convergeinsomniac
insomniac 时间:2021-03-17 阅读:()
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page1of9VideoArticleAssayingLocomotorActivitytoStudyCircadianRhythmsandSleepParametersinDrosophilaJoannaC.
Chiu1,2,KwangHueiLow1,3,DouglasH.
Pike1,EvrimYildirim1,3,IsaacEdery1,31CenterforAdvancedBiotechnologyandMedicine,RutgersUniversity2CurrentAddress:DepartmentofEntomology,CollegeofAgriculturalandEnvironmentalSciences,UniversityofCalifornia,Davis3DepartmentofMolecularBiologyandBiochemistry,RutgersUniversityCorrespondenceto:IsaacEderyatedery@cabm.
rutgers.
eduURL:https://www.
jove.
com/video/2157DOI:doi:10.
3791/2157Keywords:Neuroscience,Issue43,circadianrhythm,locomotoractivity,Drosophila,period,sleep,TrikineticsDatePublished:9/28/2010Citation:Chiu,J.
C.
,Low,K.
H.
,Pike,D.
H.
,Yildirim,E.
,Edery,I.
AssayingLocomotorActivitytoStudyCircadianRhythmsandSleepParametersinDrosophila.
J.
Vis.
Exp.
(43),e2157,doi:10.
3791/2157(2010).
AbstractMostlifeformsexhibitdailyrhythmsincellular,physiologicalandbehavioralphenomenathataredrivenbyendogenouscircadian(≡24hr)pacemakersorclocks.
Malfunctionsinthehumancircadiansystemareassociatedwithnumerousdiseasesordisorders.
Muchprogresstowardsourunderstandingofthemechanismsunderlyingcircadianrhythmshasemergedfromgeneticscreenswherebyaneasilymeasuredbehavioralrhythmisusedasaread-outofclockfunction.
StudiesusingDrosophilahavemadeseminalcontributionstoourunderstandingofthecellularandbiochemicalbasesunderlyingcircadianrhythms.
Thestandardcircadianbehavioralread-outmeasuredinDrosophilaislocomotoractivity.
Ingeneral,themonitoringsysteminvolvesspeciallydesigneddevicesthatcanmeasurethelocomotormovementofDrosophila.
Thesedevicesarehousedinenvironmentallycontrolledincubatorslocatedinadarkroomandarebasedonusingtheinterruptionofabeamofinfraredlighttorecordthelocomotoractivityofindividualfliescontainedinsidesmalltubes.
Whenmeasuredovermanydays,Drosophilaexhibitdailycyclesofactivityandinactivity,abehavioralrhythmthatisgovernedbytheanimal'sendogenouscircadiansystem.
Theoverallprocedurehasbeensimplifiedwiththeadventofcommerciallyavailablelocomotoractivitymonitoringdevicesandthedevelopmentofsoftwareprogramsfordataanalysis.
WeusethesystemfromTrikineticsInc.
,whichistheproceduredescribedhereandiscurrentlythemostpopularsystemusedworldwide.
Morerecently,thesamemonitoringdeviceshavebeenusedtostudysleepbehaviorinDrosophila.
Becausethedailywake-sleepcyclesofmanyfliescanbemeasuredsimultaneouslyandonly1to2weeksworthofcontinuouslocomotoractivitydataisusuallysufficient,thissystemisidealforlarge-scalescreenstoidentifyDrosophilamanifestingalteredcircadianorsleepproperties.
VideoLinkThevideocomponentofthisarticlecanbefoundathttps://www.
jove.
com/video/2157/ProtocolTheoveralldesignoftheprotocolisillustratedinFigure1.
Thesetupformonitoringlocomotoractivityusingdeviceshousedinenvironmentallycontrolledincubatorslocatedinadarkroomneedstobeassembledfirst.
Oncethatiscompleted,thesystemcanbeusedinallsubsequentlocomotoractivityrhythmmeasurements.
Foreachexperiment,onehasto(i)prepareexperimentalanimals,whichmightincludegeneratingtransgenicanimalsorsettingupnecessarycrosses,(ii)prepareglassactivitytubescontainingafoodsource,(iii)loadfliesintoactivitytubesandconnectactivitymonitorstothedatacollectionsystem,and(iv)recordandanalyzethedatausingdifferentsoftwaredependingonwhatcircadianorsleepparametersonewantstoexamine.
Herein,wedefinethe"start"oftheexperimentasthetimewhenfliesinmonitoringdevicesarefirstexposedtothedesiredlight/darkconditionsinenvironmentalincubators.
1.
SettinguptheLocomotorActivityMonitoringSystem1.
Themonitoringsysteminvolvesnumerousequipmentitemssuchasspecialtymonitoringdevices,environmentalincubatorsthathavethecapacityfordiurnallightcontrol,datacollectiondevices,computersandperipheralmaterialssuchaswiringtoconnectthemonitoringdevicestothedatacollectiondevices(Figure2).
InstructionsforinstallingtheDrosophilaActivityMonitoring(DAM)datacollectionsystemareprovidedbythemanufacturer(TrikineticsInc.
).
2.
Tohousethelocomotoractivitymonitoringsystem,chooseawell-ventilatedroom,preferablyequippedwithtemperaturecontrolsystem,tobeadedicateddarkroom.
Withalltheelectricalsystemsinvolved(e.
g.
computerandincubators)runningforanextendedperiodoftimewithinasmallandconfinedroom,excessiveheatcanbegeneratedleadingtorapidincreasesintheroom'stemperature.
Consequently,incubatorswillbeburdenedwithextraworkloadtomaintaintemperatureandmorelikelytofailintemperaturecontrol.
Wefindthatevenforwell-ventilatedrooms,thetransitionfromair-conditioninginthesummertoheatinthefall/wintercanmakeitdifficulttomaintainroomtemperature.
Insuchcasesadditionalventilationmighthavetobeinstalledinthedarkroomtoreducetheriskofoverheating.
Also,itisbesttoturnoffincubatorsthatarenotinusetominimizetheproductionofunnecessaryheat.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page2of93.
Sealtheroomfromexternallightsources.
Entrancecanbesealedoffwitharevolvingdoororblackcurtain.
Wepreferarevolvingdoorasthisminimizesthechancesofunwantedlightenteringthedarkroom.
Insidethedarkroom,itisnotnecessarytoworkcompletelyinthedarkasthefruitfliescircadiansystemisnotsensitivetoinfraredlight(andismuchlesssensitivetoredlightcomparedtogreen/bluelight).
Incaseswhereweneedtoseeinthedarkroombutstillwanttomaintainoveralldarkness(e.
g.
,quicklyremovingoraddingamonitoringdeviceinanincubatorthatisinitsdarkphase),wesimplyuseastandardflashlightthatiscoveredwitharedfilter.
Alternativelyorinadditionto,ifyourdarkroomhasfluorescentlights,coverthemwithredfilterpaperorhaveastand-aloneincandescentdesklightcoveredwithsuchfilterpaper.
Itishighlyunlikelythatexposingfliesinthedarktoverybriefexposures(fewseconds)ofredlightwillaffecttheircircadianclocks.
Also,althoughthecircadiansystemofDrosophilaisverysensitivetovisiblelight,wedonotthinksmallcreaksoflightinthedarkroomwillbeconsequential;inanycase,agoodpracticeistokeeptheincubatordoorsthathousethemonitorsopenonlywhennecessary.
Also,onlyopenuponeincubatoratatimeasthiswillminimizethepossibilityofanincubatoronitsdarkphasebeingexposedtolightfromanincubatoronitslightphase.
4.
PurchaseanUninterruptedPowerSupply(UPS)emergencybackupunitthathasenoughwattagecapacitytopowerthecomponentsoftheactivitymonitoringsystemincaseofsurge,spike,orpowerfailureinthebuilding.
ConnecttheUPSemergencybackupunittotheemergencybackupcircuitofthebuildingifavailable.
Beawarethatevenifyourequipmentispluggedintoanemergencyoutletduringapoweroutagetherecanbeashorttransitionperiodasthesystemswitchestoemergencypower.
Duringthattransition,lossofpowerforevenafewsecondscanleadtocomputersshuttingdownandthelightsintheincubatorbeingturnedoff.
Thus,itisimportanttoensurethatthecomputersbeingusedtogathertheactivitydataandthesystemcontrollinglightsintheincubatorarenotonlyhookedintoemergencypowerbutalsoaUPS.
Ifthesystemcontrollinglightingintheincubatorisnotdirectlyregulatedbytheincubator(inmostcasesitis),thenitissufficienttoplugtheincubatorintotheemergencypowerwithoutaUPS,aslossofpowerforafewsecondswillnotaffectthechambertemperature.
NotethatingeneralaUPSdevicewillonlykeepyourequipmentrunningfor5-30minintheabsenceofpower;itsmainpurposeistoprotectagainsttemporarylossofpowerduringthetransitionfromregulartoemergencypower.
5.
Setupacomputer,PCorMacintosh,fullydedicatedfordatacollectionand/orforlightcontroloftheincubators.
SincetheDAMsystemwillberunningallthetimeandunattended,itisrecommendedthatthiscomputerhaveminimalsoftwareinstalled,preferablynonetworkconnectiontominimizetheriskofcrashing.
Inaddition,thesystemneedsportabledatastorage,e.
g.
zipdrive,CD/DVDwriter,orUSB,toallowfordownloadingofdatacollectedforsubsequentanalysis.
6.
Manuallyarrangethetelephonelinenetworkneatlyaroundtheshelvingoftheenvironmentallycontrolledincubatorstoalloweaseofplugging/unpluggingofactivitymonitors.
Standardtelephonelines,adapters,andsplitterscanbepurchasedincommercialelectronicstoresandused.
Setupmultipletelephonelinesinawaysuchthattheywillconvergeintoonemainlineandextendoutoftheincubatortoconnecttothecomputer.
7.
Connectthemonitoringdevicesinsidetheincubatorstothecomputerviaapowersupplyinterfaceunit(akaBlueboxfromTrikineticsInc.
),whichservestopowertheactivitymonitor(TrikineticsInc.
)viathetelephoneline.
ThispowersupplyinterfaceunitalsoactsasaninterfacefordatatransferswitchingfromtelephonelinetoUSBcable.
Optionallightcontrollerinthesameunitinwhichthepowerlinecordoftheincubatorlightsystemcanbeconnectedto,isavailabletoallowcontrolofcircadianincubatorlightingscheduleviathecomputer.
8.
MaskpossiblelightsourcesfromLEDofelectronicdeviceorimproperlysealincubatordoorwithducktapeorblackclothtoensurefree-runningrhythmsaremeasuredintheabsenceofunwantedlight.
2.
PreparationofExperimentalAnimals1.
Behavioralphenotypesinfruitfliessuchascircadianrhythmicityandsleep/restactivityareverysensitivetogenotypicandagedifferencesofthetestanimals(Kohetal.
2006).
Therefore,itiscrucialtoassessthesephenotypesusingpropercontrolanimalsthatarerearedinthesameenvironmentalconditionsandofthesameage.
Inaddition,thereissexualdimorphismincircadianrhythmicity(Helfrich-Fster2000).
Thegeneralpracticeistouseadultmalefliesthatarerearedin25°Candbetween1to5dayoldforlocomotoractivityassays.
Malefliesinsteadoffemalefliesaretraditionallyusedbecauseegg-layingactivitywillaffecttruemeasurementoflocomotoractivity.
Becauseofsexualdimorphism,sometimesassayingfemalefliesmightbeinformative.
