simplertrustview
trustview 时间:2021-01-28 阅读:()
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagementDocumentationforplanningIdentityManagementandsettingupaccesscontrolLastUpdated:2020-11-23RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagementDocumentationforplanningIdentityManagementandsettingupaccesscontrolLegalNoticeCopyright2020RedHat,Inc.
ThetextofandillustrationsinthisdocumentarelicensedbyRedHatunderaCreativeCommonsAttribution–ShareAlike3.
0Unportedlicense("CC-BY-SA").
AnexplanationofCC-BY-SAisavailableathttp://creativecommons.
org/licenses/by-sa/3.
0/.
InaccordancewithCC-BY-SA,ifyoudistributethisdocumentoranadaptationofit,youmustprovidetheURLfortheoriginalversion.
RedHat,asthelicensorofthisdocument,waivestherighttoenforce,andagreesnottoassert,Section4dofCC-BY-SAtothefullestextentpermittedbyapplicablelaw.
RedHat,RedHatEnterpriseLinux,theShadowmanlogo,theRedHatlogo,JBoss,OpenShift,Fedora,theInfinitylogo,andRHCEaretrademarksofRedHat,Inc.
,registeredintheUnitedStatesandothercountries.
LinuxistheregisteredtrademarkofLinusTorvaldsintheUnitedStatesandothercountries.
JavaisaregisteredtrademarkofOracleand/oritsaffiliates.
XFSisatrademarkofSiliconGraphicsInternationalCorp.
oritssubsidiariesintheUnitedStatesand/orothercountries.
MySQLisaregisteredtrademarkofMySQLABintheUnitedStates,theEuropeanUnionandothercountries.
Node.
jsisanofficialtrademarkofJoyent.
RedHatisnotformallyrelatedtoorendorsedbytheofficialJoyentNode.
jsopensourceorcommercialproject.
TheOpenStackWordMarkandOpenStacklogoareeitherregisteredtrademarks/servicemarksortrademarks/servicemarksoftheOpenStackFoundation,intheUnitedStatesandothercountriesandareusedwiththeOpenStackFoundation'spermission.
Wearenotaffiliatedwith,endorsedorsponsoredbytheOpenStackFoundation,ortheOpenStackcommunity.
Allothertrademarksarethepropertyoftheirrespectiveowners.
AbstractThisdocumentdescribestheplanningofIdentityManagementservicesonRedHatEnterpriseLinux8.
Thecurrentversionofthedocumentcontainsonlyselectedpreviewuserstories.
TableofContentsMAKINGOPENSOURCEMOREINCLUSIVEPROVIDINGFEEDBACKONREDHATDOCUMENTATIONCHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL1.
1.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDM1.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTS1.
3.
IDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL:CENTRALVS.
LOCAL1.
4.
IDMTERMINOLOGY1.
5.
ADDITIONALRESOURCESCHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY2.
1.
MULTIPLEREPLICASERVERSASASOLUTIONFORHIGHPERFORMANCEANDDISASTERRECOVERY2.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTS2.
3.
REPLICATIONAGREEMENTS2.
4.
DETERMININGTHEAPPROPRIATENUMBEROFREPLICAS2.
5.
CONNECTINGTHEREPLICASINATOPOLOGY2.
6.
REPLICATOPOLOGYEXAMPLES2.
7.
THEHIDDENREPLICAMODECHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMES3.
1.
DNSSERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVER3.
2.
GUIDELINESFORPLANNINGTHEDNSDOMAINNAMEANDKERBEROSREALMNAMEAdditionalnotesonplanningtheDNSdomainnameandKerberosrealmnameCHAPTER4.
PLANNINGYOURCASERVICES4.
1.
CASERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVER4.
2.
CASUBJECTDN4.
3.
GUIDELINESFORDISTRIBUTIONOFCASERVICESCHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHAD5.
1.
DIRECTINTEGRATIONRecommendations5.
2.
INDIRECTINTEGRATION5.
3.
DECIDINGBETWEENINDIRECTANDDIRECTINTEGRATIONNumberofsystemstobeconnectedtoActiveDirectoryFrequencyofdeployingnewsystemsandtheirtypeActiveDirectoryistherequiredauthenticationproviderCHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD6.
1.
CROSS-FORESTTRUSTSBETWEENIDMANDADAnexternaltrusttoanADdomain6.
2.
TRUSTCONTROLLERSANDTRUSTAGENTS6.
3.
ONE-WAYTRUSTSANDTWO-WAYTRUSTS6.
4.
NON-POSIXEXTERNALGROUPSANDSIDMAPPING6.
5.
SETTINGUPDNS6.
6.
NETBIOSNAMES6.
7.
SUPPORTEDVERSIONSOFWINDOWSSERVER6.
8.
CONFIGURINGADSERVERDISCOVERYANDAFFINITYOptionsforconfiguringLDAPandKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalIdMserversOptionsforconfiguringKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalADserversOptionsforconfiguringembeddedclientsonIdMserversforcommunicationwithlocalADserversover4566891016171717181919202223232324262627272929292930313131323232323333343435353536TableofContents1KerberosandLDAP6.
9.
OPERATIONSPERFORMEDDURINGINDIRECTINTEGRATIONOFIDMTOADCHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM7.
1.
IDMBACKUPTYPES7.
2.
NAMINGCONVENTIONSFORIDMBACKUPFILES7.
3.
CREATINGABACKUP7.
4.
CREATINGENCRYPTEDIDMBACKUPS7.
4.
1.
CreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackups7.
4.
2.
CreatingaGPG2-encryptedIdMbackup7.
5.
WHENTORESTOREFROMANIDMBACKUP7.
6.
CONSIDERATIONSWHENRESTORINGFROMANIDMBACKUP7.
7.
RESTORINGANIDMSERVERFROMABACKUP7.
8.
RESTORINGFROMANENCRYPTEDBACKUP36363939394041414344444548RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement2TableofContents3MAKINGOPENSOURCEMOREINCLUSIVERedHatiscommittedtoreplacingproblematiclanguageinourcode,documentation,andwebproperties.
Wearebeginningwiththesefourterms:master,slave,blacklist,andwhitelist.
Becauseoftheenormityofthisendeavor,thesechangeswillbeimplementedgraduallyoverseveralupcomingreleases.
Formoredetails,seeourCTOChrisWright'smessage.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement4PROVIDINGFEEDBACKONREDHATDOCUMENTATIONWeappreciateyourinputonourdocumentation.
Pleaseletusknowhowwecouldmakeitbetter.
Todoso:Forsimplecommentsonspecificpassages:1.
MakesureyouareviewingthedocumentationintheMulti-pageHTMLformat.
Inaddition,ensureyouseetheFeedbackbuttonintheupperrightcornerofthedocument.
2.
Useyourmousecursortohighlightthepartoftextthatyouwanttocommenton.
3.
ClicktheAddFeedbackpop-upthatappearsbelowthehighlightedtext.
4.
Followthedisplayedinstructions.
Forsubmittingmorecomplexfeedback,createaBugzillaticket:1.
GototheBugzillawebsite.
2.
AstheComponent,useDocumentation.
3.
FillintheDescriptionfieldwithyoursuggestionforimprovement.
Includealinktotherelevantpart(s)ofdocumentation.
4.
ClickSubmitBug.
PROVIDINGFEEDBACKONREDHATDOCUMENTATION5CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHELThefollowingsectionsprovideanoverviewoftheoptionsforidentitymanagement(IdM)andaccesscontrolinRedHatEnterpriseLinux.
Afterreadingthesesections,youwillbeabletoapproachtheplanningstageforyourenvironment.
1.
1.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMThismoduleexplainsthepurposeofIdentityManagement(IdM)inRedHatEnterpriseLinux.
ItalsoprovidesbasicinformationabouttheIdMdomain,includingtheclientandservermachinesthatarepartofthedomain.
ThegoalofIdMinRedHatEnterpriseLinuxIdMinRedHatEnterpriseLinuxprovidesacentralizedandunifiedwaytomanageidentitystores,authentication,policies,andauthorizationpoliciesinaLinux-baseddomain.
IdMsignificantlyreducestheadministrativeoverheadofmanagingdifferentservicesindividuallyandusingdifferenttoolsondifferentmachines.
IdMisoneofthefewcentralizedidentity,policy,andauthorizationsoftwaresolutionsthatsupport:AdvancedfeaturesofLinuxoperatingsystemenvironmentsUnifyinglargegroupsofLinuxmachinesNativeintegrationwithActiveDirectoryIdMcreatesaLinux-basedandLinux-controlleddomain:IdMbuildsonexisting,nativeLinuxtoolsandprotocols.
Ithasitsownprocessesandconfiguration,butitsunderlyingtechnologiesarewell-establishedonLinuxsystemsandtrustedbyLinuxadministrators.
IdMserversandclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxmachines.
IdMclientscanalsobeotherLinuxandUNIXdistributionsiftheysupportstandardprotocols.
WindowsclientcannotbeamemberoftheIdMdomainbutuserloggedintoWindowssystemsmanagedbyActiveDirectory(AD)canconnecttoLinuxclientsoraccessservicesmanagedbyIdM.
ThisisaccomplishedbyestablishingcrossforesttrustbetweenADandIdMdomains.
ManagingidentitiesandpoliciesonmultipleLinuxserversWithoutIdM:Eachserverisadministeredseparately.
Allpasswordsaresavedonthelocalmachines.
TheITadministratormanagesusersoneverymachine,setsauthenticationandauthorizationpoliciesseparately,andmaintainslocalpasswords.
However,moreoftentheusersrelyonothercentralizedsolution,forexampledirectintegrationwithAD.
SystemscanbedirectlyintegratedwithADusingseveraldifferentsolutions:LegacyLinuxtools(notrecommendedtouse)SolutionbasedonSambawinbind(recommendedforspecificusecases)Solutionbasedonathird-partysoftware(usuallyrequirealicensefromanothervendor)SolutionbasedonSSSD(nativeLinuxandrecommendedforthemajorityofusecases)RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement6WithIdM:TheITadministratorcan:Maintaintheidentitiesinonecentralplace:theIdMserverApplypoliciesuniformlytomultiplesofmachinesatthesametimeSetdifferentaccesslevelsforusersbyusinghost-basedaccesscontrol,delegation,andotherrulesCentrallymanageprivilegeescalationrulesDefinehowhomedirectoriesaremountedEnterpriseSSOIncaseofIdMEnterprise,singlesign-on(SSO)isimplementedleveragingtheKerberosprotocol.
ThisprotocolispopularintheinfrastructurelevelandenablesSSOwithservicessuchasSSH,LDAP,NFS,CUPS,orDNS.
Webservicesusingdifferentwebstacks(Apache,EAP,Django,andothers)canalsobeenabledtouseKerberosforSSO.
However,practiceshowsthatusingOpenIDConnectorSAMLbasedonSSOismoreconvenientforwebapplications.
Tobridgethetwolayers,itisrecommendedtodeployanIdentityProvider(IdP)solutionthatwouldbeabletoconvertKerberosauthenticationintoaOpenIDConnectticketorSAMLassertion.
