonandHallberg,2005).
Childhoodexposuretosomemetalscanresultinlearningdifficulties,memoryimpairment,damagetothenervoussystem,andbehavioralproblemssuchasaggressivenessandhyperactivity(Rajendranetal.
,2003).
Athigherdoses,heavymetalscancauseirreversiblebraindamage.
Childrenmayreceivehigherdosesofmetalsfromfoodthanadults,sincetheyconsumemorefoodfortheirbodyweightthanadults.
Thereasonforthishydrologicalscourgeisthepresenceofalarminglevelsofheavymetalarsenicingroundwaterinseveralvillagesoftheglobe(Doganetal.
,2005).
Heavymetalsintheformofarsenicandarsenicalcompoundsareexceptionallytoxicandharmfultohumanhealth.
Theyarefoundineffluentsandleachesfrommetallurgicindustries,glasswareandceramicindustriesdye,pesticideandfertilizermanufacturingindustries,petroleumrefiningandotherchemicalindustries.
Somepartoftheworldarsenicoccursnaturallyinthesoilfromwhereitreachestothegroundwater(Choudhuryetal.
,2009).
Exposuretoantimonyisassociatedwithdamagetotheheart,lungs,andotherorgans.
Thereislimitedevidencethatchronicexposurecancausedevelopmentalandreproductiveeffects,Peoplecanbeexposedtoantimonybybreathingcontaminatedair,drinkingcontaminatedwater,orbyeatingfoodsthatcontainthismetal.
Leadisaheavy,softgraymetal.
TheEPAclassifiesleadasaprobablehumancarcinogen.
Exposuretoleadresultsfrombreathingcontaminatedair,contactingleadcontaminatedsoils,ordrinkingcontaminatedwater.
Tapwatercontaminationwithleadoccurswhenwaterpassesthrougholderpipescontaininglead,leadsolder,orbrassfixturesthatcontainlead(ATSDR,2000),Althoughaluminumisnotaheavymetal(specificgravityof2.
55-2.
80),itmakesupabout8%ofthesurfaceoftheearthandisthethirdmostabundantelement.
Whenaluminumaccumulatesacutelyintissuessuchasthebrain,ithasthepotentialtocauseseriousadverseneurologicaleffects.
Dialysisencephalopathyisaformofaluminumneurotoxicitycharacterizedbyspeechdifficulty,dementiaandconvulsions(Richard,1993).
AccordingtoEnvironmentalProtectionagencytheacceptableamountofheavymetalssuchasInt.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308301antimonyinoneliterofdrinkingwateris0.
006mg/l,forleaditis0.
015mg/l,forArsenic0.
010mg/l,andforAluminum0.
05-0.
2mg/l.
Theheavymetalsrelatedmostoftentohumanpoisoningarelead,mercury,arsenicandcadmium.
Otherheavymetals,includingcopper,zinc,andchromium,areactuallyrequiredbythebodyinsmallamounts(GoyerandClarkson,2001).
MaterialsandMethodsThepurposeofthisstudywastoevaluatetheconcentrationofheavymetalsingroundwaterfromtubewellsandtoanalyzeif,parameterssuchasdepthoftubewell,locationoftubewell,ageoftubewell,samplepH,sampleconductivity,populationburdenanduseoffertilizers,pesticidesandinsecticideshasanimpactonpresenceofheavymetalcontentsandheavymetalconcentration.
SamplecollectionFifty(50)watersamplesfromdifferenttubewellsoftwelve(12)differentvillagesofdistrictpishinnamely(MainPishincity,Malakyar,ChamanMalakyar,Manzaki,Ismailzai,Bagarzai,Dabkhanzai,mianKhanzai,SirKhanzai,KilliNawabad,BatazaiandToraShah)wereobtained.
Toavoidpossibilityofcontaminationtheemptypolythenebottleswereusedforthecollectionofwatersamplesandwerelabeledaccurately.
Twosampleswerecollectedfromeachandeverytubewellinwhichonesamplesof50mlwasmixedwith4mlofHNO3(Nitricacid)forsamplepreservation(Michael,1982;APHA,etal.
,1992).
SampleanalysisThepHofallsampleswasmeasuredbypHmeter(JENWAYMODELNo.
3520)andelectricconductivitywasmeasuredwiththehelpofconductivemeter(JENWAYMODELNO.
470).
Theconcentrationsofheavymetalswereanalyzedinallthe50samplesofwaterusing(SOLAARAASERIESS4SYSTEMATOMICABSORPTIONSPECTROSCOPY(AAS)byFlamemethodwiththehelpofnitrousoxide/Acetylenegasesasdescribedby(Michael,1982).
LampCurrentTheoperatingcurrentinmAforthelamp.
Itisimportantthatyouhaveverifiedthatthelampispresentbeforecompletingthisstep.