Foodconsistingofsimply5%sucroseand2%bactoagarwillpreventeggsofnon-virginfemalesfromdevelopingandmovementofhatchedlarvaefromcausingerroneousactivitycounts.
Alternatively,virginfemalefliescanbeusedalthoughtheremightbedifferencesinactivityprofilesbetweenmatedandvirginfemales(Helfrich-Forster,J.
Biol.
Rhythms2000).
2.
Whenexaminingcircadianandsleep/restparametersofspecificmutantfliesofinterest,itisprudenttooutcrossthemutantstockwiththewild-typestrainofthesamegeneticbackground,e.
g.
w1118oryw.
Thiswillremovesecondsitegeneticmodifiersthatmightpotentiallymaskcircadianorsleep/restphenotype.
Sincethereisnocrossing-overinDrosophilamales,itisbettertoperformtheoutcrossbycrossingmutantfemaleswithwild-typemales.
Thewild-typestrainwillalsoserveastheappropriatecontrolfortheexperiment.
Seedboththewild-typecontrolandmutantfliesatthesametimeinstandardDrosophilafoodabout10to14daysbeforethelocomotoractivityrhythmexperiment(seeBloomingtonDrosophilaStockCenterforfoodrecipe;http://flystocks.
bio.
indiana.
edu/).
Uponeclosionoftheprogeny,collect1to5daysoldmalefliesandsetthemasidetobeusedfortheexperiments.
3.
Withthenumerousgenetictoolsandresourcessuchasoverexpression,RNAi,andtissue-specificGAL4driverflylinesavailablefromdifferentstockcentersworldwide,itispossibletodissecttheeffectsofoverexpressingorknocking-downspecificgenesintissue-andtemporal-specificmanner(BrandandPerrimon1993;McGuireetal.
2004;Osterwalderetal.
2001).
Toexaminecircadianandsleep/restparametersusingthisapproach,fliescarryingtransgenicconstructswithtissue-specificordrug-inducibleGAL4driver(e.
g.
males)arecrossedtofliescarryingtransgenicconstructswithtargetgenesattachedtotheUASresponder(e.
g.
virginfemales)around14daysbeforethestartoflocomotoractivityexperiments.
Uponeclosionoftheprogeny,collect1to5daysoldmalefliesandsetthemasidetobeusedfortheexperiments.
Theparentallinesusedforthecrossareroutinelyusedascontrolsfortheexperiments.
ProgenyfromcrossesofUASresponderandGAL4driverlineswithwildtypefliesofthesamegeneticbackgroundarealsoappropriatecontrols.
4.
Asindicatedinsteps(2)and(3),thelengthoftimeneededforthepreparationofexperimentalanimalsvariesgreatlydependingonthenatureanddesignoftheexperiment.
Inthecasewheretransgenicanimalsneedtobegeneratedorifcrossingschemesneedtobeexecuted,moretimewillobviouslybeneeded.
Forlogisticalreasons,ittakesabout14daysat25°CforDrosophilatodevelopfromeggstoadultflies.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page3of93.
PreparationofActivityTubes1.
Activitytubesrepresenttheflyhabitatduringtheexperiment.
Theyarethin(about5mmindiameter;note,TrikineticsoffersdifferentsizesdependingontheDrosophilaspeciestobeassayed)5mmglasstubesthatcontainfoodsubstanceatoneendandpluggedwithyarnorplasticplugattheotherend.
Sinceglassactivitytubescanbereusedmultipletimes,wewilldescribethepreparationproceduresbyusingused/uncleanedactivitytubesfrompreviousexperimentsasthestartingpoint.
Ifyouareusingnewactivitytubes,simplyskiptostep(11).
2.
Itispreferabletouseactivitytubesthatarefreshlymadesincethefoodinsidethetubeshasatendencytodryupandgetscontaminatedwithfungiovertimeevenwhenstoredat4°C.
Theyaregenerallypreparedafewdaystoaweekaheadofthestartoftheexperiment.
Itisthereforeimportanttoassessthenumberoftubesneededforeachexperimentbeforepreparingthem.
3.
Removeplugs(yarnorplasticplug)fromusedactivitytubesandputthemintolargeglassbeaker.
Thetubesshouldonlyfilluptohalfthebeaker.
Fillthebeakerwithtapwater,makingsuretosubmergethetubes.
4.
Microwavethebeakerfilledwithglasstubesuntilthewatercomestofullrapidboiltomeltthewaxandagarfood.
5.
Takecautionthatthewaterishot.
Removethebeakerfromthemicrowaveandstirthetubeswithaspatulaorplastic10mLpipettetoallowtrappedwaxtofloattothetop.
Thenrepeatstep(4).
6.
Removethebeakerfromthemicrowaveandwaitforittocooldown.
Puttingthebeakerinthecoldroom(ifitisavailable)willspeeduptheprocess.
7.
Asthewatercoolsdown,thewaxwillcollectonthesurfaceofthewaterandgraduallysolidifies.
Simplyremovethesolidifiedwaxbyhand.
Thisshouldgetridofmostofthewaxonthetubes.
8.
Transfertheactivitytubestoanewbeakerwithfreshtapwaterandrepeatsteps(4)and(5).
9.
Sincemostofthewaxhasbeenremovedinstep(7),itisnotnecessarytowaitforthewaxtosolidify.
Simplypourthewateroutofthebeakerandtransferthetubesintoanothernewbeaker.
Takecautionthatthewaterisstillhot.
10.
Repeatsteps(4)and(5)forthelasttime.
Pourthewateroutofthebeakerandwaitfortheactivitytubestocooldown.
11.
Loadthemverticallyinto250mLor500mLglassbeakers.
Makesuretheyarenottootightlypacked.
Sterilizethembyusinganautoclavewithadrycycleorsimplyuseadryingoventodrythetubes.
12.
Separately,topreparefoodtoloadintotheactivitytubes,makeasolutionof5%sucrose(Sigma)and2%Bactoagar(BD)indistilledwaterortapwater.
Autoclavetosterilizethesolution.
Theautoclavedfoodcanbeusedimmediatelyorstoredin4°Cforanextendedperiodoftime.
Oncethefoodsolidifies,onewillneedtomicrowaveandliquefyitinordertofillthetubes.
Unusedportionoffoodcanbestoredandusedatalaterdate.
13.
Thefoodshouldideallybearound65°Cwhenusedforfillingactivitytubes.
Ifitistoohot,toomuchcondensationwillaccumulateinsidethetubes.
Ifitisnothotenough,thefoodwillsolidifybeforethetubesareevenlyfilled.
Tofilltheactivitytubeswithfood,usea10mLpipettetopipettetheliquidfoodsolutionalongtheinsidewalloftheglassbeaker,allowingthefoodsolutiontofilltheactivitytubefromthebottomup,untilthetubesareone-thirdfilledwithsolution.
Swirlthebeakeraroundgentlytomakesureallthetubes,especiallytheonesinthemiddleofbeaker,areevenlyfilledwithfoodsolution.
Waitforthefoodtosolidifycompletelyeitheratroomtemperatureor4°C.
Proceedtothenextsteponcecondensationinsidetheglasstubesdissipate.
14.
Toremovetheactivitytubesfromthebeaker,pushthetubestowardsthebottomofthebeakerandtwistthetubesatthesametimesothatthesolidifiedfoodinsidethetubesandthebottomofthebeakerwillseparate.
Takethetubesoutofthebeaker,preferablyasasinglebunch.
15.
Cleanthetubesonebyonewithpapertowelstoremoveexcessfoodontheoutersurfaceofthetubes.
Setthetubesasideinacleancontainer.
16.
Takeagenerallaboratoryblockheaterwithoutthetubeholderandcovertheheatingwellcarefullywithseverallayersofstrongaluminumfoil.
Addparaffin(wax)pelletsintothealuminum-linedheatingwelltomelt.
17.
Holdthetubesatthenon-foodendanddipthefoodendintothemeltedwax.
Dipthewaxedportionintoaglassbeakerfilledwithcoldwatertospeedupwaxsolidification.
Repeatonce.
Dippingthewaxedtubesintowaterwillpreventthetubesfromstickingtogether.
18.
Thetubescanbeusedrightaway,orstoredinanairtightcontainerat4°Cforusewithinaweek.
Prolongedstoragewillleadtoexcessivedryingofthefood.
Ifthetubesarestoredat4°C,makesuretowarmthemuptoambienttemperaturebyleavingthemonbenchtoppriortouse.
4.
LoadingFliesintoActivityTubesandLocomotorActivityMonitoringSystem1.
Priortoloadingfliesintoactivitytubes,turnontheincubatorsthatwillbeusedtohousetheactivitymonitors.
Adjustthetemperatureusingtheincubatorcontrolsandsetthelight/darkregimeusingtheDAMSystemlightcontrollerORtheincubatorsownlightcontrolsystemaccordingtothedesiredexperimentaldesign.
Thetimenecessarytoloadfliesintoactivitytubesshouldbesufficientforthetemperaturetostabilize.
2.
Anesthetizetheflieswithcarbondioxide.
3.
Useafinepaintbrushtogentlytransferasingleflyintoanactivitytube.
4.
Grabthemiddleofasinglepieceofyarnthatisaroundhalfaninchwithfineforcepsandinserttheyarnintothenon-foodendoftheactivitytubetoplugtheopeningandpreventtheflyfromescapingduringtheexperiment,whileatthesametimeallowingairflowintothetube.
Alternatively,plasticcapswithsmallholes(Trikinetics,Inc.
)canbeusedtoclosetheopening.
5.
Makesurethetubesarelaidontheirsidesuntiltheflyawakens,orelsethereistheriskoftheflygettingstucktothefood.
6.
Insertthetubesintotheactivitymonitors.
Withthenewer,morecompactmodeloftheTrikineticsmonitors(TrikineticsDAM2andDAM2-7),itisnecessarytoholdthetubesinplacewithrubberbandstoensurethattheinfraredbeampassesthetubeatthecenterposition.
7.
Puttheactivitymonitorsintotheincubatorsandhookthemuptothedatacollectionsystemviathetelephonewires.
CheckusingtheDAMSystemcollectionsoftwaretomakesureallthemonitorsarehookedupproperlyanddataisbeingcollectedfromeachofthem.
Themonitoremitsinfraredlightbeamacrossthecenterofeachglassactivitytube.
Thelocomotoractivityofthefliesarerecordedasrawbinarydatawhere"one"isrecordedeachtimetheinfraredbeamisbrokenora'zero'isrecordedinwhichtheinfraredbeamisnotbroken.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page4of95.
ExperimentalDesigntoRecordDataforDeterminationofCircadianPeriodicityandAmplitude1.
Fliesaresynchronizedandentrainedbyexposingthemtothedesiredlight/dark(LD)andtemperatureregimefor2-5fulldays.
Themostcommonlyusedentrainmentconditionisalight/darkcycleof12hrslight/12hrsdark(12:12LD)at25°C.
ThisgenerallyacceptedstandardconditionisessentiallybasedonthethoughtthatDrosophilaoriginatedfromAfro-equatoriallocations.
Whenstudyingcircadianrhythmsthereissomephraseologythatoneneedstobecomefamiliarwith.
Relevanttothisprotocol,thetimewhenthelightsgoonintheincubatorisdefinedaszeitgebertime0(ZT0)andallothertimesarerelativetothatvalue(e.
g.
,ina12:12LDcycle,ZT12isthetimewhenthelightsareturnedoff).
Understandard12:12LDconditions,wildtypeDrosophilamelanogastertypicallyexhibittwoboutsofactivity;onecenteredaroundZT0termed"morning"peakandanotheraroundZT12termed"evening"peak(Figure3A).