RedHatSSOtechnologybasedontheKeycloakopensourceprojectisanexampleofsuchanIdPWithoutIdM:Userslogintothesystemandarepromptedforapasswordeverysingletimetheyaccessaserviceorapplication.
Thesepasswordsmightbedifferent,andtheusershavetorememberwhichcredentialtouseforwhichapplication.
WithIdm:Afteruserslogintothesystem,theycanaccessmultipleservicesandapplicationswithoutbeingrepeatedlyaskedfortheircredentials.
Thishelpsto:ImproveusabilityReducethesecurityriskofpasswordsbeingwrittendownorstoredinsecurelyBoostuserproductivityManagingamixedLinuxandWindowsenvironmentWithoutIdM:WindowssystemsaremanagedinanADforest,butdevelopment,production,andotherteamshavemanyLinuxsystems.
TheLinuxsystemsareexcludedfromtheADenvironment.
WithIdM:TheITadministratorcan:ManagetheLinuxsystemsusingnativeLinuxtoolsIntegratetheLinuxsystemsintotheenvironmentscentrallymanagedbyActiveDirectory,thuspreservingacentralizeduserstore.
EasilydeploynewLinuxsystemsatscaleorasneeded.
QuicklyreacttobusinessneedsandmakedecisionsrelatedtomanagementoftheLinuxinfrastructurewithoutdependencyonotherteamsavoidingdelays.
ContrastingIdMwithaStandardLDAPDirectoryAstandardLDAPdirectory,suchasRedHatDirectoryServer,isageneral-purposedirectory:itcanbecustomizedtofitabroadrangeofusecases.
Schema:aflexibleschemathatcanbecustomizedforavastarrayofentries,suchasusers,CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL7Schema:aflexibleschemathatcanbecustomizedforavastarrayofentries,suchasusers,machines,networkentities,physicalequipment,orbuildings.
Typicallyusedas:aback-enddirectorytostoredataforotherapplications,suchasbusinessapplicationsthatprovideservicesontheInternet.
IdMhasaspecificpurpose:managinginternal,inside-the-enterpriseidentitiesaswellasauthenticationandauthorizationpoliciesthatrelatetotheseidentities.
Schema:aspecificschemathatdefinesaparticularsetofentriesrelevanttoitspurpose,suchasentriesforuserormachineidentities.
Typicallyusedas:theidentityandauthenticationservertomanageidentitieswithintheboundariesofanenterpriseoraproject.
TheunderlyingdirectoryservertechnologyisthesameforbothRedHatDirectoryServerandIdM.
However,IdMisoptimizedtomanageidentitiesinsidetheenterprise.
Thislimitsitsgeneralextensibility,butalsobringscertainbenefits:simplerconfiguration,betterautomationofresourcemanagement,andincreasedefficiencyinmanagingenterpriseidentities.
AdditionalResourcesIdentityManagementorRedHatDirectoryServer–WhichOneShouldIUseontheRedHatEnterpriseLinuxBlog.
KnowledgeBasearticleaboutStandardprotocols.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8BetaReleaseNotes1.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTSTheIdentityManagement(IdM)domainincludesthefollowingtypesofsystems:IdMserversIdMserversareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsthatrespondtoidentity,authentication,andauthorizationrequestswithinanIdMdomain.
Inmostdeployments,anintegratedcertificateauthority(CA)isalsoinstalledwiththeIdMserver.
IdMserversarethecentralrepositoriesforidentityandpolicyinformation.
IdMserverscanalsohostanyoftheoptionalservicesusedbydomainmembers:Certificateauthority(CA)KeyRecoveryAuthority(KRA)DNSActiveDirectory(AD)trustcontrollerActiveDirectory(AD)trustagentThefirstserverinstalledtocreatethedomainistheIdMmasterormasterserver.
TheIdMmasterisnottobeconfusedwiththemasterCAserver:theycanrunontwodifferentmachines.
IdMclientsIdMclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsenrolledwiththeserversandconfiguredtousetheRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement8IdMclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsenrolledwiththeserversandconfiguredtousetheIdMservicesontheseservers.
ClientsinteractwiththeIdMserverstoaccessservicesprovidedbythem.
Forexample,clientsusetheKerberosprotocoltoperformauthenticationandacquireticketsforenterprisesinglesign-on(SSO),useLDAPtogetidentityandpolicyinfromation,useDNStodetectwheretheserversandservicesarelocatedandhowtoconnecttothem.
IdMserversarealsoembeddedIdMclients.
Asclientsenrolledwiththemselves,theserversprovidethesamefunctionalityasotherclients.
Toprovideservicesforlargenumbersofclients,aswellasforredundancyandavailability,IdMallowsdeploymentonmultipleIdMserversinasingledomain.
Itispossibletodeployupto60servers.
ThisisthemaximumnumberofIdMservers,alsocalledreplicas,thatiscurrentlysupportedintheIdMdomain.
IdMserversprovidedifferentservicesfortheclient.
Notalltheserversneedtoprovideallthepossibleservices.
SomeservercomponentslikeKerberosandLDAParealwaysavailableoneveryserver.
OtherserviceslikeCA,DNS,TrustControllerorVaultareoptional.
Thismeansthatdifferentserversingeneralplaydifferentrolesinthedeployment.
IfyourIdMtopologycontainsanintegratedCA,oneserveralsohastheroleoftheCertificaterevocationlist(CRL)generationmasterandtheCArenewalmaster.
ThisserveristhemasterCA.
WARNINGThemasterCAserveriscriticalforyourIdMdeploymentbecauseitistheonlysysteminthedomainresponsiblefortrackingCAsubsystemcertificatesandkeys,andforgeneratingtheCRL.
FordetailsabouthowtorecoverfromadisasteraffectingyourIdMdeployment,seePerformingdisasterrecoverywithIdentityManagement.
Forredundancyandloadbalancing,administratorscreateadditionalserversbycreatingareplicaofanyexistingserver,eitherthemasterserveroranotherreplica.
Whencreatingareplica,IdMclonestheconfigurationoftheexistingserver.
Areplicashareswiththeinitialserveritscoreconfiguration,includinginternalinformationaboutusers,systems,certificates,andconfiguredpolicies.
NOTEAreplicaandtheserveritwascreatedfromarefunctionallyidenticalexceptfortheroleoftheCRLgenerationmaster.
Therefore,thetermserverandreplicaareusedinterchangeablyheredependingonthecontext.
1.
3.
IDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL:CENTRALVS.
LOCALInRedHatEnterpriseLinux,youcanmanageidentitiesandaccesscontrolpoliciesusingcentralizedtoolsforawholedomainofsystems,orusinglocaltoolsforasinglesystem.
ManagingidentitiesandpoliciesonmultipleRedHatEnterpriseLinuxservers:WithandwithoutIdMWithIdentityManagementIdM,theITadministratorcan:CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL9Maintaintheidentitiesandgroupingmechanismsinonecentralplace:theIdMserverCentrallymanagedifferenttypesofcredentialssuchaspasswords,PKIcertificates,OTPtokens,orSSHkeysApplypoliciesuniformlytomultiplesofmachinesatthesametimeManagePOSIXandotherattributesforexternalActiveDirectoryusersSetdifferentaccesslevelsforusersbyusinghost-basedaccesscontrol,delegation,andotherrulesCentrallymanageprivilegeescalationrules(sudo)andmandatoryaccesscontrol(SELinuxusermapping)MaintaincentralPKIinfrastructureandsecretsstoreDefinehowhomedirectoriesaremountedWithoutIdM:Eachserverisadministeredseparately.
Allpasswordsaresavedonthelocalmachines.
TheITadministratormanagesusersoneverymachine,setsauthenticationandauthorizationpoliciesseparately,andmaintainslocalpasswords.
1.
4.
IDMTERMINOLOGYActiveDirectoryforestAnActiveDirectory(AD)forestisasetofoneormoredomaintreeswhichshareacommonglobalcatalog,directoryschema,logicalstructure,anddirectoryconfiguration.
Theforestrepresentsthesecurityboundarywithinwhichusers,computers,groups,andotherobjectsareaccessible.
Formoreinformation,seetheMicrosoftdocumentonForests.
ActiveDirectoryglobalcatalogTheglobalcatalogisafeatureofActiveDirectory(AD)thatallowsadomaincontrollertoprovideinformationonanyobjectintheforest,regardlessofwhethertheobjectisamemberofthedomaincontroller'sdomain.
Domaincontrollerswiththeglobalcatalogfeatureenabledarereferredtoasglobalcatalogservers.
Theglobalcatalogprovidesasearchablecatalogofallobjectsineverydomaininamulti-domainActiveDirectoryDomainServices(ADDS).
ActiveDirectorysecurityidentifierAsecurityidentifier(SID)isauniqueIDnumberassignedtoanobjectinActiveDirectory,suchasauser,group,orhost.
ItisthefunctionalequivalentofUIDsandGIDsinLinux.
AnsibleplayAnsibleplaysarethebuildingblocksofAnsibleplaybooks.
Thegoalofaplayistomapagroupofhoststosomewell-definedroles,representedbyAnsibletasks.
AnsibleplaybookAnAnsibleplaybookisafilethatcontainsoneormoreAnsibleplays.
Formoreinformation,seetheofficialAnsibledocumentationaboutplaybooks.
AnsibletaskAnsibletasksareunitsofactioninAnsible.
AnAnsibleplaycancontainmultipletasks.
ThegoalofRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement10eachtaskistoexecuteamodule,withveryspecificarguments.
AnAnsibletaskisasetofinstructionstoachieveastatedefined,initsbroadterms,byaspecificAnsibleroleormodule,andfine-tunedbythevariablesofthatroleormodule.
Formoreinformation,seetheofficialAnsibletasksdocumentation.
CertificateAcertificateisanelectronicdocumentusedtoidentifyanindividual,aserver,acompany,orotherentityandtoassociatethatidentitywithapublickey.
Suchasadriver'slicenseorpassport,acertificateprovidesgenerallyrecognizedproofofaperson'sidentity.
Public-keycryptographyusescertificatestoaddresstheproblemofimpersonation.
CertificateAuthorities(CA)inIdMAnentitythatissuesdigitalcertificates.
InRedHatIdentityManagement,theprimaryCAisipa,theIdMCA.
TheipaCAcertificateisoneofthefollowingtypes:Self-signed.
Inthiscase,theipaCAistherootCA.
Externallysigned.
Inthiscase,theipaCAissubordinatedtotheexternalCA.
InIdM,youcanalsocreatemultiplesub-CAs.
Sub-CAsareIdMCAswhosecertificatesareoneofthefollowingtypes:SignedbytheipaCA.
SignedbyanyoftheintermediateCAsbetweenitselfandipaCA.
Thecertificateofasub-CAcannotbeself-signed.
Cross-foresttrustAtrustestablishesanaccessrelationshipbetweentwoKerberosrealms,allowingusersandservicesinonedomaintoaccessresourcesinanotherdomain.