A30mAcurrentmightdamageothertypesoflamps.
Whenthelampcurrenthasbeenentered,theamplifiergainwillbeautomaticallyset.
ReplicatesEachmeasurementisrepeated3times.
Youmaywishtochangethisnumberlater.
Theallowedrangeforthenumberofreplicatesis1-99.
StandardreagentspreparationThree(3)differentreagentsasstandardstocksolutionof1000ppmwerepreparedforthedetectionofeachandeveryheavymetal.
Thereagentspreparedwereinbelowconcentrations.
Arsenic(As):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofArsenic(Ar)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof40.
00mg/l,80.
00mg/land120.
00mg/lwereprepared.
PureArsenic(As)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308302Lead(Pb):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofLead(Pb)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof7.
00mg/l,14.
00mg/land21.
00mg/lwereprepared.
PureLead(Pb)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterandwasmadetovolumewithde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
Antimony(Sb):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofantimony(Sb)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof25.
00mg/l,50.
00mg/land75.
00mg/lwereprepared.
Pureantimony(Sb)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
Aluminum(Al):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofAluminum(Al)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof30.
00mg/l,60.
00mg/land90.
00mg/lwereprepared.
PureAluminum(Al)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
ResultsandDiscussionWatersamplescollectedfromdifferentareasofdistrictPishinwereanalyzedforpresenceofheavymetalcontents.
Thepresenceofheavymetalssuchasarsenic(As),lead(Pb),antimony(Sb),aluminum(Al),wereanalyzedfortheirpresenceandcomparedwithdifferentparameterssuchdepthoftubewell,ageoftubewell,locationoftubewell,samplepH,sampleconductivity,populationburden,useofinsecticides,pesticidesandTheaestheticandphysicalparametersweredeterminedwhichprovidedgeneralinformationaboutwaterqualityinqualitativetermsandincludewaterqualityparameterslikecolor,physicalappearance,transparency,Electricalconductivity,odors,pH,tasteandturbidity.
TheoverallaveragepHofallthecollectedsampleswere8.
38withtheminimumandmaximumvaluesof7.
9-8.
86respectively.
MostofthesamplingareaswerehavingthenormalpHvalueexceptNawabadhavingtheaveragepHof8.
69.
Theelectricalconductivity(EC)providesarapidandconvenientmeansforestimatingtheconcentrationofelectrolytesandgivesquickinformationaboutallminerals.
TheECvaluesofallthewatersampleswereinthenormalrangeof50-500uS/cm.
Theageoftubewellswerealsoassessedwiththepresenceofheavymetalsinwater.
Theaverageagesofallthetubewellswereapproximately04years.
Whiletheaveragedepthofthewellswererecordedas157meters(509feet).
ArsenicandleadwerefoundinallsamplesbuttheywerequitebelowthentherecommendedvaluesgivenbyWHO.
WatersamplescollectedfromdifferentareasofdistrictPishinwereanalyzedforpresenceofheavymetalcontents.
Thepresenceofheavymetalssuchasarsenic(As),antimony(Sb),aluminum(Al),andLead(pb)wereanalyzedfortheirpresenceandcomparedwithdifferentparameterssuchasdepthoftubewell,ageoftubewell,locationoftubewell,samplepH,sampleconductivity,populationburden,useofinsecticides,pesticidesandfertilizers.
ArsenicandleadWerepresentinallsamplescollectedfromareasofheavypopulationbutonaverageitsconcentrationwaslowerthanstandardrecommendedvalueswhichdepictsthatpopulationhaspositiveimpactonpresenceofheavymetals.
ThestudyfindingsshowsthatthedepthoftubewellshavepositiveInt.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308303Figure.
1.
0DepthofTubeWellsvs.
AntimonyContentsAntimonycontentswerecomparedwiththedepthofthetubewellsanditwasfoundthatineverysampleantimonycontentswerepresentandtheyweresignificantlyabovetherecommendedvalue.
Theantimonycontentsofcollectedwatersampleswererangedfrom0.
2774mg/lto1.
0214mg/l.
Antimonycontentswerefoundinhigheramountintubewellsoflowerdepthandthevalueofantimonycontentswassignificantlylowerintubewellsofhigherdepth.
Itwasfoundthatasthedepthoftubewellincreasedtheamountofantimonydecreasedsignificantly.
Figure.
1.
1DepthofTubeWellsvs.
AluminumContentsComparingAluminumContentswiththedepthofthetubewellsanditwasfoundthatineverysamplealuminumcontentswerepresentandtheyweresignificantlyabovethentherecommendedvalue.
Aluminumcontentswerefoundinhigheramountintubewellsoflowerdepthandthevalueofaluminumcontentswassignificantlylowerintubewellsofhigherdepth.
Itwasfoundthatasthedepthoftubewellincreasestheamountofaluminumdecreasedsignificantly.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308304Figure.