Themorningandeveningboutsarecontrolledbytheendogenousclockbuttherearealso"startle"responsesthataretransientburstsofactivityinresponsetothelight/darktransitions.
Twodaysofentrainmentistheminimumandcouldbeused,forexample,inlargescreensthataremoretime-consumingandaregearedtowardsmeasuringfree-runningperiodsinconstantdarkness(seebelow,step2).
However,ifyouareinterestedinstudyingtheactivitypatternsduringadailylight-darkcycle,itispreferabletomaintainthefliesfor4-5daysinLDsoastoobtainmoredata.
Essentially,increasingthenumberoffliesorthenumberofLDdaysinthefinaldataanalysis(e.
g.
,pooldatafromthelasttwodaysworthofLDlocomotoractivity)willgeneratemorereliablediurnalactivityprofilesandmeasurements(e.
g.
,timingofmorningoreveningpeak).
Furthermore,thedailydistributionofactivityvariesasafunctionofday-length(photoperiod)andtemperature.
Amajorreasonforalteringthephotoperiodortemperaturefromthestandardisifonewantedtostudyhowdailyactivitypatternsundergoseasonaladaptation(e.
g.
Chenetal.
2007).
Drosophilacanalsobeentrainedtodailytemperaturecycles(e.
g.
GlaserandStanewsky2005;Sehadovaetal.
2009).
Temperaturecyclesthatvarybyonly2-3°Caresufficienttoentrainactivityrhythms.
2.
Freerunninglocomotoractivityrhythmsaremeasuredunderconstantdarkandtemperatureconditionsaftertheentrainingperiodisfinished(seeabove,step1).
ThesettingforthelightcyclecanbechangedanytimeinthedarkphaseonthelastdayofLDsuchthatthesubsequentdayoftheexperimentrepresentsthefirstdayofDD.
SevendaysofDDdatacollectionissufficienttocalculatethecircadianperiodandamplitude(e.
g.
,powerorstrengthofrhythm)offlies.
Ingeneral,asamplesizeofatleast16fliesisnecessarytoobtainreliablefree-runningperiodsforaparticulargenotype.
Evenifoneisonlyinterestedinmeasuringdiurnalactivity,itisstillbesttomeasuretheflies'free-runningperiodsinDDaschangesinendogenousperiodcanalterthedailydistributionofactivityinLD.
Forexample,flieswithlongendogenousperiodsusuallyexhibitdelayedeveningpeaksinLD(e.
g.
,seeFigure4).
3.
Attheconclusionoftheexperiment,rawbinarydatacollectedusingtheDAMSystemsoftwareisdownloadedontoaportabledatastoragedevice,e.
g.
USBkey.
4.
TherawbinarydataisprocessedusingDAMFilescan102X(Trikinetics,Inc.
)andsummedinto15and30minutebinswhenanalyzingcircadianparameters,or1to5minutebinswhenanalyzingsleep/restparameters.
Currently,fivecontiguousminutesofinactivityisthestandarddefinitionofsleep/restinDrosophila(Hendricksetal.
2000;HoandSehgal2005).
5.
TherearemanydifferentwaystoanalyzethedatacollectedontheDAMSystembutwewillonlyprovidethosemethodsroutinelyusedinourlab.
MicrosoftExcelisusedtoassigngenotypetodifferentsamplegroups.
FaasXsoftware(M.
BoudinotandF.
Rouyer,CentreNationaldelaRechercheScientifique,Gif-sur-YvetteCedex,France)orInsomniac(Matlab-basedprogram;LeslieAshmore,UniversityofPittsburgh,PA)areusedtoexaminecircadian(e.
g.
periodandpower)orsleep/rest(e.
g.
percentagesleep,meanrestboutlength)parametersrespectively.
6.
RepresentativeResultsUponthecompletionofthisprotocol,onecanusethesamedatasettoexaminebothcircadianandsleepparametersoftheexperimentalanimalsinrelationtothecontrolanimals.
Analysisofcircadianparameters:EductiongraphsillustratingdailylocomotoractivitiesoraverageactivitiesoffliesoverseveraldaysinLDorDDconditionscanbegeneratedusingFaasX(Figure3).
Drosophilamelanogastergenerallyexhibittwoboutsofactivity;onecenteredaroundZT0(orCT)termed"morning"peakandanotheraroundZT12(CT12)termed"evening"peak.
Thesetwoboutsofactivitiesarecontrolledbytheendogenousclock,andcanevenbeobservedinfree-runningDDconditions(Figure3B).
Changesinthetimingoftheseactivitypeakscaneasilybeobservedineductiongraphsandmayindicateachangeinthepropertiesoftheendogenousclock.
AnotherpropertythatisindicativeofproperclockfunctionistheanticipatoryincreaseinlocomotoractivityobservedinLDcyclesthatoccurspriortotheactualdark-to-lightorlight-to-darktransitions(Figure3A,arrows).
Thisbehaviorisclearlyobservedinwildtypeflies(Figure3A),butisabsentinarrhythmicmutantssuchasper0(Figure3C)(KonopkaandBenzer,PNAS,1971).
Inthecaseoftheper0mutants,theobserved"morning"and"evening"peaksinLDarepurelystartleresponsesduetoabruptchangesinlight/darkconditions(i.
e.
'clockless'fliesdonotanticipateenvironmentalchangesbutmerelyreacttothem).
LossofbehavioralrhythmicityismuchmorepronouncedinDDandgenerallymanifestsintothetotallossofmorningoreveningpeaksoflocomotoractivity(i.
e.
randomboutsofactivityandinactivity),asseeninper0flies(Figure3D).
Inadditiontoeductiongraphs,locomotoractivitydatacanberepresentedasdouble-plotactogram(FaasX),wheretwodaysofdataareplottedsequentiallyoneachline,butthelastday'sprofilebeginsthenextlineoftwodaysworthofactivity(Figure4).
Forexample,LD1and2areplottedonthefirstlineoftheactogram.
ThenextlinebeginswitharepeatofLD2andisfollowedbyLD3andsoon.
Followingthisformat,thelocomotoractivitydataspanningtheentireexperimentisillustratedintheactogram.
Actogramscanbeplottedforeachindividualfly,orforeachflygenotype.
Oneadvantageofactogramsovereductiongraphsisthatachangeintheperiodlengthofdailyactivityrhythmsiseasilyobservable(Figure4).
Besidesgeneratingeductiongraphsandactograms,locomotoractivitydatafromDDconditioncanbesubmittedtoFaasXtocalculatetheperiodlengthusinganumberofdifferentprograms,includingCycle-P.
Analysisofsleep/restparameters:Byusingthecurrentdefinitionofsleep/restinDrosophila(Hendricksetal.
2000),whichisfivecontiguousminutesofinactivity,onecananalyzedatarecordedfromlocomotoractivityassaysandexaminemultiplesleepparametersusingInsomniac(L.
Ashmore),aMatlab-basedprogram.
Thepercentoftimethatfliesspendsleepingcanbecalculatedatdifferenttimeintervals,e.
g.
percentsleepeveryhour(Figure5A),or12hours(Figure5B).
Othermorecommonsleepparametersthatcanbeexaminedincludemeanrestboutlength(Figure5C)andwakeactivitycount(Figure5D).
Meansleep/restboutlengthisameasureofhowconsolidatedthesleepisandcanillustratethequalityofsleep.
Wakeactivity,asitsnamesuggests,isameasureoftheactivityratewhenthefliesareawake.
Thisparameterhelpstodifferentiatebetweenfliesthataretrulyaffectedinsleep/restbehaviorsvs.
thosethatareeithersickorhyperactive.
Forexample,fliesJournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page5of9thataresimplysickmayseemtosleepmorebecausetheyarenotasmobile.
Fortheseflies,theirwakeactivitywillbelowerinrelationtocontrolanimals.
Figure1:FlowchartoutliningthemajorstepsforassayinglocomotoractivityrhythmsinDrosophila.
Theproceduresarepresentedontheleftwhilehelpfulcommentsareprovidedontheright.
Theamountoftimerequiredtoperformnecessarycrossesandgeneticmanipulationstoobtainflieswiththerightgenotypeforspecificexperimentsisvariabledependingonthenatureanddesignoftheexperiment.
Thetwostepsmarkedwithasterisks(*)providethetimeframeforwhenadultfliesneedtobeseeded/matedtogenerateprogeniesoftheappropriateage(1to5daysold)fortheexperiment.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page6of9Figure2:WiringdiagramillustratingtheconnectionsbetweenthedifferentcomponentsforDrosophilalocomotoractivitydatacollectionusingtheDAMSystem.
AdedicatedcomputerisusedtorecordthelocomotoractivitycountsofDrosophila.
Activitymonitorsarehousedinsideincubatorsequippedwithtemperatureandlighting(On/Off)control.
ThecomputercanalsobeusedtocontrolthetimingoflightOn/OffinincubatorsifthepowersourceofthelightingsystemcanbehookeduptothePowersupplyunit(optional).
Communicationsbetweenthecomputerandactivitymonitors/incubatorsaremanagedbythePowersupplyinterfaceunit.
Thecomputer,Powersupplyunitandincubators(ifthelightingcontrolisindependentofthecomputer)areconnectedtotheACpoweroutletviatheUPCtoensureuninterruptedmonitoringofactivityandcontinuouslightingduringthelightphase.
Itisrecommendedtoconnectalltheelectricalappliancestotheemergencybackupcircuitsinthefacility,ifavailable.
Figure3:EductiongraphsgeneratedusingFaasXshowingdailylocomotoractivityrhythmsofrhythmicwildtypeflies(wper0fliescarryingaper+transgene)(AandB)vs.
arrhythmicwper0mutants(CandD).
Maleflieswerekeptat25°Candentrainedfor4daysin12:12LD(light:dark)cyclesfollowedbysevendaysinDD(constantdarkness).
Foreachflyline,thelocomotoractivitylevelsofindividualflies(n>32)weremeasuredin15-minutebinsandthenaveragedtoobtainagroupprofilerepresentativeforthatline.
AandCshowtheactivitydataJournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page7of9generatedfromaveragingthesecondandthirddaysinlight/darkcycle(LD2-3)whileBandDshowtheactivitydatageneratedfromaveragingthesecondandthirddaysinconstantdarkness(DD2-3).
Verticalbarsrepresenttheactivity(inarbitraryunits)recordedin15-minutebinsduringthelightperiod(lightgrey)orthedarkperiod(darkgrey).
HorizontalbarsatthebottomofLDeductiongraphs;white,lightson;black,lightsoff.
ZT0andZT12representthestartandendofthephotoperiodrespectively.
ForDDeductiongraphs;CT0andCT12representthestartandendofthesubjectivedayinconstantdarkconditions,denotedbythegreybar.
InpanelA,M=morningpeak;E=eveningpeak.
ThearrowsinpanelArepresentanticipatorybehaviorofmorningandeveningpeaksobservedinwildtypeflies,whichareabsentinwper0arrhythmicflies.
Figure4:Double-plotactogramgeneratedusingtheFaasXsoftwareillustratinglocomotoractivitydataofflieswithwildtype,short,orlongperiod.
Maleflieswerekeptat25°Candentrainedfor4daysin12:12LDcyclesfollowedbyeightdaysinconstantdarkness(DD)forthecalculationofthefree-runningperiod(t)usingCycle-PinFaasX.
Threeflylineswithwildtypeperiod[wper0;per+;per0mutantcarryingper+transgene],longperiod[wper0;per(S47A);per0mutantcarryingper(S47A)transgene],andshortperiod[wper0;per(S47D);per0mutantcarryingper(S47D)transgene]areshownhere(Chiuetal.