Withacross-foresttrustbetweenanActiveDirectory(AD)forestrootdomainandanIdMdomain,usersfromtheADforestdomainscaninteractwithLinuxmachinesandservicesfromtheIdMdomain.
FromtheperspectiveofAD,IdentityManagementrepresentsaseparateADforestwithasingleADdomain.
Formoreinformation,seeHowthetrustworks.
DNSPTRrecordsDNSpointer(PTR)recordsresolveanIPaddressofahosttoadomainorhostname.
PTRrecordsaretheoppositeofDNSAandAAAArecords,whichresolvehostnamestoIPaddresses.
DNSPTRrecordsenablereverseDNSlookups.
PTRrecordsarestoredontheDNSserver.
DNSSRVrecordsADNSservice(SRV)recorddefinesthehostname,portnumber,transportprotocol,priorityandweightofaserviceavailableinadomain.
YoucanuseSRVrecordstolocateIdMserversandreplicas.
DomainController(DC)Adomaincontroller(DC)isahostthatrespondstosecurityauthenticationrequestswithinadomainandcontrolsaccesstoresourcesinthatdomain.
IdMserversworkasDCsfortheIdMdomain.
ADCauthenticatesusers,storesuseraccountinformationandenforcessecuritypolicyforadomain.
Whenauserlogsintoadomain,theDCauthenticatesandvalidatestheircredentialsandeitherallowsordeniesaccess.
FullyqualifieddomainnameAfullyqualifieddomainname(FQDN)isadomainnamethatspecifiestheexactlocationofahostwithinthehierarchyoftheDomainNameSystem(DNS).
Adevicewiththehostnamemyhostintheparentdomainexample.
comhastheFQDNmyhost.
example.
com.
TheFQDNuniquelydistinguishesthedevicefromanyotherhostscalledmyhostinotherdomains.
CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL11IfyouareinstallinganIdMclientonhostmachine1usingDNSautodiscoveryandyourDNSrecordsarecorrectlyconfigured,theFQDNofmachine1isallyouneed.
Formoreinformation,seeHostnameandDNSrequirementsforIdM.
HiddenreplicaAhiddenreplicaisanIdMreplicathathasallservicesrunningandavailable,butitsserverrolesaredisabled,andclientscannotdiscoverthereplicabecauseithasnoSRVrecordsinDNS.
Hiddenreplicasareprimarilydesignedforservicessuchasbackups,bulkimportingandexporting,oractionsthatrequireshuttingdownIdMservices.
Sincenoclientsuseahiddenreplica,administratorscantemporarilyshutdowntheservicesonthishostwithoutaffectinganyclients.
Formoreinformation,seeThehiddenreplicamode.
IDrangesAnIDrangeisarangeofIDnumbersassignedtotheIdMtopologyoraspecificreplica.
YoucanuseIDrangestospecifythevalidrangeofUIDsandGIDsfornewusers,hostsandgroups.
IDrangesareusedtoavoidIDnumberconflicts.
TherearetwodistincttypesofIDrangesinIdM:IdMIDrangeUsethisIDrangetodefinetheUIDsandGIDsforusersandgroupsinthewholeIdMtopology.
InstallingthefirstIdMmastercreatestheIdMIDrange.
YoucannotmodifytheIdMIDrangeaftercreatingit.
However,youcancreateanadditionalIdMIDrange,forexamplewhentheoriginalonenearsdepletion.
DistributedNumericAssignment(DNA)IDrangeUsethisIDrangetodefinetheUIDsandGIDsareplicauseswhencreatingnewusers.
AddinganewuserorhostentrytoanIdMreplicaforthefirsttimeassignsaDNAIDrangetothatreplica.
AnadministratorcanmodifytheDNAIDrange,butthenewdefinitionmustfitwithinanexistingIdMIDrange.
NotethattheIdMrangeandtheDNArangematch,buttheyarenotinterconnected.
Ifyouchangeonerange,ensureyouchangetheothertomatch.
Formoreinformation,seeIDranges.
IDviewsIDviewsenableyoutospecifynewvaluesforPOSIXuserorgroupattributes,andtodefineonwhichclienthostorhoststhenewvalueswillapply.
Forexample,youcanuseIDviewsto:Definedifferentattributevaluesfordifferentenvironments.
Replaceapreviouslygeneratedattributevaluewithadifferentvalue.
InanIdM-ADtrustsetup,theDefaultTrustViewisanIDviewappliedtoADusersandgroups.
UsingtheDefaultTrustView,youcandefinecustomPOSIXattributesforADusersandgroups,thusoverridingthevaluesdefinedinAD.
Formoreinformation,seeUsinganIDviewtooverrideauserattributevalueonanIdMclient.
IdMCAserverAnIdMserveronwhichtheIdMcertificateauthority(CA)serviceisinstalledandrunning.
Alternativenames:CAserverIdMdeploymentAtermthatreferstotheentiretyofyourIdMinstallation.
YoucandescribeyourIdMdeploymentbyRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement12AtermthatreferstotheentiretyofyourIdMinstallation.
YoucandescribeyourIdMdeploymentbyansweringthefollowingquestions:IsyourIdMdeploymentatestingdeploymentorproductiondeploymentHowmanyIdMserversdoyouhaveDoesyourIdMdeploymentcontainanintegratedCAIfitdoes,istheintegratedCAself-signedorexternallysignedIfitdoes,onwhichserversistheCAroleavailableOnwhichserversistheKRAroleavailableDoesyourIdMdeploymentcontainanintegratedDNSIfitdoes,onwhichserversistheDNSroleavailableIsyourIdMdeploymentinatrustagreementwithanADforestIfitis,onwhichserversistheADtrustcontrollerorADtrustagentroleavailableIdMmasterandreplicasThefirstserverinstalledusingtheipa-server-installcommand,usedtocreatetheIdMdomain,isknownasthemasterserverorIdMmaster.
Administratorscanusetheipa-replica-installcommandtoinstallreplicasinadditiontothemaster.
Bydefault,installingareplicacreatesareplicationagreementwiththeIdMserverfromwhichitwascreated,enablingreceivingandsendingupdatestotherestofIdM.
Thereisnofunctionaldifferencebetweenamasterandareplica.
BotharefullyfunctionalIdMservers.
Alternativenames:master,masterserver,IdMmasterserverIdMmasterCAserverIfyourIdMtopologycontainsanintegratedcertificateauthority(CA),oneserverhastheroleoftheCertificaterevocationlist(CRL)generationmasterandtheCArenewalmaster.
ThisserveristhemasterCAserver.
InadeploymentwithoutintegratedCA,thereisnomasterCAserver.
Alternativenames:masterCAIMPORTANTIdMmasterandmasterCAserveraretwodifferentterms.
Forexample,inthefollowingdeploymentscenario,thefirstserveristheIdMmasterandthereplicaisthemasterCAserver:1.
YouinstallthefirstIdMserverinyourenvironmentwithoutintegratedCA.
2.
Youinstallareplica.
3.
YouinstallaCAonthereplica.
Inthisscenario,thefirstserveristheIdMmasterandthereplicaisthemasterCAserver.
CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL13IdMtopologyAtermthatreferstothestructureofyourIdMsolution,especiallythereplicationagreementsbetweenandwithinindividualdatacentersandclusters.
KerberosauthenticationindicatorsAuthenticationindicatorsareattachedtoKerberosticketsandrepresenttheinitialauthenticationmethodusedtoacquireaticket:otpfortwo-factorauthentication(password+One-TimePassword)radiusforRemoteAuthenticationDial-InUserService(RADIUS)authentication(commonlyfor802.
1xauthentication)pkinitforPublicKeyCryptographyforInitialAuthenticationinKerberos(PKINIT),smartcard,orcertificateauthenticationhardenedforpasswordshardenedagainstbrute-forceattemptsFormoreinformation,seeKerberosauthenticationindicators.
KerberoskeytabWhileapasswordisthedefaultauthenticationmethodforauser,keytabsarethedefaultauthenticationmethodforhostsandservices.
AKerberoskeytabisafilethatcontainsalistofKerberosprincipalsandtheirassociatedencryptionkeys,soaservicecanretrieveitsownKerberoskeyandverifyauser'sidentity.
Forexample,everyIdMclienthasan/etc/krb5.
keytabfilethatstoresinformationaboutthehostprincipal,whichrepresentstheclientmachineintheKerberosrealm.
KerberosprincipalUniqueKerberosprincipalsidentifyeachuser,service,andhostinaKerberosrealm:EntityNamingconventionExampleUsersidentifier@REALMadmin@EXAMPLE.
COMServicesservice/fully-qualified-hostname@REALMhttp/master.
example.
com@EXAMPLE.
COMHostshost/fully-qualified-hostname@REALMhost/client.
example.
com@EXAMPLE.
COMKerberosprotocolKerberosisanetworkauthenticationprotocolthatprovidesstrongauthenticationforclientandserverapplicationsbyusingsecret-keycryptography.
IdMandActiveDirectoryuseKerberosforauthenticatingusers,hostsandservices.
KerberosrealmAKerberosrealmencompassesalltheprincipalsmanagedbyaKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC).
InanIdMdeployment,theKerberosrealmincludesallIdMusers,hosts,andservices.
KerberosticketpoliciesTheKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC)enforcesticketaccesscontrolthroughconnectionpolicies,andmanagesthedurationofKerberosticketsthroughticketlifecyclepolicies.
Forexample,RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement14thedefaultglobalticketlifetimeisoneday,andthedefaultglobalmaximumrenewalageisoneweek.
Formoreinformation,seeIdMKerberosticketpolicytypes.
KeyDistributionCenter(KDC)TheKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC)isaservicethatactsasthecentral,trustedauthoritythatmanagesKerberoscredentialinformation.
TheKDCissuesKerberosticketsandensurestheauthenticityofdataoriginatingfromentitieswithintheIdMnetwork.
Formoreinformation,seeTheroleoftheIdMKDC.
Lightweightsub-CAInIdM,alightweightsub-CAisacertificateauthority(CA)whosecertificateissignedbyanIdMrootCAoroneoftheCAsthataresubordinatetoit.
Alightweightsub-CAissuescertificatesonlyforaspecificpurpose,forexampletosecureaVPNorHTTPconnection.
Formoreinformation,seeRestrictinganapplicationtotrustonlyasubsetofcertificates.
PasswordpolicyApasswordpolicyisasetofconditionsthatthepasswordsofaparticularIdMusergroupmustmeet.
Theconditionscanincludethefollowingparameters:ThelengthofthepasswordThenumberofcharacterclassesusedThemaximumlifetimeofapassword.
Formoreinformation,seeWhatisapasswordpolicy.
POSIXattributesPOSIXattributesareuserattributesformaintainingcompatibilitybetweenoperatingsystems.
InaRedHatIdentityManagementenvironment,POSIXattributesforusersinclude:cn,theuser'snameuid,theaccountname(login)uidNumber,ausernumber(UID)gidNumber,theprimarygroupnumber(GID)homeDirectory,theuser'shomedirectoryInaRedHatIdentityManagementenvironment,POSIXattributesforgroupsinclude:cn,thegroup'snamegidNumber,thegroupnumber(GID)Theseattributesidentifyusersandgroupsasseparateentities.