1.
2DepthofTubeWellsvs.
ArsenicContentsTheDepthoftubewellswerecomparedwithArseniccontentsinwhichitwasfoundthatineverysamplearseniccontentswerepresentbuttheywerebelowtherecommendedvalue.
Arseniccontentswerefoundinhigheramountintubewellsoflowerdepthandthevalueofarseniccontentswassignificantlylowerintubewellsofhigherdepthbutallofthemwerebelowtherecommendedvalue.
Itwasfoundthatasthedepthoftubewellincreasedtheamountofarsenicdecreasedsignificantly.
Figure.
1.
3DepthofTubeWellsvs.
LeadContentsLeadcontentswerecomparedwiththedepthofthetubewellsanditwasfoundthatineverysampleLeadcontentswerepresentbuttheyweresignificantlybelowtherecommendedvalue.
Theleadcontentsofcollectedwatersampleswererangedfrom0.
001mg/lto0.
0078mg/l.
literallyleadcontentswerefoundalmostequalinalldepthsoftubewellswhichshowthatthereisnosignificanceofdepthonleadcontents.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308305Figure.
1.
4AgeofTubeWellsVs.
AntimonyContentsTheageoftubewellswerestudiedanditsimpactwascomparedonAntimonycontents.
Thestudyfoundthatantimonywaspresentinalmostallwatersamplescollectedfromdifferenttubewells.
Theantimonycontentswerepresentinsignificantproportion.
Whenstudiedforitscomparisonwithageoftubewellsitwasseenthatantimonycontentswerepresentinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellageandtherewerenosignificantchangeregardingageoftubewell.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehaveantimonycontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigherantimonycontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigherantimonycontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofantimonycontentsinstudiedwatersamples.
Figure.
1.
5AgeofTubeWellsVs.
AluminumContentsTheageoftubewellswerecalculatedanditsimpactwascomparedonaluminumcontents.
Itwasfoundthataluminumcontentswereinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellage.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehavealuminumcontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigheraluminumcontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigheraluminumcontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofaluminumcontents.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308306Figure.
1.
6AgeofTubewellsVs.
ArsenicContentsLeadContentswerecomparedwiththeageoftubewells.
Itwasfoundthatleadcontentswereinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellage.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehaveleadcontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigherleadcontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigherleadcontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofleadcontents.
Figure.
1.
7AgeoftubewellsVs.
ArsenicLeadContentsTheageoftubewellswerecalculatedanditsimpactwascomparedonArseniccontents.
ItwasfoundthatArseniccontentswereinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellage.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehavearseniccontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigherarseniccontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigherarseniccontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofarseniccontents.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308307Figure.
1.
8AreaComparisonVs.
Antimony(Sb)ContentsAntimonycontentswerecomparedwithdifferentstudyareas.
Itwasfoundthatantimonycontentswerefoundineveryareawatersamplecollectedfromtubewells.
Antimony3contentshadalmostequalamountinallstudiedareasandnosignificantchangewasfoundFigure.
1.
9AreaComparisonVs.
Aluminum(Al)ContentsAluminumcontentswerecomparedwithdifferentstudyareas.
Itwasfoundthataluminumcontentswerefoundineveryareawatersamplecollectedfromtubewells.
Howeverinsomeareasincluding(Pishincity,Ismailzai,NawabadandBagarzai)thealuminumcontentswerefoundsignificantlyhigherthanotherstudiedareas.
Itwasassumedthattheincreaseinaluminumcontentsintheseareasmightbeduetowaterturbidityandmuddysoilinnaturefoundintheseareas.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308308impactonconcentrationoftheseheavymetalsinparticularsuchasAntimony(Sb),Arsenic(As),andAluminum(Al).
Theabovediscussionleadstotheconclusionthatthegeologicconditionofthearea,useoffertilizers,insectrepellantsanddepthoftubewellsmaycontaminatetheundergroundwater.
ReferencesATSDR.
2000.
CaseStudiesinEnvironmentalMedicine.
LeadToxicity.
U.
S.
DepartmentofHealthandHumanServices,Atlanta,GA,Pp.
31-33.
APHA,AWWAandWEF,D.
E.
1992.
StandardmethodsfortheExaminationofwaterandwastewater.
AmericanpublicHealthAssociation,AmericanwaterworkAssociationandWaterEnvironmentalFederation,18thEdition,Washington,DC.
Pp.
11-19.
Choudhury,R.
Q.
,T.
S.
Shaikh,RAlam,R.
Sen,J.
Hasan,andI.
A.
Chowdhur.
2009.
EffectofArsenicContaminatedIrrigationWaterontheCultivationofRedAmaranth.
American-EurasianJ.
ScientificRes.
.
4(1):pp.
14-19.
Dogan,M.