2008).
X-axisrepresentsZTorCTtimeinLDorDDrespectively,andY-axisrepresentsactivitycounts(arbitraryunits)summedinto15-minutebins.
Thereddottedlinesconnecttheeveningpeaksforeachdayoftheexperiments.
NotethatduringLDtheeveningpeakis'forced'tomaintainsynchronywiththe24-hrLDcycle,whereasinDDthefree-runningperiodcandeviatefrom24hr.
Forexample,forflieswithshortperiodsthetimingoftheeveningactivitywilloccurearlieroneachsuccessivedayinDD(whenplottedagainsta24hrtimescale,asshownhere),whereasashifttotherightisobservedforflieswithlongperiods.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page8of9Figure5:QuantifyingsleepparametersinDrosophila.
Flies(Canton-S;CS)wereexposedtostandard12:12LDcycleat25°C.
Insomniac(L.
Ashmore)wasusedtoprocessthedataandMicrosoftExcelwasusedtogeneratethechartsshownhere.
Atleast70flieswerepooledtoobtainthegroupaveragesanderrorbars(standarderrorofthemean)shown.
(A)Baselinesleepcalculatedeveryhour;shownisarepresentativedailycycle.
(B)Baselinesleepofrepresentativedailycyclecalculatedevery12hours.
(C)Averagelengthofeachrestboutcalculatedin12-hourincrements.
(D)Rateofwakingactivitycalculatedevery12hours.
DiscussionInthisprotocol,wedescribedproceduresformeasuringDrosophilalocomotoractivityrhythms,areliablebehavioraloutputofflycircadianclocksthatisusedasthestandardreadoutofclockfunction.
Thisassayhasbeenusedinlarge-scalescreensfornovelclockmutants(e.
g.
KonopkaandBenzer1971;Dubruilleetal.
2009)andiscontinuallyusedtodissectandunderstandclockfunctioninvivo.
Ithasalsobeenusedtostudysleepwakecycleinflies,eventhoughrecentreportssuggestthatvideodigitalanalysisismuchmorereliableinquantifyingsleepthanusinglocomotoractivityrhythms(Zimmermanetal.
2008).
Whenusinglocomotoractivityrhythmstoanalyzesleep,percentageofsleepinthedaytimetendtobeoverestimated.
Toensurethesuccessandreproducibilityofthisprotocol,itiscriticaltoassayfliesthataresimilarinage,geneticbackground,andrearedunderthesameconditions,asbehavioralphenotypesinfruitfliessuchascircadianrhythmicityandsleep/restactivityareverysensitivetoallthesefactors.
Whenusingmultipleincubatorsforasingleexperiment,itisimportanttomakesureallincubatorsareattheanticipatedtemperaturesincesomecircadianparametersmaychangeasafunctionoftemperature.
Onewordofcautionwhenconsideringpurchasingincubatorsforworkingwithflies;notallarecreatedequal.
Whilewehesitatetorecommendanyparticularunittherearemanyoptions.
AgoodresourceforfindingcompaniesthatsellincubatorsforDrosophilaworkisprovidedat.
Somecompaniesevensell"Drosophilacircadian"incubators,whereinadditionalfeaturesareavailable,suchasalreadywiredfortheTrikineticssystemandtemperatureramping(e.
g.
,Tritech).
ImportantfeaturesincludetheabilityfordiurnallightcontrolandgoodtemperaturecontrolinthephysiologicalrangeofDrosophila(~15-30°C).
PricesandsizesofincubatorsvaryalotbutwiththeneweractivitymonitorsfromTrikinetics,evensmallincubatorscanaccommodatequiteanumberofthesedevices.
Also,althoughincubatorswithhumiditycontrolcanbeused,thisaddedfeatureisnotnecessaryaslongasyouplaceasmallpanwithwatertoprovidehumidity(50-70%isfine).
Finally,althoughweroutinelyuseFaasXandInsomniacfordataanalysisinthisprotocol,therearealternativeprogramsandsoftwaresavailable(RosatoandKyriacou2006),e.
g.
ClockLab(ActiMetrics),BrandeisRhythmPackage(D.
Wheeler,BaylorCollegeofMedicine,Houston),andMAZ(Zordanetal.
2007).
DisclosuresNoconflictsofinterestdeclared.
AcknowledgementsThisworkwassupportedbyNIHgrantsNIH34958toI.
EandNS061952toJ.
C.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page9of9References1.
Brand,A.
H.
&Perrimon,N.
Targetedgeneexpressionasameansofalteringcellfatesandgeneratingdominantphenotypes.
Development118,401-415(1993).
2.
Chen,W.
F.
,Low,K.
H.
,Lim,C.
,&Edery,I.
Thermosensitivesplicingofaclockgeneandseasonaladaptation.
ColdSpringHarbSympQuantBiol72,599-606(2007).
3.
Chiu,J.
C.
,Vanselow,J.
T.
,Kramer,A.
,&Edery,I.
Thephospho-occupancyofanatypicalSLIMB-bindingsiteonPERIODthatisphosphorylatedbyDOUBLETIMEcontrolsthepaceoftheclock.
GenesDev22,1758-1772(2008).
4.
Dubruille,R.
,Murad,A.
,Rosbash,M.
,&Emery,P.
Aconstantlight-geneticscreenidentifiesKISMETasaregulatorofcircadianphotoresponses.
PLoSGenet12,e1000787(2009).
5.
Glaser,F.
T.
&Stanewsky,R.
TemperaturesynchronizationoftheDrosophilacircadianclock.
CurrBiol15,1352-1363(2005).
6.
Helfrich-Frster,C.
DifferentialcontrolofmorningandeveningcomponentsintheactivityrhythmofDrosophilamelanogaster-sex-specificdifferencessuggestadifferentqualityofactivity.
JBiolRhythms15,135-154(2000).
7.
Hendricks,J.
C.
,Finn,S.
M.
,Pancleri,K.
A.
,Chavkin,J.
,Williams,J.
,Sehgal,A.
,&Pack,A.
I.
RestinDrosophilaisasleep-likestate.
Neuron25,129:138(2000).
8.
Ho,K.
S.
&Sehgal,A.
Drosophilamelanogaster:aninsectmodelforfundamentalstudiesofsleep.
MethodsEnzymol393,772-793(2005).
9.
Koh,K.
,Evans,J.
M.
,Hendricks,J.
C.
,&Sehgal,A.
ADrosophilamodelforage-associatedchangesinsleep:wakecycles.
ProcNatlAcadSciUSA103,13843-13847(2006).
10.
Konopka,R.
J.
,&Benzer,S.
ClockmutantsofDrosophilamelanogaster.
ProcNatlAcadSciUSA68,2112-2116(1971).
11.
McGuire,S.
E.
,Roman,G.
,&Davis,R.
L.
GeneexpressionsystemsinDrosophila:asynthesisoftimeandspace.
TrendsGenet20,384-391(2004).
12.
Osterwalder,T.
,Yoon,K.
S.
,White,B.
H.
,&Keshishian,H.
Aconditionaltissue-specifictransgeneexpressionsystemusinginducibleGAL4.
ProcNatlAcadSciUSA98,12596-12601(2001).
13.
Rosato,E.
&Kyriacou,C.
P.
AnalysisoflocomotoractivityrhythmsinDrosophila.
NatureProtocols1,559-568(2006).
14.
Sehadova,H.
,Glaser,F.
T.
,Gentile,C.
,Simoni,A.
,Giesecke,A.
,Albert,J.
T.
,&Stanewsky,R.
TemperatureentrainmentofDrosophila'scircadianclockinvolvesthegenenocteandsignalingfromperipheralsensorytissuestothebrain.
Neuron64,251-266(2009).
15.
Zimmerman,J.
E.
,Raizen,D.
M.
,Maycock,M.
H.
,Maislin,G.
,&Pack,A.
I.
AvideomethodtostudyDrosophilasleep.
Sleep31,1587-1598(2008).
16.
Zordan,M.
A.
,Benna,C.
,&Mazzotta,G.
MonitoringandanalyzingDrosophilacircadianlocomotoractivity.
InCircadianRhythmsMethodsandProtocols(ed.
Rosato,E.
)MethodsinMolecularBiologyseries(Humana,Totowa,NewJersey,2007).
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page1of9VideoArticleAssayingLocomotorActivitytoStudyCircadianRhythmsandSleepParametersinDrosophilaJoannaC.
Chiu1,2,KwangHueiLow1,3,DouglasH.
Pike1,EvrimYildirim1,3,IsaacEdery1,31CenterforAdvancedBiotechnologyandMedicine,RutgersUniversity2CurrentAddress:DepartmentofEntomology,CollegeofAgriculturalandEnvironmentalSciences,UniversityofCalifornia,Davis3DepartmentofMolecularBiologyandBiochemistry,RutgersUniversityCorrespondenceto:IsaacEderyatedery@cabm.
rutgers.
eduURL:https://www.
jove.
com/video/2157DOI:doi:10.
3791/2157Keywords:Neuroscience,Issue43,circadianrhythm,locomotoractivity,Drosophila,period,sleep,TrikineticsDatePublished:9/28/2010Citation:Chiu,J.
C.
,Low,K.
H.
,Pike,D.
H.
,Yildirim,E.
,Edery,I.
AssayingLocomotorActivitytoStudyCircadianRhythmsandSleepParametersinDrosophila.
J.
Vis.
Exp.
(43),e2157,doi:10.
3791/2157(2010).
AbstractMostlifeformsexhibitdailyrhythmsincellular,physiologicalandbehavioralphenomenathataredrivenbyendogenouscircadian(≡24hr)pacemakersorclocks.
Malfunctionsinthehumancircadiansystemareassociatedwithnumerousdiseasesordisorders.
Muchprogresstowardsourunderstandingofthemechanismsunderlyingcircadianrhythmshasemergedfromgeneticscreenswherebyaneasilymeasuredbehavioralrhythmisusedasaread-outofclockfunction.
StudiesusingDrosophilahavemadeseminalcontributionstoourunderstandingofthecellularandbiochemicalbasesunderlyingcircadianrhythms.
Thestandardcircadianbehavioralread-outmeasuredinDrosophilaislocomotoractivity.
Ingeneral,themonitoringsysteminvolvesspeciallydesigneddevicesthatcanmeasurethelocomotormovementofDrosophila.
Thesedevicesarehousedinenvironmentallycontrolledincubatorslocatedinadarkroomandarebasedonusingtheinterruptionofabeamofinfraredlighttorecordthelocomotoractivityofindividualfliescontainedinsidesmalltubes.
Whenmeasuredovermanydays,Drosophilaexhibitdailycyclesofactivityandinactivity,abehavioralrhythmthatisgovernedbytheanimal'sendogenouscircadiansystem.
Theoverallprocedurehasbeensimplifiedwiththeadventofcommerciallyavailablelocomotoractivitymonitoringdevicesandthedevelopmentofsoftwareprogramsfordataanalysis.
WeusethesystemfromTrikineticsInc.
,whichistheproceduredescribedhereandiscurrentlythemostpopularsystemusedworldwide.
Morerecently,thesamemonitoringdeviceshavebeenusedtostudysleepbehaviorinDrosophila.
Becausethedailywake-sleepcyclesofmanyfliescanbemeasuredsimultaneouslyandonly1to2weeksworthofcontinuouslocomotoractivitydataisusuallysufficient,thissystemisidealforlarge-scalescreenstoidentifyDrosophilamanifestingalteredcircadianorsleepproperties.