ReplicationagreementAreplicationagreementisanagreementbetweentwoIdMserversinthesameIdMdeployment.
Thereplicationagreementensuresthatthedataandconfigurationiscontinuouslyreplicatedbetweenthetwoservers.
IdMusestwotypesofreplicationagreements:domainreplicationagreements,whichreplicateidentityinformation,andcertificatereplicationagreements,whichreplicatecertificateinformation.
CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL15Formoreinformation,see:ReplicationagreementsDeterminingtheappropriatenumberofreplicasConnectingthereplicasinatopologyReplicatopologyexamplesSmartcardAsmartcardisaremovabledeviceorcardusedtocontrolaccesstoaresource.
Theycanbeplasticcreditcard-sizedcardswithanembeddedintegratedcircuit(IC)chip,smallUSBdevicessuchasaYubikey,orothersimilardevices.
Smartcardscanprovideauthenticationbyallowinguserstoconnectasmartcardtoahostcomputer,andsoftwareonthathostcomputerinteractswithkeymaterialstoredonthesmartcardtoauthenticatetheuser.
SSSDTheSystemSecurityServicesDaemon(SSSD)isasystemservicethatmanagesuserauthenticationanduserauthorizationonaRHELhost.
SSSDoptionallykeepsacacheofuseridentitiesandcredentialsretrievedfromremoteprovidersforofflineauthentication.
Formoreinformation,seeUnderstandingSSSDanditsbenefits.
SSSDbackendAnSSSDbackend,oftenalsocalledadataprovider,isanSSSDchildprocessthatmanagesandcreatestheSSSDcache.
ThisprocesscommunicateswithanLDAPserver,performsdifferentlookupqueriesandstorestheresultsinthecache.
ItalsoperformsonlineauthenticationagainstLDAPorKerberosandappliesaccessandpasswordpolicytotheuserthatisloggingin.
Ticket-grantingticket(TGT)AfterauthenticatingtoaKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC),auserreceivesaticket-grantingticket(TGT),whichisatemporarysetofcredentialsthatcanbeusedtorequestaccessticketstootherservices,suchaswebsitesandemail.
UsingaTGTtorequestfurtheraccessprovidestheuserwithaSingleSign-Onexperience,astheuseronlyneedstoauthenticateonceinordertoaccessmultipleservices.
TGTsarerenewable,andKerberosticketpoliciesdetermineticketrenewallimitsandaccesscontrol.
Formoreinformation,seeManagingKerberosticketpolicies.
AdditionalGlossariesIfyouareunabletofindanIdentityManagementterminthisglossary,seetheDirectoryServerandCertificateSystemglossaries:DirectoryServer11GlossaryCertificateSystem9Glossary1.
5.
ADDITIONALRESOURCESForgeneralinformationonRedHatIdM,seetheRedHatIdentityManagementproductpageontheRedHatCustomerPortal.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement16CHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGYThefollowingsectionsprovideadviceondeterminingtheappropriatereplicatopologyforyourusecase.
2.
1.
MULTIPLEREPLICASERVERSASASOLUTIONFORHIGHPERFORMANCEANDDISASTERRECOVERYContinuousfunctionalityandhighavailabilityofIdentityManagement(IdM)servicesisvitalforuserswhoaccessresources.
Oneofthebuilt-insolutionsforaccomplishingcontinuousfunctionalityandhighavailabilityoftheIdMinfrastructurethroughloadbalancingisthereplicationofthecentraldirectorybycreatingreplicaserversofthemasterserver.
IdMallowsplacingadditionalserversingeographicallydisperseddatacenterstoreflectyourenterpriseorganizationalstructure.
Inthisway,thepathbetweenIdMclientsandthenearestaccessibleserverisshortened.
Inaddition,havingmultipleserversallowsspreadingtheloadandscalingformoreclients.
MaintainingmultipleredundantIdMserversandlettingthemreplicatewitheachotherisalsoacommonbackupmechanismtomitigateorpreventserverloss.
Forexample,ifoneserverfails,theotherserverskeepprovidingservicestothedomain.
Youcanalsorecoverthelostserverbycreatinganewreplicabasedononeoftheremainingservers.
2.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTSTheIdentityManagement(IdM)domainincludesthefollowingtypesofsystems:IdMserversIdMserversareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsthatrespondtoidentity,authentication,andauthorizationrequestswithinanIdMdomain.
Inmostdeployments,anintegratedcertificateauthority(CA)isalsoinstalledwiththeIdMserver.
IdMserversarethecentralrepositoriesforidentityandpolicyinformation.
IdMserverscanalsohostanyoftheoptionalservicesusedbydomainmembers:Certificateauthority(CA)KeyRecoveryAuthority(KRA)DNSActiveDirectory(AD)trustcontrollerActiveDirectory(AD)trustagentThefirstserverinstalledtocreatethedomainistheIdMmasterormasterserver.
TheIdMmasterisnottobeconfusedwiththemasterCAserver:theycanrunontwodifferentmachines.
IdMclientsIdMclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsenrolledwiththeserversandconfiguredtousetheIdMservicesontheseservers.
ClientsinteractwiththeIdMserverstoaccessservicesprovidedbythem.
Forexample,clientsusetheKerberosprotocoltoperformauthenticationandacquireticketsforenterprisesinglesign-on(SSO),useLDAPtogetidentityandpolicyinfromation,useDNStodetectwheretheserversandservicesarelocatedandhowtoconnecttothem.
IdMserversarealsoembeddedIdMclients.
Asclientsenrolledwiththemselves,theserversprovideCHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY17IdMserversarealsoembeddedIdMclients.
Asclientsenrolledwiththemselves,theserversprovidethesamefunctionalityasotherclients.
Toprovideservicesforlargenumbersofclients,aswellasforredundancyandavailability,IdMallowsdeploymentonmultipleIdMserversinasingledomain.
Itispossibletodeployupto60servers.
ThisisthemaximumnumberofIdMservers,alsocalledreplicas,thatiscurrentlysupportedintheIdMdomain.
IdMserversprovidedifferentservicesfortheclient.
Notalltheserversneedtoprovideallthepossibleservices.
SomeservercomponentslikeKerberosandLDAParealwaysavailableoneveryserver.
OtherserviceslikeCA,DNS,TrustControllerorVaultareoptional.
Thismeansthatdifferentserversingeneralplaydifferentrolesinthedeployment.
IfyourIdMtopologycontainsanintegratedCA,oneserveralsohastheroleoftheCertificaterevocationlist(CRL)generationmasterandtheCArenewalmaster.
ThisserveristhemasterCA.
WARNINGThemasterCAserveriscriticalforyourIdMdeploymentbecauseitistheonlysysteminthedomainresponsiblefortrackingCAsubsystemcertificatesandkeys,andforgeneratingtheCRL.
FordetailsabouthowtorecoverfromadisasteraffectingyourIdMdeployment,seePerformingdisasterrecoverywithIdentityManagement.
Forredundancyandloadbalancing,administratorscreateadditionalserversbycreatingareplicaofanyexistingserver,eitherthemasterserveroranotherreplica.
Whencreatingareplica,IdMclonestheconfigurationoftheexistingserver.
Areplicashareswiththeinitialserveritscoreconfiguration,includinginternalinformationaboutusers,systems,certificates,andconfiguredpolicies.
NOTEAreplicaandtheserveritwascreatedfromarefunctionallyidenticalexceptfortheroleoftheCRLgenerationmaster.
Therefore,thetermserverandreplicaareusedinterchangeablyheredependingonthecontext.
2.
3.
REPLICATIONAGREEMENTSWhenanadministratorcreatesareplicabasedonanexistingserver,IdentityManagement(IdM)createsareplicationagreementbetweentheinitialserverandthereplica.
Thereplicationagreementensuresthatthedataandconfigurationiscontinuouslyreplicatedbetweenthetwoservers.
Replicationagreementsarealwaysbilateral:thedataisreplicatedfromoneservertotheotheraswellasfromtheotherservertothefirstserver.
IdMusesmulti-masterreplication.
Inmulti-masterreplication,allreplicasjoinedinareplicationagreementreceiveupdates,andarethereforeconsidereddatamasters.
Figure2.
1.
ServerandreplicaagreementsRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement18Figure2.
1.
ServerandreplicaagreementsIdMusestwotypesofreplicationagreements:DomainreplicationagreementsTheseagreementsreplicatetheidentityinformation.
CertificatereplicationagreementsTheseagreementsreplicatethecertificateinformation.
Bothreplicationchannelsareindependent.
Twoserverscanhaveoneorbothtypesofreplicationagreementsconfiguredbetweenthem.
Forexample,whenserverAandserverBhaveonlydomainreplicationagreementconfigured,onlyidentityinformationisreplicatedbetweenthem,notthecertificateinformation.
2.
4.
DETERMININGTHEAPPROPRIATENUMBEROFREPLICASSetupatleasttworeplicasineachdatacenter(notahardrequirement)Adatacentercanbe,forexample,amainofficeorageographicallocation.
SetupasufficientnumberofserverstoserveyourclientsOneIdentityManagement(IdM)servercanprovideservicesto2000-3000clients.
Thisassumestheclientsquerytheserversmultipletimesaday,butnot,forexample,everyminute.
Ifyouexpectmorefrequentqueries,planformoreservers.
Setupamaximumof60replicasinasingleIdMdomainRedHatguaranteestosupportenvironmentswith60replicasorfewer.
2.
5.
CONNECTINGTHEREPLICASINATOPOLOGYConnecteachreplicatoatleasttwootherreplicasConfiguringadditionalreplicationagreementsensuresthatinformationisreplicatednotjustbetweentheinitialreplicaandthemasterserver,butbetweenotherreplicasaswell.
Connectareplicatoamaximumoffourotherreplicas(notahardrequirement)Alargenumberofreplicationagreementsperserverdoesnotaddsignificantbenefits.
Areceivingreplicacanonlybeupdatedbyoneotherreplicaatatimeandmeanwhile,theotherreplicationagreementsareidle.
Morethanfourreplicationagreementsperreplicatypicallymeansawasteofresources.
NOTECHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY19NOTEThisrecommendationappliestobothcertificatereplicationanddomainreplicationagreements.
Therearetwoexceptionstothelimitoffourreplicationagreementsperreplica:Youwantfailoverpathsifcertainreplicasarenotonlineorresponding.
Inlargerdeployments,youwantadditionaldirectlinksbetweenspecificnodes.
Configuringahighnumberofreplicationagreementscanhaveanegativeimpactonoverallperformance:whenmultiplereplicationagreementsinthetopologyaresendingupdates,certainreplicascanexperienceahighcontentiononthechangelogdatabasefilebetweenincomingupdatesandtheoutgoingupdates.
Ifyoudecidetousemorereplicationagreementsperreplica,ensurethatyoudonotexperiencereplicationissuesandlatency.
However,notethatlargedistancesandhighnumbersofintermediatenodescanalsocauselatencyproblems.