,A.
U.
Dogan,C.
Celebi,andY.
I.
Baris.
2005.
IndoorBuiltEnviron,Vol.
14(6):pp.
533-536.
Goyer,R.
A.
,andT.
M.
Clarkson.
2001.
Toxiceffectsofmetals.
Chapter23.
In:Klaassen,C.
D.
,Casarett&Doullstoxicology.
NewYork:McGraw-Hill,pp.
811-868.
Johnson,D.
B.
,andK.
B.
Hallberg.
2005.
Acidminedrainageremediationoptions:areview.
Sci.
TotalEnviron.
,Vol.
338:pp.
3-14.
Micheal,J.
S.
,1982.
Physical,chemical&radiologicalExamination,Vol.
2(170):pp.
202-210.
Rajendran,P.
,J.
Muthukrishnan,andP.
Gunasekaran,2003.
Microbesinheavymetalremediation.
IndianJ.
Exp.
Biol.
41(9):935-944.
Richard,S.
R.
,1993.
Review:alzheimersdiseaseandenvironmentalaluminium.
AgeandAgeing,22:138-153.
TheSurroundingareasofPishinareBarshore,Milkyar,Nowabad,SarananandYaro;thisdistrictliesbetween30-04to31-17northlatitudesand66-13to67-50eastlongitudes.
GenerallydistrictPishinismountainousanditsnorthernhalfiscoveredbyTobaPlateau.
Themountainsarefairlyuniform,ISSN:2319-7706Volume3Number1(2014)pp.
299-308http://www.
ijcmas.
comKeywordsHeavyMetal;AtomicabsorptionSpectroscopy;Antimony;Aluminum.
ThisstudywasdesignedtodetectheavymetaltracessuchasAntimony,Arsenic,Lead,andAluminuminwatersamplesobtainedfromtubewellshavingdifferentdepthsindistrictPishin,Baluchistan,Pakistan.
Analysisof50freshwatersampleswasdonethroughAtomicabsorptionspectroscopyinordertocomparevariousparameterssuchasageoftubewell,EC,Area,pH,depthoftubewell,populationburdenanduseoffertilizersintheselectedareas.
Thestudyrevealedthatageoftubewellhadnoimpactonquantitiesofstudiedheavymetals,however,significantimpactoftubewellsdepthwasobservedindecreasingdepthorder.
AntimonyandAluminumvalueswerefoundinhigherquantitiesthanstandardrecommendedvaluesintubewellsoflowerdepth.
Arsenicandleadwerefoundinbelowrecommendedvaluesalltubewellwatersamples.
Thearsenicpresenceinthesamplesmaybeattributedtothepopulationburdenandtheuseofchemicalfertilizersinthesurroundingareaoftubewellsrespectively,thequantityofAluminumandAntimonywerefoundhigherthansafelevelswhichisanalarmingindicationforthedrinkingwaterforpublicuse.
TheconductivityandpHwerefoundhigherinshallowdepthsoftubewells.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308300withlongcentralridgesfromwhichfrequentspursdescend.
Theclimateofthisregioniscoldanddry,minimumtemperatureinwinterreachesbelowfreezingpointwhileinsummeritcanreachashighas400Pishinissituatedatanelevationof5104feetabovesealevel.
Pishindistrictisfamousforitsagricultureproducts,mostnotablyfruitorchardsincludingapples,grapes,somecropsandvegetables.
Theartificialirrigationchannelsinthearea,madebyboringholesintorockstobringwatertothesurfaceforagriculturaluseandhumanconsumption.
Karezandmodernagriculturalmethodshavedonewondersinthearea.
ThegroundwaterresourcesofdistrictPishinmostlydependsontubewells,riversandKarezsystem.
WaterandHeavymetalsSafeandgoodqualitydrinkingwateristhebasisforgoodhumanhealth.
Waterprovidessomeelements,butwhenpolluteditmaybecomethesourceofundesirablesubstances,dangeroustohumanhealthandcausediseasesuchas,variouscancers,adversereproductiveoutcomes,cardiovasculardisease,teethdecayandneurologicaldiseases.
Theinfantsandyoungerpopulationaremorepronetothetoxiceffectsofheavymetals,astherapidlydevelopingbodysystemsinthefetus,infantsandyoungchildrenarefarmoresensitive(JohnsonandHallberg,2005).
Childhoodexposuretosomemetalscanresultinlearningdifficulties,memoryimpairment,damagetothenervoussystem,andbehavioralproblemssuchasaggressivenessandhyperactivity(Rajendranetal.
,2003).
Athigherdoses,heavymetalscancauseirreversiblebraindamage.
Childrenmayreceivehigherdosesofmetalsfromfoodthanadults,sincetheyconsumemorefoodfortheirbodyweightthanadults.