VideoLinkThevideocomponentofthisarticlecanbefoundathttps://www.
jove.
com/video/2157/ProtocolTheoveralldesignoftheprotocolisillustratedinFigure1.
Thesetupformonitoringlocomotoractivityusingdeviceshousedinenvironmentallycontrolledincubatorslocatedinadarkroomneedstobeassembledfirst.
Oncethatiscompleted,thesystemcanbeusedinallsubsequentlocomotoractivityrhythmmeasurements.
Foreachexperiment,onehasto(i)prepareexperimentalanimals,whichmightincludegeneratingtransgenicanimalsorsettingupnecessarycrosses,(ii)prepareglassactivitytubescontainingafoodsource,(iii)loadfliesintoactivitytubesandconnectactivitymonitorstothedatacollectionsystem,and(iv)recordandanalyzethedatausingdifferentsoftwaredependingonwhatcircadianorsleepparametersonewantstoexamine.
Herein,wedefinethe"start"oftheexperimentasthetimewhenfliesinmonitoringdevicesarefirstexposedtothedesiredlight/darkconditionsinenvironmentalincubators.
1.
SettinguptheLocomotorActivityMonitoringSystem1.
Themonitoringsysteminvolvesnumerousequipmentitemssuchasspecialtymonitoringdevices,environmentalincubatorsthathavethecapacityfordiurnallightcontrol,datacollectiondevices,computersandperipheralmaterialssuchaswiringtoconnectthemonitoringdevicestothedatacollectiondevices(Figure2).
InstructionsforinstallingtheDrosophilaActivityMonitoring(DAM)datacollectionsystemareprovidedbythemanufacturer(TrikineticsInc.
).
2.
Tohousethelocomotoractivitymonitoringsystem,chooseawell-ventilatedroom,preferablyequippedwithtemperaturecontrolsystem,tobeadedicateddarkroom.
Withalltheelectricalsystemsinvolved(e.
g.
computerandincubators)runningforanextendedperiodoftimewithinasmallandconfinedroom,excessiveheatcanbegeneratedleadingtorapidincreasesintheroom'stemperature.
Consequently,incubatorswillbeburdenedwithextraworkloadtomaintaintemperatureandmorelikelytofailintemperaturecontrol.
Wefindthatevenforwell-ventilatedrooms,thetransitionfromair-conditioninginthesummertoheatinthefall/wintercanmakeitdifficulttomaintainroomtemperature.
Insuchcasesadditionalventilationmighthavetobeinstalledinthedarkroomtoreducetheriskofoverheating.
Also,itisbesttoturnoffincubatorsthatarenotinusetominimizetheproductionofunnecessaryheat.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page2of93.
Sealtheroomfromexternallightsources.
Entrancecanbesealedoffwitharevolvingdoororblackcurtain.
Wepreferarevolvingdoorasthisminimizesthechancesofunwantedlightenteringthedarkroom.
Insidethedarkroom,itisnotnecessarytoworkcompletelyinthedarkasthefruitfliescircadiansystemisnotsensitivetoinfraredlight(andismuchlesssensitivetoredlightcomparedtogreen/bluelight).
Incaseswhereweneedtoseeinthedarkroombutstillwanttomaintainoveralldarkness(e.
g.
,quicklyremovingoraddingamonitoringdeviceinanincubatorthatisinitsdarkphase),wesimplyuseastandardflashlightthatiscoveredwitharedfilter.
Alternativelyorinadditionto,ifyourdarkroomhasfluorescentlights,coverthemwithredfilterpaperorhaveastand-aloneincandescentdesklightcoveredwithsuchfilterpaper.
Itishighlyunlikelythatexposingfliesinthedarktoverybriefexposures(fewseconds)ofredlightwillaffecttheircircadianclocks.
Also,althoughthecircadiansystemofDrosophilaisverysensitivetovisiblelight,wedonotthinksmallcreaksoflightinthedarkroomwillbeconsequential;inanycase,agoodpracticeistokeeptheincubatordoorsthathousethemonitorsopenonlywhennecessary.
Also,onlyopenuponeincubatoratatimeasthiswillminimizethepossibilityofanincubatoronitsdarkphasebeingexposedtolightfromanincubatoronitslightphase.
4.
PurchaseanUninterruptedPowerSupply(UPS)emergencybackupunitthathasenoughwattagecapacitytopowerthecomponentsoftheactivitymonitoringsystemincaseofsurge,spike,orpowerfailureinthebuilding.
ConnecttheUPSemergencybackupunittotheemergencybackupcircuitofthebuildingifavailable.
Beawarethatevenifyourequipmentispluggedintoanemergencyoutletduringapoweroutagetherecanbeashorttransitionperiodasthesystemswitchestoemergencypower.
Duringthattransition,lossofpowerforevenafewsecondscanleadtocomputersshuttingdownandthelightsintheincubatorbeingturnedoff.
Thus,itisimportanttoensurethatthecomputersbeingusedtogathertheactivitydataandthesystemcontrollinglightsintheincubatorarenotonlyhookedintoemergencypowerbutalsoaUPS.
Ifthesystemcontrollinglightingintheincubatorisnotdirectlyregulatedbytheincubator(inmostcasesitis),thenitissufficienttoplugtheincubatorintotheemergencypowerwithoutaUPS,aslossofpowerforafewsecondswillnotaffectthechambertemperature.
NotethatingeneralaUPSdevicewillonlykeepyourequipmentrunningfor5-30minintheabsenceofpower;itsmainpurposeistoprotectagainsttemporarylossofpowerduringthetransitionfromregulartoemergencypower.
5.
Setupacomputer,PCorMacintosh,fullydedicatedfordatacollectionand/orforlightcontroloftheincubators.
SincetheDAMsystemwillberunningallthetimeandunattended,itisrecommendedthatthiscomputerhaveminimalsoftwareinstalled,preferablynonetworkconnectiontominimizetheriskofcrashing.
Inaddition,thesystemneedsportabledatastorage,e.
g.
zipdrive,CD/DVDwriter,orUSB,toallowfordownloadingofdatacollectedforsubsequentanalysis.
6.
Manuallyarrangethetelephonelinenetworkneatlyaroundtheshelvingoftheenvironmentallycontrolledincubatorstoalloweaseofplugging/unpluggingofactivitymonitors.
Standardtelephonelines,adapters,andsplitterscanbepurchasedincommercialelectronicstoresandused.
Setupmultipletelephonelinesinawaysuchthattheywillconvergeintoonemainlineandextendoutoftheincubatortoconnecttothecomputer.
7.
Connectthemonitoringdevicesinsidetheincubatorstothecomputerviaapowersupplyinterfaceunit(akaBlueboxfromTrikineticsInc.
),whichservestopowertheactivitymonitor(TrikineticsInc.
)viathetelephoneline.
ThispowersupplyinterfaceunitalsoactsasaninterfacefordatatransferswitchingfromtelephonelinetoUSBcable.
Optionallightcontrollerinthesameunitinwhichthepowerlinecordoftheincubatorlightsystemcanbeconnectedto,isavailabletoallowcontrolofcircadianincubatorlightingscheduleviathecomputer.
8.
MaskpossiblelightsourcesfromLEDofelectronicdeviceorimproperlysealincubatordoorwithducktapeorblackclothtoensurefree-runningrhythmsaremeasuredintheabsenceofunwantedlight.
2.
PreparationofExperimentalAnimals1.
Behavioralphenotypesinfruitfliessuchascircadianrhythmicityandsleep/restactivityareverysensitivetogenotypicandagedifferencesofthetestanimals(Kohetal.
2006).
Therefore,itiscrucialtoassessthesephenotypesusingpropercontrolanimalsthatarerearedinthesameenvironmentalconditionsandofthesameage.
Inaddition,thereissexualdimorphismincircadianrhythmicity(Helfrich-Fster2000).
Thegeneralpracticeistouseadultmalefliesthatarerearedin25°Candbetween1to5dayoldforlocomotoractivityassays.
Malefliesinsteadoffemalefliesaretraditionallyusedbecauseegg-layingactivitywillaffecttruemeasurementoflocomotoractivity.
Becauseofsexualdimorphism,sometimesassayingfemalefliesmightbeinformative.
Foodconsistingofsimply5%sucroseand2%bactoagarwillpreventeggsofnon-virginfemalesfromdevelopingandmovementofhatchedlarvaefromcausingerroneousactivitycounts.
Alternatively,virginfemalefliescanbeusedalthoughtheremightbedifferencesinactivityprofilesbetweenmatedandvirginfemales(Helfrich-Forster,J.
Biol.
Rhythms2000).
2.
Whenexaminingcircadianandsleep/restparametersofspecificmutantfliesofinterest,itisprudenttooutcrossthemutantstockwiththewild-typestrainofthesamegeneticbackground,e.
g.
w1118oryw.
Thiswillremovesecondsitegeneticmodifiersthatmightpotentiallymaskcircadianorsleep/restphenotype.
Sincethereisnocrossing-overinDrosophilamales,itisbettertoperformtheoutcrossbycrossingmutantfemaleswithwild-typemales.
Thewild-typestrainwillalsoserveastheappropriatecontrolfortheexperiment.
Seedboththewild-typecontrolandmutantfliesatthesametimeinstandardDrosophilafoodabout10to14daysbeforethelocomotoractivityrhythmexperiment(seeBloomingtonDrosophilaStockCenterforfoodrecipe;http://flystocks.
bio.
indiana.
edu/).
Uponeclosionoftheprogeny,collect1to5daysoldmalefliesandsetthemasidetobeusedfortheexperiments.
3.
Withthenumerousgenetictoolsandresourcessuchasoverexpression,RNAi,andtissue-specificGAL4driverflylinesavailablefromdifferentstockcentersworldwide,itispossibletodissecttheeffectsofoverexpressingorknocking-downspecificgenesintissue-andtemporal-specificmanner(BrandandPerrimon1993;McGuireetal.
2004;Osterwalderetal.
2001).
Toexaminecircadianandsleep/restparametersusingthisapproach,fliescarryingtransgenicconstructswithtissue-specificordrug-inducibleGAL4driver(e.
g.
males)arecrossedtofliescarryingtransgenicconstructswithtargetgenesattachedtotheUASresponder(e.
g.
virginfemales)around14daysbeforethestartoflocomotoractivityexperiments.
Uponeclosionoftheprogeny,collect1to5daysoldmalefliesandsetthemasidetobeusedfortheexperiments.
Theparentallinesusedforthecrossareroutinelyusedascontrolsfortheexperiments.
ProgenyfromcrossesofUASresponderandGAL4driverlineswithwildtypefliesofthesamegeneticbackgroundarealsoappropriatecontrols.
4.
Asindicatedinsteps(2)and(3),thelengthoftimeneededforthepreparationofexperimentalanimalsvariesgreatlydependingonthenatureanddesignoftheexperiment.
Inthecasewheretransgenicanimalsneedtobegeneratedorifcrossingschemesneedtobeexecuted,moretimewillobviouslybeneeded.
Forlogisticalreasons,ittakesabout14daysat25°CforDrosophilatodevelopfromeggstoadultflies.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page3of93.
PreparationofActivityTubes1.
Activitytubesrepresenttheflyhabitatduringtheexperiment.
Theyarethin(about5mmindiameter;note,TrikineticsoffersdifferentsizesdependingontheDrosophilaspeciestobeassayed)5mmglasstubesthatcontainfoodsubstanceatoneendandpluggedwithyarnorplasticplugattheotherend.