ConnectthereplicasinadatacenterwitheachotherThisensuresdomainreplicationwithinthedatacenter.
ConnecteachdatacentertoatleasttwootherdatacentersThisensuresdomainreplicationbetweendatacenters.
ConnectdatacentersusingatleastapairofreplicationagreementsIfdatacentersAandBhaveareplicationagreementfromA1toB1,havingareplicationagreementfromA2toB2ensuresthatifoneoftheserversisdown,thereplicationcancontinuebetweenthetwodatacenters.
2.
6.
REPLICATOPOLOGYEXAMPLESThefiguresbelowshowexamplesofIdentityManagement(IdM)topologiesbasedontheguidelinesforcreatingareliabletopology.
Figure2.
2,"ReplicaTopologyExample1"showsfourdatacenters,eachwithfourservers.
Theserversareconnectedwithreplicationagreements.
Figure2.
2.
ReplicaTopologyExample1RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement20Figure2.
2.
ReplicaTopologyExample1Figure2.
3,"ReplicaTopologyExample2"showsthreedatacenters,eachwithadifferentnumberofservers.
Theserversareconnectedwithreplicationagreements.
Figure2.
3.
ReplicaTopologyExample2CHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY212.
7.
THEHIDDENREPLICAMODEBydefault,whenyousetupanewreplica,theinstallerautomaticallycreatesservice(SRV)resourcerecordsinDNS.
Theserecordsenableclientstoauto-discoverthereplicaanditsservices.
AhiddenreplicaisanIdMserverthathasallservicesrunningandavailable.
However,ithasnoSRVrecordsinDNS,andLDAPserverrolesarenotenabled.
Therefore,clientscannotuseservicediscoverytodetectthesehiddenreplicas.
NOTEThehiddenreplicafeatureisavailableinRedHatEnterpriseLinux8.
1andlaterasaTechnologyPreviewand,therefore,notsupported.
Hiddenreplicasareprimarilydesignedfordedicatedservicesthatcanotherwisedisruptclients.
Forexample,afullbackupofIdMrequirestoshutdownallIdMservicesonthemasterorreplica.
Sincenoclientsuseahiddenreplica,administratorscantemporarilyshutdowntheservicesonthishostwithoutaffectinganyclients.
NOTERestoringabackupfromahiddenreplicaonanewhostalwaysresultsinanon-hidden(regular)replica.
Allserverrolesusedinacluster,especiallytheCertificateAuthorityroleiftheintegratedCAisused,mustbeinstalledonthehiddenreplicaforthebackuptobeabletorestorethoseservices.
FormoreinformationoncreatingandworkingwithIdMbackups,seeBackingUpandRestoringIdM.
Otherusecasesincludehigh-loadoperationsontheIdMAPIortheLDAPserver,suchasamassimportorextensivequeries.
Toinstallareplicaashidden,passthe--hidden-replicaparametertotheipa-replica-installcommand.
Forfurtherdetailsaboutinstallingareplica,seeInstallinganIdentityManagementreplica.
Alternatively,youcanchangethestateofanexistingreplica.
Fordetails,seeDemotionandPromotionofHiddenReplicas.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement22CHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMESIdentityManagement(IdM)providesdifferenttypesofDNSconfigurationsintheIdMserver.
Thefollowingsectionsdescribethemandprovideadviceonhowtodeterminewhichisthebestforyourusecase.
3.
1.
DNSSERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVERYoucaninstallanIdentityManagement(IdM)serverwithorwithoutintegratedDNS.
Table3.
1.
ComparingIdMwithintegratedDNSandwithoutintegratedDNSWithintegratedDNSWithoutintegratedDNSOverview:IdMrunsitsownDNSservicefortheIdMdomain.
IdMusesDNSservicesprovidedbyanexternalDNSserver.
Limitations:TheintegratedDNSserverprovidedbyIdMonlysupportsfeaturesrelatedtoIdMdeploymentandmaintenance.
ItdoesnotsupportsomeoftheadvancedDNSfeatures.
Itisnotdesignedtobeusedasageneral-purposeDNSserver.
DNSisnotintegratedwithnativeIdMtools.
Forexample,IdMdoesnotupdatetheDNSrecordsautomaticallyafterachangeinthetopology.
Worksbestfor:BasicusagewithintheIdMdeployment.
WhentheIdMservermanagesDNS,DNSistightlyintegratedwithnativeIdMtools,whichenablesautomatingsomeoftheDNSrecordmanagementtasks.
EnvironmentswhereadvancedDNSfeaturesbeyondthescopeoftheIdMDNSareneeded.
Environmentswithawell-establishedDNSinfrastructurewhereyouwanttokeepusinganexternalDNSserver.
EvenifanIdentityManagementserverisusedasaprimaryDNSserver,otherexternalDNSserverscanstillbeusedassecondaryservers.
Forexample,ifyourenvironmentisalreadyusinganotherDNSserver,suchasaDNSserverintegratedwithActiveDirectory(AD),youcandelegateonlytheIdMprimarydomaintotheDNSintegratedwithIdM.
ItisnotnecessarytomigrateDNSzonestotheIdMDNS.
NOTEIfyouneedtoissuecertificatesforIdMclientswithanIPaddressintheSubjectAlternativeName(SAN)extension,youmustusetheIdMintegratedDNSservice.
3.
2.
GUIDELINESFORPLANNINGTHEDNSDOMAINNAMEANDKERBEROSREALMNAMEWheninstallingthefirstIdentityManagement(IdM)server,theinstallationpromptsforaprimaryDNSnameoftheIdMdomainandKerberosrealmname.
Theguidelinesinthissectioncanhelpyousetthenamescorrectly.
CHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMES23WARNINGYouwillnotbeabletochangetheIdMprimarydomainnameandKerberosrealmnameaftertheserverisalreadyinstalled.
Donotexpecttobeabletomovefromatestingenvironmenttoaproductionenvironmentbychangingthenames,forexamplefromlab.
example.
comtoproduction.
example.
com.
AseparateDNSdomainforservicerecordsEnsurethattheprimaryDNSdomainusedforIdMisnotsharedwithanyothersystem.
ThishelpsavoidconflictsontheDNSlevel.
ProperDNSdomainnamedelegationEnsureyouhavevaliddelegationinthepublicDNStreefortheDNSdomain.
Donotuseadomainnamethatisnotdelegatedtoyou,notevenonaprivatenetwork.
Multi-labelDNSdomainDonotusesingle-labeldomainnames,forexample.
company.
TheIdMdomainmustbecomposedofoneormoresubdomainsandatopleveldomain,forexampleexample.
comorcompany.
example.
com.
AuniqueKerberosrealmnameEnsuretherealmnameisnotinconflictwithanyotherexistingKerberosrealmname,suchasanameusedbyActiveDirectory(AD).
Kerberosrealmnameasanupper-caseversionoftheprimaryDNSnameConsidersettingtherealmnametoanupper-case(EXAMPLE.
COM)versionoftheprimaryDNSdomainname(example.
com).
WARNINGIfyoudonotsettheKerberosrealmnametobetheupper-caseversionoftheprimaryDNSname,youwillnotbeabletouseADtrusts.
AdditionalnotesonplanningtheDNSdomainnameandKerberosrealmnameOneIdMdeploymentalwaysrepresentsoneKerberosrealm.
YoucanjoinIdMclientsfrommultipledistinctDNSdomains(example.
com,example.
net,example.
org)toasingleKerberosrealm(EXAMPLE.
COM).
IdMclientsdonotneedtobeintheprimaryDNSdomain.
Forexample,iftheIdMdomainisidm.
example.
com,theclientscanbeintheclients.
example.
comdomain,butclearmappingmustbeconfiguredbetweentheDNSdomainandtheKerberosrealm.
NOTERedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement24NOTEThestandardmethodtocreatethemappingisusingthe_kerberosTXTDNSrecords.
TheIdMintegratedDNSaddstheserecordsautomatically.
CHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMES25CHAPTER4.
PLANNINGYOURCASERVICESIdentityManagement(IdM)inRedHatEnterpriseLinuxprovidesdifferenttypesofcertificateauthority(CA)configurations.
Thefollowingsectionsdescribedifferentscenariosandprovideadvicetohelpyoudeterminewhichconfigurationisbestforyourusecase.
4.
1.
CASERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVERYoucaninstallanIdentityManagement(IdM)serverwithanintegratedIdMcertificateauthority(CA)orwithoutaCA.
Table4.
1.
ComparingIdMwithintegratedCAandwithoutaCAIntegratedCAWithoutaCAOverview:IdMusesitsownpublickeyinfrastructure(PKI)servicewithaCAsigningcertificatetocreateandsignthecertificatesintheIdMdomain.
IftherootCAistheintegratedCA,IdMusesaself-signedCAcertificate.
IftherootCAisanexternalCA,theintegratedIdMCAissubordinatetotheexternalCA.
TheCAcertificateusedbyIdMissignedbytheexternalCA,butallcertificatesfortheIdMdomainareissuedbytheintegratedCertificateSysteminstance.
IntegratedCAisalsoabletoissuecertificatesforusers,hosts,orservices.
TheexternalCAcanbeacorporateCAorathird-partyCA.
IdMdoesnotsetupitsownCA,butusessignedhostcertificatesfromanexternalCA.
InstallingaserverwithoutaCArequiresyoutorequestthefollowingcertificatesfromathird-partyauthority:AnLDAPservercertificateAnApacheservercertificateAPKINITcertificateFullCAcertificatechainoftheCAthatissuedtheLDAPandApacheservercertificatesRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement26Limitations:IftheintegratedCAissubordinatetoanexternalCA,thecertificatesissuedwithintheIdMdomainarepotentiallysubjecttorestrictionssetbytheexternalCAforvariouscertificateattributes,suchas:Thevalidityperiod.
ConstraintsonwhatsubjectnamescanappearoncertificatesissuedbytheIDMCAoritssubordinates.
.
ConstraintsonwhethertheIDMCAcanitself,issuesubordinateCAcertificates,orhow"deep"thechainofsubordinatecertificatescango.
ManagingcertificatesoutsideofIdMcausesalotofadditionalactivities,suchas:Creating,uploading,andrenewingcertificatesisamanualprocess.
ThecertmongerservicedoesnottracktheIPAcertificates(LDAPserver,Apacheserver,andPKINITcertificates)anddoesnotnotifyyouwhenthecertificatesareabouttoexpire.
Theadministratorsmustmanuallysetupnotificationsforexternallyissuedcertificates,orsettrackingrequestsforthosecertificatesiftheywantcertmongertotrackthem.
Worksbestfor:Environmentsthatallowyoutocreateanduseyourowncertificateinfrastructure.
Veryrarecaseswhenrestrictionswithintheinfrastructuredonotallowyoutoinstallcertificateservicesintegratedwiththeserver.
IntegratedCAWithoutaCANOTESwitchingfromtheself-signedCAtoanexternally-signedCA,ortheotherwayaround,aswellaschangingwhichexternalCAissuestheIdMCAcertificate,ispossibleevenaftertheinstallation.