Thereasonforthishydrologicalscourgeisthepresenceofalarminglevelsofheavymetalarsenicingroundwaterinseveralvillagesoftheglobe(Doganetal.
,2005).
Heavymetalsintheformofarsenicandarsenicalcompoundsareexceptionallytoxicandharmfultohumanhealth.
Theyarefoundineffluentsandleachesfrommetallurgicindustries,glasswareandceramicindustriesdye,pesticideandfertilizermanufacturingindustries,petroleumrefiningandotherchemicalindustries.
Somepartoftheworldarsenicoccursnaturallyinthesoilfromwhereitreachestothegroundwater(Choudhuryetal.
,2009).
Exposuretoantimonyisassociatedwithdamagetotheheart,lungs,andotherorgans.
Thereislimitedevidencethatchronicexposurecancausedevelopmentalandreproductiveeffects,Peoplecanbeexposedtoantimonybybreathingcontaminatedair,drinkingcontaminatedwater,orbyeatingfoodsthatcontainthismetal.
Leadisaheavy,softgraymetal.
TheEPAclassifiesleadasaprobablehumancarcinogen.
Exposuretoleadresultsfrombreathingcontaminatedair,contactingleadcontaminatedsoils,ordrinkingcontaminatedwater.
Tapwatercontaminationwithleadoccurswhenwaterpassesthrougholderpipescontaininglead,leadsolder,orbrassfixturesthatcontainlead(ATSDR,2000),Althoughaluminumisnotaheavymetal(specificgravityof2.
55-2.
80),itmakesupabout8%ofthesurfaceoftheearthandisthethirdmostabundantelement.
Whenaluminumaccumulatesacutelyintissuessuchasthebrain,ithasthepotentialtocauseseriousadverseneurologicaleffects.
Dialysisencephalopathyisaformofaluminumneurotoxicitycharacterizedbyspeechdifficulty,dementiaandconvulsions(Richard,1993).
AccordingtoEnvironmentalProtectionagencytheacceptableamountofheavymetalssuchasInt.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308301antimonyinoneliterofdrinkingwateris0.
006mg/l,forleaditis0.
015mg/l,forArsenic0.
010mg/l,andforAluminum0.
05-0.
2mg/l.
Theheavymetalsrelatedmostoftentohumanpoisoningarelead,mercury,arsenicandcadmium.
Otherheavymetals,includingcopper,zinc,andchromium,areactuallyrequiredbythebodyinsmallamounts(GoyerandClarkson,2001).
MaterialsandMethodsThepurposeofthisstudywastoevaluatetheconcentrationofheavymetalsingroundwaterfromtubewellsandtoanalyzeif,parameterssuchasdepthoftubewell,locationoftubewell,ageoftubewell,samplepH,sampleconductivity,populationburdenanduseoffertilizers,pesticidesandinsecticideshasanimpactonpresenceofheavymetalcontentsandheavymetalconcentration.
SamplecollectionFifty(50)watersamplesfromdifferenttubewellsoftwelve(12)differentvillagesofdistrictpishinnamely(MainPishincity,Malakyar,ChamanMalakyar,Manzaki,Ismailzai,Bagarzai,Dabkhanzai,mianKhanzai,SirKhanzai,KilliNawabad,BatazaiandToraShah)wereobtained.
Toavoidpossibilityofcontaminationtheemptypolythenebottleswereusedforthecollectionofwatersamplesandwerelabeledaccurately.
Twosampleswerecollectedfromeachandeverytubewellinwhichonesamplesof50mlwasmixedwith4mlofHNO3(Nitricacid)forsamplepreservation(Michael,1982;APHA,etal.
,1992).
SampleanalysisThepHofallsampleswasmeasuredbypHmeter(JENWAYMODELNo.
3520)andelectricconductivitywasmeasuredwiththehelpofconductivemeter(JENWAYMODELNO.
470).
Theconcentrationsofheavymetalswereanalyzedinallthe50samplesofwaterusing(SOLAARAASERIESS4SYSTEMATOMICABSORPTIONSPECTROSCOPY(AAS)byFlamemethodwiththehelpofnitrousoxide/Acetylenegasesasdescribedby(Michael,1982).
LampCurrentTheoperatingcurrentinmAforthelamp.
Itisimportantthatyouhaveverifiedthatthelampispresentbeforecompletingthisstep.
A30mAcurrentmightdamageothertypesoflamps.
Whenthelampcurrenthasbeenentered,theamplifiergainwillbeautomaticallyset.
ReplicatesEachmeasurementisrepeated3times.
Youmaywishtochangethisnumberlater.
Theallowedrangeforthenumberofreplicatesis1-99.
StandardreagentspreparationThree(3)differentreagentsasstandardstocksolutionof1000ppmwerepreparedforthedetectionofeachandeveryheavymetal.
Thereagentspreparedwereinbelowconcentrations.