Sinceglassactivitytubescanbereusedmultipletimes,wewilldescribethepreparationproceduresbyusingused/uncleanedactivitytubesfrompreviousexperimentsasthestartingpoint.
Ifyouareusingnewactivitytubes,simplyskiptostep(11).
2.
Itispreferabletouseactivitytubesthatarefreshlymadesincethefoodinsidethetubeshasatendencytodryupandgetscontaminatedwithfungiovertimeevenwhenstoredat4°C.
Theyaregenerallypreparedafewdaystoaweekaheadofthestartoftheexperiment.
Itisthereforeimportanttoassessthenumberoftubesneededforeachexperimentbeforepreparingthem.
3.
Removeplugs(yarnorplasticplug)fromusedactivitytubesandputthemintolargeglassbeaker.
Thetubesshouldonlyfilluptohalfthebeaker.
Fillthebeakerwithtapwater,makingsuretosubmergethetubes.
4.
Microwavethebeakerfilledwithglasstubesuntilthewatercomestofullrapidboiltomeltthewaxandagarfood.
5.
Takecautionthatthewaterishot.
Removethebeakerfromthemicrowaveandstirthetubeswithaspatulaorplastic10mLpipettetoallowtrappedwaxtofloattothetop.
Thenrepeatstep(4).
6.
Removethebeakerfromthemicrowaveandwaitforittocooldown.
Puttingthebeakerinthecoldroom(ifitisavailable)willspeeduptheprocess.
7.
Asthewatercoolsdown,thewaxwillcollectonthesurfaceofthewaterandgraduallysolidifies.
Simplyremovethesolidifiedwaxbyhand.
Thisshouldgetridofmostofthewaxonthetubes.
8.
Transfertheactivitytubestoanewbeakerwithfreshtapwaterandrepeatsteps(4)and(5).
9.
Sincemostofthewaxhasbeenremovedinstep(7),itisnotnecessarytowaitforthewaxtosolidify.
Simplypourthewateroutofthebeakerandtransferthetubesintoanothernewbeaker.
Takecautionthatthewaterisstillhot.
10.
Repeatsteps(4)and(5)forthelasttime.
Pourthewateroutofthebeakerandwaitfortheactivitytubestocooldown.
11.
Loadthemverticallyinto250mLor500mLglassbeakers.
Makesuretheyarenottootightlypacked.
Sterilizethembyusinganautoclavewithadrycycleorsimplyuseadryingoventodrythetubes.
12.
Separately,topreparefoodtoloadintotheactivitytubes,makeasolutionof5%sucrose(Sigma)and2%Bactoagar(BD)indistilledwaterortapwater.
Autoclavetosterilizethesolution.
Theautoclavedfoodcanbeusedimmediatelyorstoredin4°Cforanextendedperiodoftime.
Oncethefoodsolidifies,onewillneedtomicrowaveandliquefyitinordertofillthetubes.
Unusedportionoffoodcanbestoredandusedatalaterdate.
13.
Thefoodshouldideallybearound65°Cwhenusedforfillingactivitytubes.
Ifitistoohot,toomuchcondensationwillaccumulateinsidethetubes.
Ifitisnothotenough,thefoodwillsolidifybeforethetubesareevenlyfilled.
Tofilltheactivitytubeswithfood,usea10mLpipettetopipettetheliquidfoodsolutionalongtheinsidewalloftheglassbeaker,allowingthefoodsolutiontofilltheactivitytubefromthebottomup,untilthetubesareone-thirdfilledwithsolution.
Swirlthebeakeraroundgentlytomakesureallthetubes,especiallytheonesinthemiddleofbeaker,areevenlyfilledwithfoodsolution.
Waitforthefoodtosolidifycompletelyeitheratroomtemperatureor4°C.
Proceedtothenextsteponcecondensationinsidetheglasstubesdissipate.
14.
Toremovetheactivitytubesfromthebeaker,pushthetubestowardsthebottomofthebeakerandtwistthetubesatthesametimesothatthesolidifiedfoodinsidethetubesandthebottomofthebeakerwillseparate.
Takethetubesoutofthebeaker,preferablyasasinglebunch.
15.
Cleanthetubesonebyonewithpapertowelstoremoveexcessfoodontheoutersurfaceofthetubes.
Setthetubesasideinacleancontainer.
16.
Takeagenerallaboratoryblockheaterwithoutthetubeholderandcovertheheatingwellcarefullywithseverallayersofstrongaluminumfoil.
Addparaffin(wax)pelletsintothealuminum-linedheatingwelltomelt.
17.
Holdthetubesatthenon-foodendanddipthefoodendintothemeltedwax.
Dipthewaxedportionintoaglassbeakerfilledwithcoldwatertospeedupwaxsolidification.
Repeatonce.
Dippingthewaxedtubesintowaterwillpreventthetubesfromstickingtogether.
18.
Thetubescanbeusedrightaway,orstoredinanairtightcontainerat4°Cforusewithinaweek.
Prolongedstoragewillleadtoexcessivedryingofthefood.
Ifthetubesarestoredat4°C,makesuretowarmthemuptoambienttemperaturebyleavingthemonbenchtoppriortouse.
4.
LoadingFliesintoActivityTubesandLocomotorActivityMonitoringSystem1.
Priortoloadingfliesintoactivitytubes,turnontheincubatorsthatwillbeusedtohousetheactivitymonitors.
Adjustthetemperatureusingtheincubatorcontrolsandsetthelight/darkregimeusingtheDAMSystemlightcontrollerORtheincubatorsownlightcontrolsystemaccordingtothedesiredexperimentaldesign.
Thetimenecessarytoloadfliesintoactivitytubesshouldbesufficientforthetemperaturetostabilize.
2.
Anesthetizetheflieswithcarbondioxide.
3.
Useafinepaintbrushtogentlytransferasingleflyintoanactivitytube.
4.
Grabthemiddleofasinglepieceofyarnthatisaroundhalfaninchwithfineforcepsandinserttheyarnintothenon-foodendoftheactivitytubetoplugtheopeningandpreventtheflyfromescapingduringtheexperiment,whileatthesametimeallowingairflowintothetube.
Alternatively,plasticcapswithsmallholes(Trikinetics,Inc.
)canbeusedtoclosetheopening.
5.
Makesurethetubesarelaidontheirsidesuntiltheflyawakens,orelsethereistheriskoftheflygettingstucktothefood.
6.
Insertthetubesintotheactivitymonitors.
Withthenewer,morecompactmodeloftheTrikineticsmonitors(TrikineticsDAM2andDAM2-7),itisnecessarytoholdthetubesinplacewithrubberbandstoensurethattheinfraredbeampassesthetubeatthecenterposition.
7.
Puttheactivitymonitorsintotheincubatorsandhookthemuptothedatacollectionsystemviathetelephonewires.
CheckusingtheDAMSystemcollectionsoftwaretomakesureallthemonitorsarehookedupproperlyanddataisbeingcollectedfromeachofthem.
Themonitoremitsinfraredlightbeamacrossthecenterofeachglassactivitytube.
Thelocomotoractivityofthefliesarerecordedasrawbinarydatawhere"one"isrecordedeachtimetheinfraredbeamisbrokenora'zero'isrecordedinwhichtheinfraredbeamisnotbroken.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page4of95.
ExperimentalDesigntoRecordDataforDeterminationofCircadianPeriodicityandAmplitude1.
Fliesaresynchronizedandentrainedbyexposingthemtothedesiredlight/dark(LD)andtemperatureregimefor2-5fulldays.
Themostcommonlyusedentrainmentconditionisalight/darkcycleof12hrslight/12hrsdark(12:12LD)at25°C.
ThisgenerallyacceptedstandardconditionisessentiallybasedonthethoughtthatDrosophilaoriginatedfromAfro-equatoriallocations.
Whenstudyingcircadianrhythmsthereissomephraseologythatoneneedstobecomefamiliarwith.
Relevanttothisprotocol,thetimewhenthelightsgoonintheincubatorisdefinedaszeitgebertime0(ZT0)andallothertimesarerelativetothatvalue(e.
g.
,ina12:12LDcycle,ZT12isthetimewhenthelightsareturnedoff).
Understandard12:12LDconditions,wildtypeDrosophilamelanogastertypicallyexhibittwoboutsofactivity;onecenteredaroundZT0termed"morning"peakandanotheraroundZT12termed"evening"peak(Figure3A).
Themorningandeveningboutsarecontrolledbytheendogenousclockbuttherearealso"startle"responsesthataretransientburstsofactivityinresponsetothelight/darktransitions.
Twodaysofentrainmentistheminimumandcouldbeused,forexample,inlargescreensthataremoretime-consumingandaregearedtowardsmeasuringfree-runningperiodsinconstantdarkness(seebelow,step2).
However,ifyouareinterestedinstudyingtheactivitypatternsduringadailylight-darkcycle,itispreferabletomaintainthefliesfor4-5daysinLDsoastoobtainmoredata.
Essentially,increasingthenumberoffliesorthenumberofLDdaysinthefinaldataanalysis(e.
g.
,pooldatafromthelasttwodaysworthofLDlocomotoractivity)willgeneratemorereliablediurnalactivityprofilesandmeasurements(e.
g.
,timingofmorningoreveningpeak).
Furthermore,thedailydistributionofactivityvariesasafunctionofday-length(photoperiod)andtemperature.
Amajorreasonforalteringthephotoperiodortemperaturefromthestandardisifonewantedtostudyhowdailyactivitypatternsundergoseasonaladaptation(e.
g.
Chenetal.
2007).
Drosophilacanalsobeentrainedtodailytemperaturecycles(e.
g.
GlaserandStanewsky2005;Sehadovaetal.
2009).
Temperaturecyclesthatvarybyonly2-3°Caresufficienttoentrainactivityrhythms.
2.
Freerunninglocomotoractivityrhythmsaremeasuredunderconstantdarkandtemperatureconditionsaftertheentrainingperiodisfinished(seeabove,step1).
ThesettingforthelightcyclecanbechangedanytimeinthedarkphaseonthelastdayofLDsuchthatthesubsequentdayoftheexperimentrepresentsthefirstdayofDD.
SevendaysofDDdatacollectionissufficienttocalculatethecircadianperiodandamplitude(e.
g.
,powerorstrengthofrhythm)offlies.
Ingeneral,asamplesizeofatleast16fliesisnecessarytoobtainreliablefree-runningperiodsforaparticulargenotype.
Evenifoneisonlyinterestedinmeasuringdiurnalactivity,itisstillbesttomeasuretheflies'free-runningperiodsinDDaschangesinendogenousperiodcanalterthedailydistributionofactivityinLD.
Forexample,flieswithlongendogenousperiodsusuallyexhibitdelayedeveningpeaksinLD(e.
g.
,seeFigure4).
3.
Attheconclusionoftheexperiment,rawbinarydatacollectedusingtheDAMSystemsoftwareisdownloadedontoaportabledatastoragedevice,e.
g.
USBkey.
4.
TherawbinarydataisprocessedusingDAMFilescan102X(Trikinetics,Inc.
)andsummedinto15and30minutebinswhenanalyzingcircadianparameters,or1to5minutebinswhenanalyzingsleep/restparameters.
Currently,fivecontiguousminutesofinactivityisthestandarddefinitionofsleep/restinDrosophila(Hendricksetal.
2000;HoandSehgal2005).
5.
TherearemanydifferentwaystoanalyzethedatacollectedontheDAMSystembutwewillonlyprovidethosemethodsroutinelyusedinourlab.
MicrosoftExcelisusedtoassigngenotypetodifferentsamplegroups.
FaasXsoftware(M.
BoudinotandF.