ItisalsopossibletoconfigureanintegratedCAevenafteraninstallationwithoutaCA.
4.
2.
CASUBJECTDNTheCertificateAuthority(CA)subjectdistinguishedname(DN)isthenameoftheCA.
ItmustbegloballyuniqueintheIdentityManagement(IdM)CAinfrastructureandcannotbechangedaftertheinstallation.
IncaseyouneedtheIdMCAtobeexternallysigned,youmightneedtoconsulttheadministratoroftheexternalCAabouttheformyourIdMCASubjectDNshouldtake.
4.
3.
GUIDELINESFORDISTRIBUTIONOFCASERVICESFollowingstepsprovideguidelinesforthedistributionofyourcertificateauthority(CA)services.
InstalltheCAservicesonmorethanoneserverinthetopologyReplicasconfiguredwithoutaCAforwardallcertificateoperationsrequeststotheCAserversinyourtopology.
CHAPTER4.
PLANNINGYOURCASERVICES27WARNINGIfyouloseallserverswithaCA,youwilllosealltheCAconfigurationwithoutanychanceofrecovery.
InsuchcaseyouneedtosetupnewCAandissueandinstallnewcertificates.
MaintainasufficientnumberofCAserverstohandletheCArequestsinyourdeploymentForrecommendationseethefollowingtable:Table4.
2.
GuidelinesforsettingupappropriatenumberofCAserversDescriptionofthedeploymentSuggestednumberofCAserversAdeploymentwithaverylargenumberofcertificatesissuedThreeorfourCAserversAdeploymentwithbandwidthoravailabilityproblemsbetweenmultipleregionsOneCAserverperregion,withaminimumofthreeserverstotalforthedeploymentAllotherdeploymentsTwoCAserversRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement28CHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHADThefollowingsectionsintroducetheoptionsforintegratingRedHatEnterpriseLinuxwithActiveDirectory(AD).
Foranoverviewofdirectintegration,seeSection5.
1,"Directintegration".
Foranoverviewofindirectintegration,seeSection5.
2,"Indirectintegration".
Foradviceonhowtodecidebetweenthem,seeSection5.
3,"Decidingbetweenindirectanddirectintegration".
5.
1.
DIRECTINTEGRATIONIndirectintegration,LinuxsystemsareconnecteddirectlytoActiveDirectory(AD).
Thefollowingtypesofintegrationarepossible:IntegrationwiththeSystemSecurityServicesDaemon(SSSD)SSSDcanconnectaLinuxsystemwithvariousidentityandauthenticationstores:AD,IdentityManagement(IdM),oragenericLDAPorKerberosserver.
NotablerequirementsforintegrationwithSSSD:WhenintegratingwithAD,SSSDworksonlywithinasingleADforestbydefault.
Formulti-forestsetup,configuremanualdomainenumeration.
RemoteADforestsmusttrustthelocalforesttoensurethattheidmap_adplug-inhandlesremoteforestuserscorrectly.
SSSDsupportsbothdirectandindirectintegration.
Italsoenablesswitchingfromoneintegrationapproachtotheotherwithoutsignificantmigrationcosts.
IntegrationwithSambaWinbindTheWinbindcomponentoftheSambasuiteemulatesaWindowsclientonaLinuxsystemandcommunicateswithADservers.
NotablerequirementsforintegrationwithSambaWinbind:DirectintegrationwithWinbindinamulti-forestADsetuprequiresbidirectionaltrusts.
AbidirectionalpathfromthelocaldomainofaLinuxsystemmustexisttothedomainofauserinaremoteADforesttoallowfullinformationabouttheuserfromtheremoteADdomaintobeavailabletotheidmap_adplug-in.
RecommendationsSSSDsatisfiesmostoftheusecasesforADintegrationandprovidesarobustsolutionasagenericgatewaybetweenaclientsystemanddifferenttypesofidentityandauthenticationproviders-AD,IdM,Kerberos,andLDAP.
WinbindisrecommendedfordeploymentonthoseADdomainmemberserversonwhichyouplantodeploySambaFS.
5.
2.
INDIRECTINTEGRATIONInindirectintegration,LinuxsystemsarefirstconnectedtoacentralserverwhichisthenconnectedtoCHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHAD29Inindirectintegration,LinuxsystemsarefirstconnectedtoacentralserverwhichisthenconnectedtoActiveDirectory(AD).
IndirectintegrationenablestheadministratortomanageLinuxsystemsandpoliciescentrally,whileusersfromADcantransparentlyaccessLinuxsystemsandservices.
Integrationbasedoncross-foresttrustwithADTheIdentityManagement(IdM)serveractsasthecentralservertocontrolLinuxsystems.
Across-realmKerberostrustwithADisestablished,enablingusersfromADtologontoaccessLinuxsystemsandresources.
IdMpresentsitselftoADasaseparateforestandtakesadvantageoftheforest-leveltrustssupportedbyAD.
Whenusingatrust:ADuserscanaccessIdMresources.
IdMserversandclientscanresolvetheidentitiesofADusersandgroups.
ADusersandgroupsaccessIdMundertheconditionsdefinedbyIdM,suchashost-basedaccesscontrol.
ADusersandgroupscontinuebeingmanagedontheADside.
IntegrationbasedonsynchronizationThisapproachisbasedontheWinSynctool.
AWinSyncreplicationagreementsynchronizesuseraccountsfromADtoIdM.
WARNINGWinSyncisnolongeractivelydevelopedinRedHatEnterpriseLinux8.
Thepreferredsolutionforindirectintegrationiscross-foresttrust.
Thelimitationsofintegrationbasedonsynchronizationinclude:GroupsarenotsynchronizedfromIdMtoAD.
UsersareduplicatedinADandIdM.
WinSyncsupportsonlyasingleADdomain.
OnlyonedomaincontrollerinADcanbeusedtosynchronizedatatooneinstanceofIdM.
Userpasswordsmustbesynchronized,whichrequiresthePassSynccomponenttobeinstalledonalldomaincontrollersintheADdomain.
Afterconfiguringthesynchronization,allADusersmustmanuallychangepasswordsbeforePassSynccansynchronizethem.
5.
3.
DECIDINGBETWEENINDIRECTANDDIRECTINTEGRATIONTheguidelinesinthissectioncanhelpdecidewhichtypeofintegrationfitsyourusecase.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement30NumberofsystemstobeconnectedtoActiveDirectoryConnectinglessthan30-50systems(notahardlimit)Ifyouconnectlessthan30-50systems,considerdirectintegration.
Indirectintegrationmightintroduceunnecessaryoverhead.
Connectingmorethan30-50systems(notahardlimit)Ifyouconnectmorethan30-50systems,considerindirectintegrationwithIdentityManagement.
Withthisapproach,youcanbenefitfromthecentralizedmanagementforLinuxsystems.
ManagingasmallnumberofLinuxsystems,butexpectingthenumbertogrowrapidlyInthisscenario,considerindirectintegrationtoavoidhavingtomigratetheenvironmentlater.
FrequencyofdeployingnewsystemsandtheirtypeDeployingbaremetalsystemsonanirregularbasisIfyoudeploynewsystemsrarelyandtheyareusuallybaremetalsystems,considerdirectintegration.
Insuchcases,directintegrationisusuallysimplestandeasiest.
DeployingvirtualsystemsfrequentlyIfyoudeploynewsystemsoftenandtheyareusuallyvirtualsystemsprovisionedondemand,considerindirectintegration.
Withindirectintegration,youcanuseacentralservertomanagethenewsystemsdynamicallyandintegratewithorchestrationtools,suchasRedHatSatellite.
ActiveDirectoryistherequiredauthenticationproviderDoyourinternalpoliciesstatethatallusersmustauthenticateagainstActiveDirectoryYoucanchooseeitherdirectorindirectintegration.
IfyouuseindirectintegrationwithatrustbetweenIdentityManagementandActiveDirectory,theusersthataccessLinuxsystemsauthenticateagainstActiveDirectory.
PoliciesthatexistinActiveDirectoryareexecutedandenforcedduringauthentication.
CHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHAD31CHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDADActiveDirectory(AD)andIdentityManagement(IdM)aretwoalternativeenvironmentsmanagingavarietyofcoreservices,suchasKerberos,LDAP,DNS,andcertificateservices.
Across-foresttrustrelationshiptransparentlyintegratesthesetwodiverseenvironmentsbyenablingallcoreservicestointeractseamlessly.
Thefollowingsectionsprovideadviceonhowtoplananddesignacross-foresttrustdeployment.
6.
1.
CROSS-FORESTTRUSTSBETWEENIDMANDADInapureActiveDirectory(AD)environment,across-foresttrustconnectstwoseparateADforestrootdomains.
Whenyoucreateacross-foresttrustbetweenADandIdM,theIdMdomainpresentsitselftoADasaseparateforestwithasingledomain.
AtrustrelationshipisthenestablishedbetweentheADforestrootdomainandtheIdMdomain.
Asaresult,usersfromtheADforestcanaccesstheresourcesintheIdMdomain.
IdMcanestablishatrustwithoneADforestormultipleunrelatedforests.
NOTETwoseparateKerberosrealmscanbeconnectedinacross-realmtrust.
However,aKerberosrealmonlyconcernsauthentication,nototherservicesandprotocolsinvolvedinidentityandauthorizationoperations.
Therefore,establishingaKerberoscross-realmtrustisnotenoughtoenableusersfromonerealmtoaccessresourcesinanotherrealm.
AnexternaltrusttoanADdomainAnexternaltrustisatrustrelationshipbetweenIdMandanActiveDirectorydomain.
WhileaforesttrustalwaysrequiresestablishingatrustbetweenIdMandtherootdomainofanActiveDirectoryforest,anexternaltrustcanbeestablishedfromIdMtoanydomainwithinaforest.
6.
2.
TRUSTCONTROLLERSANDTRUSTAGENTSIdentityManagement(IdM)providesthefollowingtypesofIdMserversthatsupporttrusttoActiveDirectory(AD):TrustagentsIdMserversthatcanperformidentitylookupsagainstADdomaincontrollers.
TrustcontrollersTrustagentsthatalsoruntheSambasuite.
ADdomaincontrollerscontacttrustcontrollerswhenestablishingandverifyingthetrusttoAD.
Thefirsttrustcontrolleriscreatedwhenyouconfigurethetrust.
Trustcontrollersrunmorenetwork-facingservicesthantrustagents,andthuspresentagreaterattacksurfaceforpotentialintruders.
Inadditiontotrustagentsandcontrollers,theIdMdomaincanalsoincludestandardIdMservers.
However,theseserversdonotcommunicatewithAD.
Therefore,clientsthatcommunicatewiththestandardserverscannotresolveADusersandgroupsorauthenticateandauthorizeADusers.
Table6.
1.
ComparingthecapabilitiessupportedbytrustcontrollersandtrustagentsRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement32CapabilityTrustagentTrustcontrollerResolveADusersandgroupsYesYesEnrollIdMclientsthatrunservicesaccessiblebyusersfromtrustedADforestsYesYesManagethetrust(forexample,addtrustagreements)NoYesWhenplanningthedeploymentoftrustcontrollersandtrustagents,considertheseguidelines:ConfigureatleasttwotrustcontrollersperIdMdeployment.
Configureatleasttwotrustcontrollersineachdatacenter.
Ifyoueverwanttocreateadditionaltrustcontrollersorifanexistingtrustcontrollerfails,createanewtrustcontrollerbypromotingatrustagentorastandardserver.
Todothis,usetheipa-adtrust-installutilityontheIdMserver.
IMPORTANTYoucannotdowngradeanexistingtrustcontrollertoatrustagent.
6.
3.
ONE-WAYTRUSTSANDTWO-WAYTRUSTSInonewaytrusts,IdentityManagement(IdM)trustsActiveDirectory(AD)butADdoesnottrustIdM.
ADuserscanaccessresourcesintheIdMdomainbutusersfromIdMcannotaccessresourceswithintheADdomain.
TheIdMserverconnectstoADusingaspecialaccount,andreadsidentityinformationthatisthendeliveredtoIdMclientsoverLDAP.
Intwowaytrusts,IdMuserscanauthenticatetoAD,andADuserscanauthenticatetoIdM.
ADuserscanauthenticatetoandaccessresourcesintheIdMdomainasintheonewaytrustcase.
IdMuserscanauthenticatebutcannotaccessmostoftheresourcesinAD.
TheycanonlyaccessthoseKerberizedservicesinADforeststhatdonotrequireanyaccesscontrolcheck.
TobeabletograntaccesstotheADresources,IdMneedstoimplementtheGlobalCatalogservice.
ThisservicedoesnotyetexistinthecurrentversionoftheIdMserver.
Becauseofthat,atwo-waytrustbetweenIdMandADisnearlyfunctionallyequivalenttoaone-waytrustbetweenIdMandAD.
6.
4.
NON-POSIXEXTERNALGROUPSANDSIDMAPPINGIdentityManagement(IdM)usesLDAPformanaginggroups.
ActiveDirectory(AD)entriesarenotsynchronizedorcopiedovertoIdM,whichmeansthatADusersandgroupshavenoLDAPobjectsintheLDAPserver,sotheycannotbedirectlyusedtoexpressgroupmembershipintheIdMLDAP.
Forthisreason,administratorsinIdMneedtocreatenon-POSIXexternalgroups,referencedasnormalIdMLDAPobjectstosignifygroupmembershipforADusersandgroupsinIdM.
SecurityIDs(SIDs)fornon-POSIXexternalgroupsareprocessedbySSSD,whichmapstheSIDsofgroupsinActiveDirectorytoPOSIXgroupsinIdM.
InActiveDirectory,SIDsareassociatedwithusernames.
WhenanADusernameisusedtoaccessIdMresources,SSSDusestheuser'sSIDtobuildupafullgroupmembershipinformationfortheuserintheIdMdomain.
CHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD336.
5.
SETTINGUPDNSTheseguidelinescanhelpyouachievetherightDNSconfigurationforestablishingacross-foresttrustbetweenIdentityManagement(IdM)andActiveDirectory(AD).
UniqueprimaryDNSdomainsEnsurebothADandIdMhavetheirownuniqueprimaryDNSdomainsconfigured.
Forexample:ad.
example.
comforADandidm.
example.
comforIdMexample.
comforADandidm.
example.
comforIdMThemostconvenientmanagementsolutionisanenvironmentwhereeachDNSdomainismanagedbyintegratedDNSservers,butyoucanalsouseanyotherstandard-compliantDNSserver.
NooverlapbetweenIdMandADDNSDomainsSystemsjoinedtoIdMcanbedistributedovermultipleDNSdomains.
EnsuretheDNSdomainsthatcontainIdMclientsdonotoverlapwithDNSdomainsthatcontainsystemsjoinedtoAD.
ProperSRVrecordsEnsuretheprimaryIdMDNSdomainhasproperSRVrecordstosupportADtrusts.
ForotherDNSdomainsthatarepartofthesameIdMrealm,theSRVrecordsdonothavetobeconfiguredwhenthetrusttoADisestablished.
ThereasonisthatADdomaincontrollersdonotuseSRVrecordstodiscoverKerberoskeydistributioncenters(KDCs)butratherbasetheKDCdiscoveryonnamesuffixroutinginformationforthetrust.
DNSrecordsresolvablefromallDNSdomainsinthetrustEnsureallmachinescanresolveDNSrecordsfromallDNSdomainsinvolvedinthetrustrelationship:WhenconfiguringtheIdMDNS,followtheinstructionsdescribedinInstallinganIdMserverwithanexternalCA.
IfyouareusingIdMwithoutintegratedDNS,followtheinstructionsdescribedinInstallinganIdMserverwithoutintegratedDNS.
Kerberosrealmnamesasupper-caseversionsofprimaryDNSdomainnamesEnsureKerberosrealmnamesarethesameastheprimaryDNSdomainnames,withalllettersuppercase.
Forexample,ifthedomainnamesaread.
example.
comforADandidm.
example.
comforIdM,theKerberosrealmnamesmustbeAD.
EXAMPLE.
COMandIDM.
EXAMPLE.
COM.
6.
6.
NETBIOSNAMESTheNetBIOSnameisusuallythefar-leftcomponentofthedomainname.
Forexample:Inthedomainnamelinux.
example.
com,theNetBIOSnameislinux.
Inthedomainnameexample.
com,theNetBIOSnameisexample.
DifferentNetBIOSnamesfortheIdentityManagement(IdM)andActiveDirectory(AD)domainsEnsuretheIdMandADdomainshavedifferentNetBIOSnames.
TheNetBIOSnameiscriticalforidentifyingtheADdomain.
IftheIdMdomainiswithinasubdomainoftheADDNS,theNetBIOSnameisalsocriticalforidentifyingtheIdMdomainandservices.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement34CharacterlimitforNetBIOSnamesThemaximumlengthofaNetBIOSnameis15characters.
6.
7.
SUPPORTEDVERSIONSOFWINDOWSSERVERYoucanestablishatrustrelationshipwithActiveDirectory(AD)foreststhatusethefollowingforestanddomainfunctionallevels:Forestfunctionallevelrange:WindowsServer2008—WindowsServer2016Domainfunctionallevelrange:WindowsServer2008—WindowsServer2016IdentityManagement(IdM)supportsthefollowingoperatingsystems:WindowsServer2008WindowsServer2008R2WindowsServer2012WindowsServer2012R2WindowsServer2016WindowsServer20196.
8.
CONFIGURINGADSERVERDISCOVERYANDAFFINITYServerdiscoveryandaffinityconfigurationaffectswhichActiveDirectory(AD)serversanIdentityManagement(IdM)clientcommunicateswith.
Thissectionprovidesanoverviewofhowdiscoveryandaffinityworkinanenvironmentwithacross-foresttrustbetweenIdMandAD.
Configuringclientstopreferserversinthesamegeographicallocationhelpspreventtimelagsandotherproblemsthatoccurwhenclientscontactserversfromanother,remotedatacenter.
Tomakesureclientscommunicatewithlocalservers,youmustensurethat:ClientscommunicatewithlocalIdMserversoverLDAPandoverKerberosClientscommunicatewithlocalADserversoverKerberosEmbeddedclientsonIdMserverscommunicatewithlocalADserversoverLDAPandoverKerberosOptionsforconfiguringLDAPandKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalIdMserversWhenusingIdMwithintegratedDNSBydefault,clientsuseautomaticservicelookupbasedontheDNSrecords.
Inthissetup,youcanalsousetheDNSlocationsfeaturetoconfigureDNS-basedservicediscovery.
Tooverridetheautomaticlookup,youcandisabletheDNSdiscoveryinoneofthefollowingways:DuringtheIdMclientinstallationbyprovidingfailoverparametersfromthecommandlineAftertheclientinstallationbymodifyingtheSystemSecurityServicesDaemon(SSSD)configurationCHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD35WhenusingIdMwithoutintegratedDNSYoumustexplicitlyconfigureclientsinoneofthefollowingways:DuringtheIdMclientinstallationbyprovidingfailoverparametersfromthecommandlineAftertheclientinstallationbymodifyingtheSSSDconfigurationOptionsforconfiguringKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalADserversIdMclientsareunabletoautomaticallydiscoverwhichADserverstocommunicatewith.
TospecifytheADserversmanually,modifythekrb5.
conffile:AddtheADrealminformationExplicitlylisttheADserverstocommunicatewithForexample:[realms]AD.
EXAMPLE.
COM={kdc=server1.
ad.
example.
comkdc=server2.
ad.
example.
com}OptionsforconfiguringembeddedclientsonIdMserversforcommunicationwithlocalADserversoverKerberosandLDAPTheembeddedclientonanIdMserverworksalsoasaclientoftheADserver.
ItcanautomaticallydiscoverandusetheappropriateADsite.
Whentheembeddedclientperformsthediscovery,itmightfirstdiscoveranADserverinaremotelocation.
Iftheattempttocontacttheremoteservertakestoolong,theclientmightstoptheoperationwithoutestablishingtheconnection.
Usethedns_resolver_timeoutoptioninthesssd.
conffileontheclienttoincreasetheamountoftimeforwhichtheclientwaitsforareplyfromtheDNSresolver.
Seethesssd.
conf(5)manpagefordetails.
OncetheembeddedclienthasbeenconfiguredtocommunicatewiththelocalADservers,theSSSDrememberstheADsitetheembeddedclientbelongsto.
Thankstothis,SSSDnormallysendsanLDAPpingdirectlytoalocaldomaincontrollertorefreshitssiteinformation.
Ifthesitenolongerexistsortheclienthasmeanwhilebeenassignedtoadifferentsite,SSSDstartsqueryingforSRVrecordsintheforestandgoesthroughawholeprocessofautodiscovery.
Usingtrusteddomainsectionsinsssd.
conf,youcanalsoexplicitlyoverridesomeoftheinformationthatisdiscoveredautomaticallybydefault.
6.
9.
OPERATIONSPERFORMEDDURINGINDIRECTINTEGRATIONOFIDMTOADTable6.
2,"OperationsperformedfromanIdMtrustcontrollertowardsADdomaincontrollers"showswhichoperationsandrequestsareperformedduringthecreationofanIdentityManagement(IdM)toActiveDirectory(AD)trustfromtheIdMtrustcontrollertowardsADdomaincontrollers.
Table6.
2.