Arsenic(As):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofArsenic(Ar)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof40.
00mg/l,80.
00mg/land120.
00mg/lwereprepared.
PureArsenic(As)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308302Lead(Pb):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofLead(Pb)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof7.
00mg/l,14.
00mg/land21.
00mg/lwereprepared.
PureLead(Pb)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterandwasmadetovolumewithde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
Antimony(Sb):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofantimony(Sb)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof25.
00mg/l,50.
00mg/land75.
00mg/lwereprepared.
Pureantimony(Sb)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
Aluminum(Al):Forthepreparationof1000ppmstocksolutionofAluminum(Al)withthreedifferentconcentrationsof30.
00mg/l,60.
00mg/land90.
00mg/lwereprepared.
PureAluminum(Al)wasdissolvedinde-ionizedwaterin25mlvolumetricflask.
ResultsandDiscussionWatersamplescollectedfromdifferentareasofdistrictPishinwereanalyzedforpresenceofheavymetalcontents.
Thepresenceofheavymetalssuchasarsenic(As),lead(Pb),antimony(Sb),aluminum(Al),wereanalyzedfortheirpresenceandcomparedwithdifferentparameterssuchdepthoftubewell,ageoftubewell,locationoftubewell,samplepH,sampleconductivity,populationburden,useofinsecticides,pesticidesandTheaestheticandphysicalparametersweredeterminedwhichprovidedgeneralinformationaboutwaterqualityinqualitativetermsandincludewaterqualityparameterslikecolor,physicalappearance,transparency,Electricalconductivity,odors,pH,tasteandturbidity.
TheoverallaveragepHofallthecollectedsampleswere8.
38withtheminimumandmaximumvaluesof7.
9-8.
86respectively.
MostofthesamplingareaswerehavingthenormalpHvalueexceptNawabadhavingtheaveragepHof8.
69.
Theelectricalconductivity(EC)providesarapidandconvenientmeansforestimatingtheconcentrationofelectrolytesandgivesquickinformationaboutallminerals.
TheECvaluesofallthewatersampleswereinthenormalrangeof50-500uS/cm.
Theageoftubewellswerealsoassessedwiththepresenceofheavymetalsinwater.
Theaverageagesofallthetubewellswereapproximately04years.
Whiletheaveragedepthofthewellswererecordedas157meters(509feet).
ArsenicandleadwerefoundinallsamplesbuttheywerequitebelowthentherecommendedvaluesgivenbyWHO.
WatersamplescollectedfromdifferentareasofdistrictPishinwereanalyzedforpresenceofheavymetalcontents.
Thepresenceofheavymetalssuchasarsenic(As),antimony(Sb),aluminum(Al),andLead(pb)wereanalyzedfortheirpresenceandcomparedwithdifferentparameterssuchasdepthoftubewell,ageoftubewell,locationoftubewell,samplepH,sampleconductivity,populationburden,useofinsecticides,pesticidesandfertilizers.
ArsenicandleadWerepresentinallsamplescollectedfromareasofheavypopulationbutonaverageitsconcentrationwaslowerthanstandardrecommendedvalueswhichdepictsthatpopulationhaspositiveimpactonpresenceofheavymetals.
ThestudyfindingsshowsthatthedepthoftubewellshavepositiveInt.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308303Figure.
1.
0DepthofTubeWellsvs.
AntimonyContentsAntimonycontentswerecomparedwiththedepthofthetubewellsanditwasfoundthatineverysampleantimonycontentswerepresentandtheyweresignificantlyabovetherecommendedvalue.
Theantimonycontentsofcollectedwatersampleswererangedfrom0.
2774mg/lto1.
0214mg/l.
Antimonycontentswerefoundinhigheramountintubewellsoflowerdepthandthevalueofantimonycontentswassignificantlylowerintubewellsofhigherdepth.
Itwasfoundthatasthedepthoftubewellincreasedtheamountofantimonydecreasedsignificantly.
Figure.
1.
1DepthofTubeWellsvs.
AluminumContentsComparingAluminumContentswiththedepthofthetubewellsanditwasfoundthatineverysamplealuminumcontentswerepresentandtheyweresignificantlyabovethentherecommendedvalue.
Aluminumcontentswerefoundinhigheramountintubewellsoflowerdepthandthevalueofaluminumcontentswassignificantlylowerintubewellsofhigherdepth.
Itwasfoundthatasthedepthoftubewellincreasestheamountofaluminumdecreasedsignificantly.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308304Figure.
1.
2DepthofTubeWellsvs.
ArsenicContentsTheDepthoftubewellswerecomparedwithArseniccontentsinwhichitwasfoundthatineverysamplearseniccontentswerepresentbuttheywerebelowtherecommendedvalue.