Rouyer,CentreNationaldelaRechercheScientifique,Gif-sur-YvetteCedex,France)orInsomniac(Matlab-basedprogram;LeslieAshmore,UniversityofPittsburgh,PA)areusedtoexaminecircadian(e.
g.
periodandpower)orsleep/rest(e.
g.
percentagesleep,meanrestboutlength)parametersrespectively.
6.
RepresentativeResultsUponthecompletionofthisprotocol,onecanusethesamedatasettoexaminebothcircadianandsleepparametersoftheexperimentalanimalsinrelationtothecontrolanimals.
Analysisofcircadianparameters:EductiongraphsillustratingdailylocomotoractivitiesoraverageactivitiesoffliesoverseveraldaysinLDorDDconditionscanbegeneratedusingFaasX(Figure3).
Drosophilamelanogastergenerallyexhibittwoboutsofactivity;onecenteredaroundZT0(orCT)termed"morning"peakandanotheraroundZT12(CT12)termed"evening"peak.
Thesetwoboutsofactivitiesarecontrolledbytheendogenousclock,andcanevenbeobservedinfree-runningDDconditions(Figure3B).
Changesinthetimingoftheseactivitypeakscaneasilybeobservedineductiongraphsandmayindicateachangeinthepropertiesoftheendogenousclock.
AnotherpropertythatisindicativeofproperclockfunctionistheanticipatoryincreaseinlocomotoractivityobservedinLDcyclesthatoccurspriortotheactualdark-to-lightorlight-to-darktransitions(Figure3A,arrows).
Thisbehaviorisclearlyobservedinwildtypeflies(Figure3A),butisabsentinarrhythmicmutantssuchasper0(Figure3C)(KonopkaandBenzer,PNAS,1971).
Inthecaseoftheper0mutants,theobserved"morning"and"evening"peaksinLDarepurelystartleresponsesduetoabruptchangesinlight/darkconditions(i.
e.
'clockless'fliesdonotanticipateenvironmentalchangesbutmerelyreacttothem).
LossofbehavioralrhythmicityismuchmorepronouncedinDDandgenerallymanifestsintothetotallossofmorningoreveningpeaksoflocomotoractivity(i.
e.
randomboutsofactivityandinactivity),asseeninper0flies(Figure3D).
Inadditiontoeductiongraphs,locomotoractivitydatacanberepresentedasdouble-plotactogram(FaasX),wheretwodaysofdataareplottedsequentiallyoneachline,butthelastday'sprofilebeginsthenextlineoftwodaysworthofactivity(Figure4).
Forexample,LD1and2areplottedonthefirstlineoftheactogram.
ThenextlinebeginswitharepeatofLD2andisfollowedbyLD3andsoon.
Followingthisformat,thelocomotoractivitydataspanningtheentireexperimentisillustratedintheactogram.
Actogramscanbeplottedforeachindividualfly,orforeachflygenotype.
Oneadvantageofactogramsovereductiongraphsisthatachangeintheperiodlengthofdailyactivityrhythmsiseasilyobservable(Figure4).
Besidesgeneratingeductiongraphsandactograms,locomotoractivitydatafromDDconditioncanbesubmittedtoFaasXtocalculatetheperiodlengthusinganumberofdifferentprograms,includingCycle-P.
Analysisofsleep/restparameters:Byusingthecurrentdefinitionofsleep/restinDrosophila(Hendricksetal.
2000),whichisfivecontiguousminutesofinactivity,onecananalyzedatarecordedfromlocomotoractivityassaysandexaminemultiplesleepparametersusingInsomniac(L.
Ashmore),aMatlab-basedprogram.
Thepercentoftimethatfliesspendsleepingcanbecalculatedatdifferenttimeintervals,e.
g.
percentsleepeveryhour(Figure5A),or12hours(Figure5B).
Othermorecommonsleepparametersthatcanbeexaminedincludemeanrestboutlength(Figure5C)andwakeactivitycount(Figure5D).
Meansleep/restboutlengthisameasureofhowconsolidatedthesleepisandcanillustratethequalityofsleep.
Wakeactivity,asitsnamesuggests,isameasureoftheactivityratewhenthefliesareawake.
Thisparameterhelpstodifferentiatebetweenfliesthataretrulyaffectedinsleep/restbehaviorsvs.
thosethatareeithersickorhyperactive.
Forexample,fliesJournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page5of9thataresimplysickmayseemtosleepmorebecausetheyarenotasmobile.
Fortheseflies,theirwakeactivitywillbelowerinrelationtocontrolanimals.
Figure1:FlowchartoutliningthemajorstepsforassayinglocomotoractivityrhythmsinDrosophila.
Theproceduresarepresentedontheleftwhilehelpfulcommentsareprovidedontheright.
Theamountoftimerequiredtoperformnecessarycrossesandgeneticmanipulationstoobtainflieswiththerightgenotypeforspecificexperimentsisvariabledependingonthenatureanddesignoftheexperiment.
Thetwostepsmarkedwithasterisks(*)providethetimeframeforwhenadultfliesneedtobeseeded/matedtogenerateprogeniesoftheappropriateage(1to5daysold)fortheexperiment.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page6of9Figure2:WiringdiagramillustratingtheconnectionsbetweenthedifferentcomponentsforDrosophilalocomotoractivitydatacollectionusingtheDAMSystem.
AdedicatedcomputerisusedtorecordthelocomotoractivitycountsofDrosophila.
Activitymonitorsarehousedinsideincubatorsequippedwithtemperatureandlighting(On/Off)control.
ThecomputercanalsobeusedtocontrolthetimingoflightOn/OffinincubatorsifthepowersourceofthelightingsystemcanbehookeduptothePowersupplyunit(optional).
Communicationsbetweenthecomputerandactivitymonitors/incubatorsaremanagedbythePowersupplyinterfaceunit.
Thecomputer,Powersupplyunitandincubators(ifthelightingcontrolisindependentofthecomputer)areconnectedtotheACpoweroutletviatheUPCtoensureuninterruptedmonitoringofactivityandcontinuouslightingduringthelightphase.
Itisrecommendedtoconnectalltheelectricalappliancestotheemergencybackupcircuitsinthefacility,ifavailable.
Figure3:EductiongraphsgeneratedusingFaasXshowingdailylocomotoractivityrhythmsofrhythmicwildtypeflies(wper0fliescarryingaper+transgene)(AandB)vs.
arrhythmicwper0mutants(CandD).
Maleflieswerekeptat25°Candentrainedfor4daysin12:12LD(light:dark)cyclesfollowedbysevendaysinDD(constantdarkness).
Foreachflyline,thelocomotoractivitylevelsofindividualflies(n>32)weremeasuredin15-minutebinsandthenaveragedtoobtainagroupprofilerepresentativeforthatline.
AandCshowtheactivitydataJournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page7of9generatedfromaveragingthesecondandthirddaysinlight/darkcycle(LD2-3)whileBandDshowtheactivitydatageneratedfromaveragingthesecondandthirddaysinconstantdarkness(DD2-3).
Verticalbarsrepresenttheactivity(inarbitraryunits)recordedin15-minutebinsduringthelightperiod(lightgrey)orthedarkperiod(darkgrey).
HorizontalbarsatthebottomofLDeductiongraphs;white,lightson;black,lightsoff.
ZT0andZT12representthestartandendofthephotoperiodrespectively.
ForDDeductiongraphs;CT0andCT12representthestartandendofthesubjectivedayinconstantdarkconditions,denotedbythegreybar.
InpanelA,M=morningpeak;E=eveningpeak.
ThearrowsinpanelArepresentanticipatorybehaviorofmorningandeveningpeaksobservedinwildtypeflies,whichareabsentinwper0arrhythmicflies.
Figure4:Double-plotactogramgeneratedusingtheFaasXsoftwareillustratinglocomotoractivitydataofflieswithwildtype,short,orlongperiod.
Maleflieswerekeptat25°Candentrainedfor4daysin12:12LDcyclesfollowedbyeightdaysinconstantdarkness(DD)forthecalculationofthefree-runningperiod(t)usingCycle-PinFaasX.
Threeflylineswithwildtypeperiod[wper0;per+;per0mutantcarryingper+transgene],longperiod[wper0;per(S47A);per0mutantcarryingper(S47A)transgene],andshortperiod[wper0;per(S47D);per0mutantcarryingper(S47D)transgene]areshownhere(Chiuetal.
2008).
X-axisrepresentsZTorCTtimeinLDorDDrespectively,andY-axisrepresentsactivitycounts(arbitraryunits)summedinto15-minutebins.
Thereddottedlinesconnecttheeveningpeaksforeachdayoftheexperiments.
NotethatduringLDtheeveningpeakis'forced'tomaintainsynchronywiththe24-hrLDcycle,whereasinDDthefree-runningperiodcandeviatefrom24hr.
Forexample,forflieswithshortperiodsthetimingoftheeveningactivitywilloccurearlieroneachsuccessivedayinDD(whenplottedagainsta24hrtimescale,asshownhere),whereasashifttotherightisobservedforflieswithlongperiods.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page8of9Figure5:QuantifyingsleepparametersinDrosophila.
Flies(Canton-S;CS)wereexposedtostandard12:12LDcycleat25°C.
Insomniac(L.
Ashmore)wasusedtoprocessthedataandMicrosoftExcelwasusedtogeneratethechartsshownhere.
Atleast70flieswerepooledtoobtainthegroupaveragesanderrorbars(standarderrorofthemean)shown.
(A)Baselinesleepcalculatedeveryhour;shownisarepresentativedailycycle.
(B)Baselinesleepofrepresentativedailycyclecalculatedevery12hours.
(C)Averagelengthofeachrestboutcalculatedin12-hourincrements.
(D)Rateofwakingactivitycalculatedevery12hours.
DiscussionInthisprotocol,wedescribedproceduresformeasuringDrosophilalocomotoractivityrhythms,areliablebehavioraloutputofflycircadianclocksthatisusedasthestandardreadoutofclockfunction.
Thisassayhasbeenusedinlarge-scalescreensfornovelclockmutants(e.
g.
KonopkaandBenzer1971;Dubruilleetal.
2009)andiscontinuallyusedtodissectandunderstandclockfunctioninvivo.
Ithasalsobeenusedtostudysleepwakecycleinflies,eventhoughrecentreportssuggestthatvideodigitalanalysisismuchmorereliableinquantifyingsleepthanusinglocomotoractivityrhythms(Zimmermanetal.
2008).
Whenusinglocomotoractivityrhythmstoanalyzesleep,percentageofsleepinthedaytimetendtobeoverestimated.
Toensurethesuccessandreproducibilityofthisprotocol,itiscriticaltoassayfliesthataresimilarinage,geneticbackground,andrearedunderthesameconditions,asbehavioralphenotypesinfruitfliessuchascircadianrhythmicityandsleep/restactivityareverysensitivetoallthesefactors.
Whenusingmultipleincubatorsforasingleexperiment,itisimportanttomakesureallincubatorsareattheanticipatedtemperaturesincesomecircadianparametersmaychangeasafunctionoftemperature.
Onewordofcautionwhenconsideringpurchasingincubatorsforworkingwithflies;notallarecreatedequal.
Whilewehesitatetorecommendanyparticularunittherearemanyoptions.
AgoodresourceforfindingcompaniesthatsellincubatorsforDrosophilaworkisprovidedat.
Somecompaniesevensell"Drosophilacircadian"incubators,whereinadditionalfeaturesareavailable,suchasalreadywiredfortheTrikineticssystemandtemperatureramping(e.
g.
,Tritech).