Arseniccontentswerefoundinhigheramountintubewellsoflowerdepthandthevalueofarseniccontentswassignificantlylowerintubewellsofhigherdepthbutallofthemwerebelowtherecommendedvalue.
Itwasfoundthatasthedepthoftubewellincreasedtheamountofarsenicdecreasedsignificantly.
Figure.
1.
3DepthofTubeWellsvs.
LeadContentsLeadcontentswerecomparedwiththedepthofthetubewellsanditwasfoundthatineverysampleLeadcontentswerepresentbuttheyweresignificantlybelowtherecommendedvalue.
Theleadcontentsofcollectedwatersampleswererangedfrom0.
001mg/lto0.
0078mg/l.
literallyleadcontentswerefoundalmostequalinalldepthsoftubewellswhichshowthatthereisnosignificanceofdepthonleadcontents.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308305Figure.
1.
4AgeofTubeWellsVs.
AntimonyContentsTheageoftubewellswerestudiedanditsimpactwascomparedonAntimonycontents.
Thestudyfoundthatantimonywaspresentinalmostallwatersamplescollectedfromdifferenttubewells.
Theantimonycontentswerepresentinsignificantproportion.
Whenstudiedforitscomparisonwithageoftubewellsitwasseenthatantimonycontentswerepresentinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellageandtherewerenosignificantchangeregardingageoftubewell.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehaveantimonycontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigherantimonycontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigherantimonycontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofantimonycontentsinstudiedwatersamples.
Figure.
1.
5AgeofTubeWellsVs.
AluminumContentsTheageoftubewellswerecalculatedanditsimpactwascomparedonaluminumcontents.
Itwasfoundthataluminumcontentswereinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellage.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehavealuminumcontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigheraluminumcontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigheraluminumcontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofaluminumcontents.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308306Figure.
1.
6AgeofTubewellsVs.
ArsenicContentsLeadContentswerecomparedwiththeageoftubewells.
Itwasfoundthatleadcontentswereinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellage.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehaveleadcontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigherleadcontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigherleadcontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofleadcontents.
Figure.
1.
7AgeoftubewellsVs.
ArsenicLeadContentsTheageoftubewellswerecalculatedanditsimpactwascomparedonArseniccontents.
ItwasfoundthatArseniccontentswereinequalproportionregardlessoftubewellage.
Thegraphshowsthattubewellsoflongandshortagehavearseniccontentsinmixproportion.
Sometubewellsofshortagehavehigherarseniccontentswhilesometubewellsoflongagehavehigherarseniccontentsviceversa.
Literallyitdepictstruepicturethatagehasnoimpactonproportionofarseniccontents.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308307Figure.
1.
8AreaComparisonVs.
Antimony(Sb)ContentsAntimonycontentswerecomparedwithdifferentstudyareas.
Itwasfoundthatantimonycontentswerefoundineveryareawatersamplecollectedfromtubewells.
Antimony3contentshadalmostequalamountinallstudiedareasandnosignificantchangewasfoundFigure.
1.
9AreaComparisonVs.
Aluminum(Al)ContentsAluminumcontentswerecomparedwithdifferentstudyareas.
Itwasfoundthataluminumcontentswerefoundineveryareawatersamplecollectedfromtubewells.
Howeverinsomeareasincluding(Pishincity,Ismailzai,NawabadandBagarzai)thealuminumcontentswerefoundsignificantlyhigherthanotherstudiedareas.
Itwasassumedthattheincreaseinaluminumcontentsintheseareasmightbeduetowaterturbidityandmuddysoilinnaturefoundintheseareas.
Int.
J.
Curr.
Microbiol.
App.
Sci(2014)3(1):299-308308impactonconcentrationoftheseheavymetalsinparticularsuchasAntimony(Sb),Arsenic(As),andAluminum(Al).
Theabovediscussionleadstotheconclusionthatthegeologicconditionofthearea,useoffertilizers,insectrepellantsanddepthoftubewellsmaycontaminatetheundergroundwater.
ReferencesATSDR.
2000.
CaseStudiesinEnvironmentalMedicine.
LeadToxicity.
U.
S.
DepartmentofHealthandHumanServices,Atlanta,GA,Pp.
31-33.
APHA,AWWAandWEF,D.
E.
1992.
StandardmethodsfortheExaminationofwaterandwastewater.
AmericanpublicHealthAssociation,AmericanwaterworkAssociationandWaterEnvironmentalFederation,18thEdition,Washington,DC.
Pp.
11-19.
Choudhury,R.
Q.
,T.
S.
Shaikh,RAlam,R.
Sen,J.
Hasan,andI.
A.
Chowdhur.
2009.
EffectofArsenicContaminatedIrrigationWaterontheCultivationofRedAmaranth.
American-EurasianJ.
ScientificRes.
.
4(1):pp.
14-19.
Dogan,M.
,A.