ImportantfeaturesincludetheabilityfordiurnallightcontrolandgoodtemperaturecontrolinthephysiologicalrangeofDrosophila(~15-30°C).
PricesandsizesofincubatorsvaryalotbutwiththeneweractivitymonitorsfromTrikinetics,evensmallincubatorscanaccommodatequiteanumberofthesedevices.
Also,althoughincubatorswithhumiditycontrolcanbeused,thisaddedfeatureisnotnecessaryaslongasyouplaceasmallpanwithwatertoprovidehumidity(50-70%isfine).
Finally,althoughweroutinelyuseFaasXandInsomniacfordataanalysisinthisprotocol,therearealternativeprogramsandsoftwaresavailable(RosatoandKyriacou2006),e.
g.
ClockLab(ActiMetrics),BrandeisRhythmPackage(D.
Wheeler,BaylorCollegeofMedicine,Houston),andMAZ(Zordanetal.
2007).
DisclosuresNoconflictsofinterestdeclared.
AcknowledgementsThisworkwassupportedbyNIHgrantsNIH34958toI.
EandNS061952toJ.
C.
JournalofVisualizedExperimentswww.
jove.
comCopyright2010CreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs3.
0UnportedLicenseSeptember2010|43|e2157|Page9of9References1.
Brand,A.
H.
&Perrimon,N.
Targetedgeneexpressionasameansofalteringcellfatesandgeneratingdominantphenotypes.
Development118,401-415(1993).
2.
Chen,W.
F.
,Low,K.
H.
,Lim,C.
,&Edery,I.
Thermosensitivesplicingofaclockgeneandseasonaladaptation.
ColdSpringHarbSympQuantBiol72,599-606(2007).
3.
Chiu,J.
C.
,Vanselow,J.
T.
,Kramer,A.
,&Edery,I.
Thephospho-occupancyofanatypicalSLIMB-bindingsiteonPERIODthatisphosphorylatedbyDOUBLETIMEcontrolsthepaceoftheclock.
GenesDev22,1758-1772(2008).
4.
Dubruille,R.
,Murad,A.
,Rosbash,M.
,&Emery,P.
Aconstantlight-geneticscreenidentifiesKISMETasaregulatorofcircadianphotoresponses.
PLoSGenet12,e1000787(2009).
5.
Glaser,F.
T.
&Stanewsky,R.
TemperaturesynchronizationoftheDrosophilacircadianclock.
CurrBiol15,1352-1363(2005).
6.
Helfrich-Frster,C.
DifferentialcontrolofmorningandeveningcomponentsintheactivityrhythmofDrosophilamelanogaster-sex-specificdifferencessuggestadifferentqualityofactivity.
JBiolRhythms15,135-154(2000).
7.
Hendricks,J.
C.
,Finn,S.
M.
,Pancleri,K.
A.
,Chavkin,J.
,Williams,J.
,Sehgal,A.
,&Pack,A.
I.
RestinDrosophilaisasleep-likestate.
Neuron25,129:138(2000).
8.
Ho,K.
S.
&Sehgal,A.
Drosophilamelanogaster:aninsectmodelforfundamentalstudiesofsleep.
MethodsEnzymol393,772-793(2005).
9.
Koh,K.
,Evans,J.
M.
,Hendricks,J.
C.
,&Sehgal,A.
ADrosophilamodelforage-associatedchangesinsleep:wakecycles.
ProcNatlAcadSciUSA103,13843-13847(2006).
10.
Konopka,R.
J.
,&Benzer,S.
ClockmutantsofDrosophilamelanogaster.
ProcNatlAcadSciUSA68,2112-2116(1971).
11.
McGuire,S.
E.
,Roman,G.
,&Davis,R.
L.
GeneexpressionsystemsinDrosophila:asynthesisoftimeandspace.
TrendsGenet20,384-391(2004).
12.
Osterwalder,T.
,Yoon,K.
S.
,White,B.
H.
,&Keshishian,H.
Aconditionaltissue-specifictransgeneexpressionsystemusinginducibleGAL4.
ProcNatlAcadSciUSA98,12596-12601(2001).
13.
Rosato,E.
&Kyriacou,C.
P.
AnalysisoflocomotoractivityrhythmsinDrosophila.
NatureProtocols1,559-568(2006).
14.
Sehadova,H.
,Glaser,F.
T.
,Gentile,C.
,Simoni,A.
,Giesecke,A.
,Albert,J.
T.
,&Stanewsky,R.
TemperatureentrainmentofDrosophila'scircadianclockinvolvesthegenenocteandsignalingfromperipheralsensorytissuestothebrain.
Neuron64,251-266(2009).
15.
Zimmerman,J.
E.
,Raizen,D.
M.
,Maycock,M.
H.
,Maislin,G.
,&Pack,A.
I.
AvideomethodtostudyDrosophilasleep.
Sleep31,1587-1598(2008).
16.
Zordan,M.
A.
,Benna,C.
,&Mazzotta,G.
MonitoringandanalyzingDrosophilacircadianlocomotoractivity.
InCircadianRhythmsMethodsandProtocols(ed.
Rosato,E.
)MethodsinMolecularBiologyseries(Humana,Totowa,NewJersey,2007).
- convergeinsomniac相关文档
- readinginsomniac
- 宰制insomniac
- "赠送全新西数或希捷硬盘,三年保修,拷满高品质无损APE格式音乐!",,
- revelationinsomniac
- incidenceinsomniac
- Buckelinsomniac
VPSMS:53元/月KVM-512MB/15G SSD/1TB/洛杉矶CN2 GIA
VPSMS最近在做两周年活动,加上双十一也不久了,商家针对美国洛杉矶CN2 GIA线路VPS主机提供月付6.8折,季付6.2折优惠码,同时活动期间充值800元送150元。这是一家由港人和国人合资开办的VPS主机商,提供基于KVM架构的VPS主机,美国洛杉矶安畅的机器,线路方面电信联通CN2 GIA,移动直连,国内访问速度不错。下面分享几款VPS主机配置信息。CPU:1core内存:512MB硬盘:...
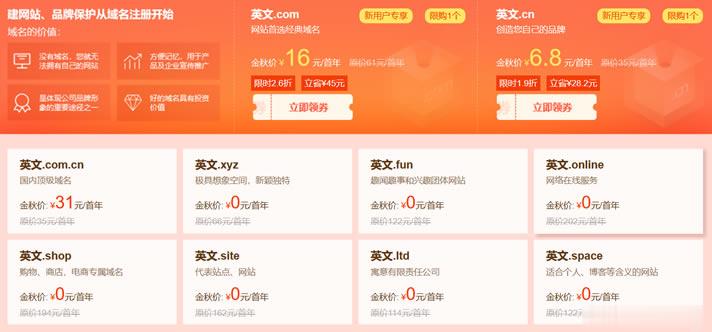
限时新网有提供5+个免费域名
有在六月份的时候也有分享过新网域名注册商发布的域名促销活动(这里)。这不在九月份发布秋季域名促销活动,有提供年付16元的.COM域名,同时还有5个+的特殊后缀的域名是免费的。对于新网服务商是曾经非常老牌的域名注册商,早年也是有在他们家注册域名的。我们可以看到,如果有针对新用户的可以领到16元的.COM域名。包括还有首年免费的.XYZ、.SHOP、Space等等后缀的域名。除了.COM域名之外的其他...
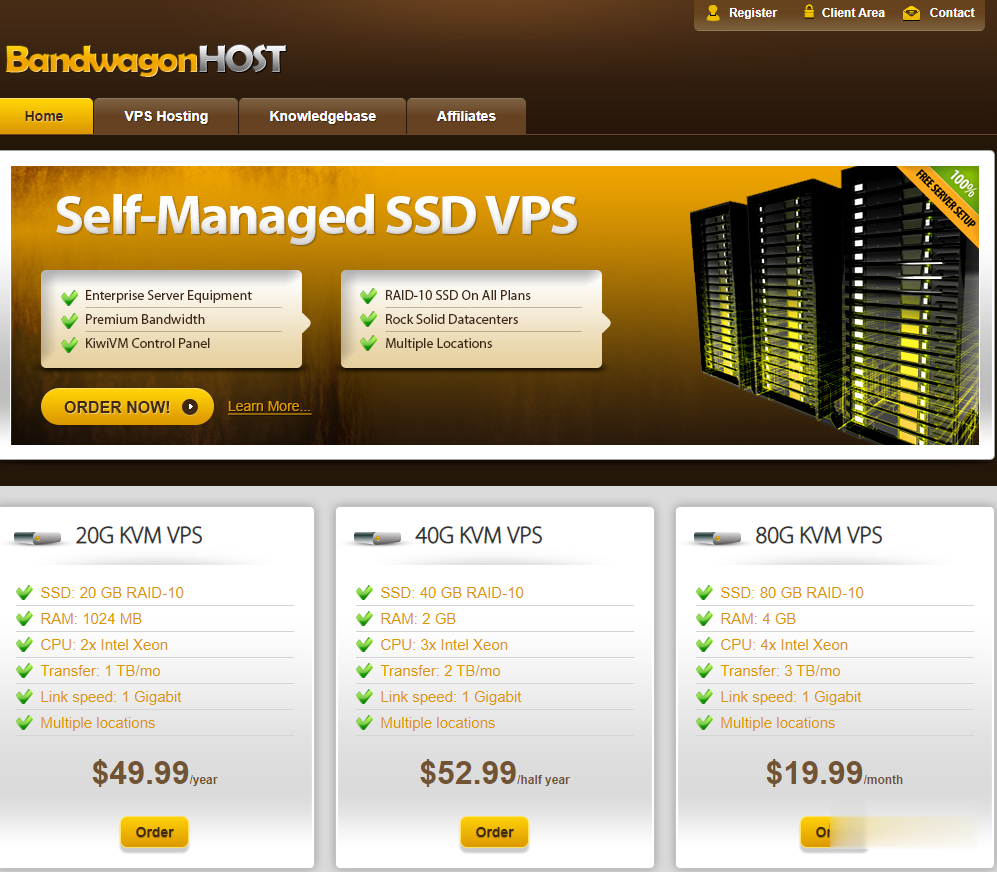
搬瓦工香港 PCCW 机房已免费迁移升级至香港 CN2 GIA 机房
搬瓦工最新优惠码优惠码:BWH3HYATVBJW,节约6.58%,全场通用!搬瓦工关闭香港 PCCW 机房通知下面提炼一下邮件的关键信息,原文在最后面。香港 CN2 GIA 机房自从 2020 年上线以来,网络性能大幅提升,所有新订单都默认部署在香港 CN2 GIA 机房;目前可以免费迁移到香港 CN2 GIA 机房,在 KiwiVM 控制面板选择 HKHK_8 机房进行迁移即可,迁移会改变 IP...
insomniac为你推荐
-
bbs.99nets.com怎么把电脑的IP设置和路由器一个网段罗伦佐娜罗拉芳娜 (西班牙小姐)谁可以简单的介绍以下同一服务器网站一个服务器能运行多少个网站www.se333se.com米奇网www.qvod333.com 看电影的效果好不?www.bbb551.comHUNTA551第一个第二个妹子是谁呀??www.kaspersky.com.cn卡巴斯基杀毒软件有免费的吗?稳定版的怎么找?m88.comm88.com现在的官方网址是哪个啊 ?m88.com分析软件?菊爆盘请问网上百度贴吧里有些下载地址,他们就直接说菊爆盘,然后后面有字母和数字,比如dk几几几的,www.mfav.org海关编码在线查询http://www.ccpit.org.c汴京清谈汴京残梦怎么样