U.
Dogan,C.
Celebi,andY.
I.
Baris.
2005.
IndoorBuiltEnviron,Vol.
14(6):pp.
533-536.
Goyer,R.
A.
,andT.
M.
Clarkson.
2001.
Toxiceffectsofmetals.
Chapter23.
In:Klaassen,C.
D.
,Casarett&Doullstoxicology.
NewYork:McGraw-Hill,pp.
811-868.
Johnson,D.
B.
,andK.
B.
Hallberg.
2005.
Acidminedrainageremediationoptions:areview.
Sci.
TotalEnviron.
,Vol.
338:pp.
3-14.
Micheal,J.
S.
,1982.
Physical,chemical&radiologicalExamination,Vol.
2(170):pp.
202-210.
Rajendran,P.
,J.
Muthukrishnan,andP.
Gunasekaran,2003.
Microbesinheavymetalremediation.
IndianJ.
Exp.
Biol.
41(9):935-944.
Richard,S.
R.
,1993.
Review:alzheimersdiseaseandenvironmentalaluminium.
AgeandAgeing,22:138-153.
- Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci相关文档
- 8.www.299pp.com
- Ilwww.299pp.com
- MAXwww.299pp.com
- spindlewww.299pp.com
- vFQwww.299pp.com
- putwww.299pp.com
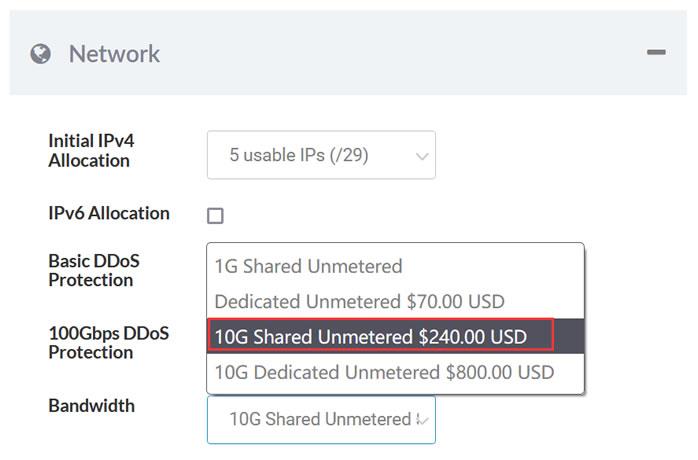
Sharktech10Gbps带宽,不限制流量,自带5个IPv4,100G防御
Sharktech荷兰10G带宽的独立服务器月付319美元起,10Gbps共享带宽,不限制流量,自带5个IPv4,免费60Gbps的 DDoS防御,可加到100G防御。CPU内存HDD价格购买地址E3-1270v216G2T$319/月链接E3-1270v516G2T$329/月链接2*E5-2670v232G2T$389/月链接2*E5-2678v364G2T$409/月链接这里我们需要注意,默...
ZJI-全场八折优惠,香港服务器 600元起,还有日本/美国/韩国服务器
ZJI怎么样?ZJI是一家成立于2011年的商家,原名维翔主机,主要从事独立服务器产品销售,目前主打中国香港、日本、美国独立服务器产品,是一个稳定、靠谱的老牌商家。详情如下:月付/年付优惠码:zji??下物理服务器/VDS/虚拟主机空间订单八折终身优惠(长期有效)一、ZJI官网点击直达香港葵湾特惠B型 CPU:E5-2650L核心:6核12线程内存:16GB硬盘:480GB SSD带宽:5Mbps...

NameCheap优惠活动 新注册域名38元
今天上午有网友在群里聊到是不是有新注册域名的海外域名商家的优惠活动。如果我们并非一定要在国外注册域名的话,最近年中促销期间,国内的服务商优惠力度还是比较大的,以前我们可能较多选择海外域名商家注册域名在于海外商家便宜,如今这几年国内的商家价格也不贵的。比如在前一段时间有分享到几个商家的年中活动:1、DNSPOD域名欢购活动 - 提供域名抢购活动、DNS解析折扣、SSL证书活动2、难得再次关注新网商家...
www.299pp.com为你推荐
-
甲骨文不满赔偿劳动法员工工作不满一个月辞退赔偿标准地陷裂口地陷是由什么原因引起的lunwenjiance知网论文检测查重系统百花百游“百花竟放贺阳春 万物从今尽转新 末数莫言穷运至 不知否极泰来临”是什么意思啊?同ip网站一个域名能对应多个IP吗haokandianyingwang有什么好看的电影网站m.2828dy.com电影虫www.dyctv.com这个电影站能下载电影吗?4400av.com在www.dadady.com 达达电影看片子很快的啊朴容熙这个人男的女的,哪国人。叫什么。b.faloo.com坏蛋是这样炼成的2出的最快的网站是那个?