OperationsperformedfromanIdMtrustcontrollertowardsADdomaincontrollersRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement36OperationProtocolusedPurposeDNSresolutionagainsttheADDNSresolversconfiguredonanIdMtrustcontrollerDNSTodiscovertheIPaddressesofADdomaincontrollersRequeststoUDP/UDP6port389onanADDCConnectionlessLDAP(CLDAP)ToperformADDCdiscoveryRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports389and3268onanADDCLDAPToqueryADuserandgroupinformationRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports389and3268onanADDCDCERPCandSMBTosetupandsupportcross-foresttrusttoADRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports135,139,445onanADDCDCERPCandSMBTosetupandsupportcross-foresttrusttoADRequeststodynamicallyopenedportsonanADDCasdirectedbytheActiveDirectorydomaincontroller,likelyintherangeof49152-65535(TCP/TCP6)DCERPCandSMBTorespondtorequestsbyDCERPCEnd-pointmapper(port135TCP/TCP6)Requeststoports88(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),464(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),and749(TCP/TCP6)onanADDCKerberosToobtainaKerberosticket;changeaKerberospassword;administerKerberosremotelyTable6.
3,"OperationsperformedfromanADdomaincontrollertowardsIdMtrustcontrollers"showswhichoperationsandrequestsareperformedduringthecreationofanIdMtoADtrustfromtheADdomaincontrollertowardsIdMtrustcontrollers.
Table6.
3.
OperationsperformedfromanADdomaincontrollertowardsIdMtrustcontrollersOperationProtocolusedPurposeDNSresolutionagainsttheIdMDNSresolversconfiguredonanADdomaincontrollerDNSTodiscovertheIPaddressesofIdMtrustcontrollersRequeststoUDP/UDP6port389onanIdMtrustcontrollerCLDAPToperformIdMtrustcontrollerdiscoveryRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports135,139,445onanIdMtrustcontrollerDCERPCandSMBToverifythecross-foresttrusttoADCHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD37RequeststodynamicallyopenedportsonanIdMtrustcontrollerasdirectedbytheIdMtrustcontroller,likelyintherangeof49152-65535(TCP/TCP6)DCERPCandSMBTorespondtorequestsbyDCERPCEnd-pointmapper(port135TCP/TCP6)Requeststoports88(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),464(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),and749(TCP/TCP6)onanIdMtrustcontrollerKerberosToobtainaKerberosticket;changeaKerberospassword;administerKerberosremotelyOperationProtocolusedPurposeRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement38CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDMRedHatEnterpriseLinuxIdentityManagementprovidesasolutiontomanuallybackupandrestoretheIdMsystem.
Thismaybenecessaryafteradatalossevent.
Duringbackup,thesystemcreatesadirectorycontaininginformationonyourIdMsetupandstoresit.
Duringrestore,youcanusethisbackupdirectorytobringyouroriginalIdMsetupback.
NOTETheIdMbackupandrestorefeaturesaredesignedtohelppreventdataloss.
Tomitigatetheimpactoflosingaserver,andensurecontinuedoperationbyprovidingalternativeserverstoclients,ensureyouhaveareplicatopologyaccordingtoMitigatingserverlosswithreplication.
7.
1.
IDMBACKUPTYPESIdMprovidestwotypesofbackups:afull-serverbackup,andadata-onlybackup.
BackuptypeBackupcontentsPerformedOnlineorOfflineSuitableforFull-serverbackupAllserverconfigurationfilesrelatedtoIdMLDAPdatainLDAPDataInterchangeFormat(LDIF)Offlineonly.
IdMservicesmustbetemporarilystopped.
RebuildinganIdMdeploymentfromscratchData-onlybackupLDAPdatainLDAPDataInterchangeFormat(LDIF)ReplicationChangelogOnlineorOffline.
RestoringIdMdatatoastateinthepast7.
2.
NAMINGCONVENTIONSFORIDMBACKUPFILESBydefault,IdMstoresbackupsinthe/var/lib/ipa/backup/directory,andthenamingconventionsforthesesubdirectoriesare:Full-serverbackup:ipa-full-YEAR-MM-DD-HH-MM-SSinGMTtimeData-onlybackup:ipa-data-YEAR-MM-DD-HH-MM-SSinGMTtimeNOTEUninstallinganIdMserverdoesnotautomaticallyremoveanybackupfiles.
CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM397.
3.
CREATINGABACKUPThissectiondescribeshowtocreateafull-serveranddata-onlybackupinofflineandonlinemodesusingtheipa-backupcommand.
IMPORTANTBydefault,ipa-backuprunsinofflinemode,whichwillstopallIdMservices.
Theserviceswillstartautomaticallyafterthebackupisfinished.
Afull-serverbackupmustalwaysrunwithIdMservicesoffline,butadata-onlybackupmaybeperformedwithservicesonline.
Bydefault,backupsarecreatedonthefilesystemcontainingthe/var/lib/ipa/backup/directory.
WerecommendcreatingbackupsregularlyonafilesystemseparatefromtheproductionfilesystemusedbyIdM,andarchivingthebackupstoafixedmedium(tapeoropticalstorage,forexample).
Considerperformingbackupsonhiddenreplicas.
IdMservicescanbeshutdownonhiddenreplicaswithoutaffectingIdMclients.
StartingwithRHEL8.
3.
0,theipa-backuputilitychecksifalloftheservicesusedinyourIdMcluster,suchasaCertificateAuthority(CA),DomainNameSystem(DNS),andKeyRecoveryAgent(KRA),areinstalledontheserverwhereyouarerunningthebackup.
Iftheserverdoesnothavealltheseservicesinstalled,theipa-backuputilityexitswithawarning,becausebackupstakenonthathostwouldnotbesufficientforafullclusterrestoration.
Forexample,ifyourIdMdeploymentusesanintegratedCertificateAuthority(CA),abackuprunonanon-CAreplicawillnotcaptureCAdata.
RedHatrecommendsverifyingthatthereplicawhereyouperformanipa-backuphasalloftheIdMservicesusedintheclusterinstalled.
YoucanbypasstheIdMserverrolecheckwiththeipa-backup--disable-role-checkcommand,buttheresultingbackupwillnotcontainallthedatanecessarytorestoreIdMfully.
Examplesofusingtheipa-backupcommandTocreateafull-serverbackupinofflinemode,usetheipa-backuputilitywithoutadditionaloptions.
[root@server~]#ipa-backupPreparingbackuponserver.
example.
comStoppingIPAservicesBackingupipacainEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupuserRootinEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupEXAMPLE-COMBackingupfilesStartingIPAserviceBackedupto/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-14-11-26-06Theipa-backupcommandwassuccessfulTocreateanofflinedata-onlybackup,specifythe--dataoption.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--dataRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement40Tocreateafull-serverbackupthatincludesIdMlogfiles,usethe--logsoption.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--logsTocreateadata-onlybackupwhileIdMservicesarerunning,specifyboth--dataand--onlineoptions.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--data--onlineNOTEIfthebackupfailsduetoinsufficientspaceinthe/tmpdirectory,usetheTMPDIRenvironmentvariabletochangethedestinationfortemporaryfilescreatedbythebackupprocess:[root@server~]#TMPDIR=/new/locationipa-backupFormoredetails,seeipa-backupCommandFailstoFinish.
VerificationStepsThebackupdirectorycontainsanarchivewiththebackup.
[root@server~]#ls/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-14-11-26-06headeripa-full.
tar7.
4.
CREATINGENCRYPTEDIDMBACKUPSYoucancreateencryptedbackupsusingGNUPrivacyGuard(GPG)encryption.
TocreateencryptedIdMbackups,youwillfirstneedtocreateaGPG2key.
7.
4.
1.
CreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackupsThefollowingproceduredescribeshowtogenerateaGPG2keyfortheipa-backuputility.
Procedure1.
Installandconfigurethepinentryutility.
[root@server~]#dnfinstallpinentry[root@server~]#mkdir~/.
gnupg-m700[root@server~]#echo"pinentry-program/usr/bin/pinentry-curses">>~/.
gnupg/gpg-agent.
conf2.
Createakey-inputfileusedforgeneratingaGPGkeypairwithyourpreferreddetails.
Forexample:[root@server~]#cat>key-inputb.
Confirmthecorrectpassphrasebyenteringitagain.
Pleasere-enterthispassphrasePassphrase:SecretPassphrase42c.
ThenewGPG2keyisnowcreated.
gpg:keybox'/root/backup/pubring.
kbx'createdgpg:Generatingastandardkeygpg:/root/backup/trustdb.
gpg:trustdbcreatedgpg:keyBF28FFA302EF4557markedasultimatelytrustedgpg:directory'/root/backup/openpgp-revocs.
d'createdgpg:revocationcertificatestoredas'/root/backup/openpgp-revocs.
d/8F6FCF10C80359D5A05AED67BF28FFA302EF4557.
rev'gpg:FinishedcreatingstandardkeyVerificationStepsRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement42VerificationStepsListtheGPGkeysontheserver.
[root@server~]#gpg2--list-secret-keysgpg:checkingthetrustdbgpg:marginalsneeded:3completesneeded:1trustmodel:pgpgpg:depth:0valid:1signed:0trust:0-,0q,0n,0m,0f,1u/root/backup/pubring.
kbxsecrsa20482020-01-13[SCEA]8F6FCF10C80359D5A05AED67BF28FFA302EF4557uid[ultimate]IPABackup(IPABackup)AdditionalresourcesFormoreinformationonGPGencryptionanditsuses,seetheGNUPrivacyGuardwebsite.
7.
4.
2.
CreatingaGPG2-encryptedIdMbackupThefollowingprocedurecreatesanIdMbackupandencryptsitusingaGPG2key.
PrerequisitesYouhavecreatedaGPG2key.
SeeCreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackups.
ProcedureCreateaGPG-encryptedbackupbyspecifyingthe--gpgoption.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--gpgPreparingbackuponserver.
example.
comStoppingIPAservicesBackingupipacainEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupuserRootinEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupEXAMPLE-COMBackingupfilesStartingIPAserviceEncrypting/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-13-14-38-00/ipa-full.
tarBackedupto/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-13-14-38-00Theipa-backupcommandwassuccessfulVerificationStepsEnsurethatthebackupdirectorycontainsanencryptedarchivewitha.
gpgfileextension.
[root@server~]#ls/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-13-14-38-00headeripa-full.
tar.
gpgAdditionalresourcesForgeneralinformationoncreatingabackup,seeCreatingabackup.
CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM437.
5.
WHENTORESTOREFROMANIDMBACKUPYoucanrespondtoseveraldisasterscenariosbyrestoringfromanIdMbackup:UndesirablechangesweremadetotheLDAPcontent:Entriesweremodifiedordeleted,replicationcarriedoutthosechangesthroughoutthedeployment,andyouwanttorevertthosechanges.
Restoringadata-onlybackupreturnstheLDAPentriestothepreviousstatewithoutaffectingtheIdMconfigurationitself.
TotalInfrastructureLoss,orlossofallCAinstances:IfadisasterdamagesallCertificateAuthorityreplicas,thedeploymenthaslosttheabilitytorebuilditselfbydeployingadditionalservers.
Inthissituation,restoreabackupofaCAReplicaandbuildnewreplicasfromit.
Anupgradeonanisolatedserverfailed:Theoperatingsystemremainsfunctional,buttheIdMdataiscorrupted,whichiswhyyouwanttorestoretheIdMsystemtoaknowngoodstate.
RedHatrecommendsworkingwithTechnicalSupportinordertodiagnoseandtroubleshoottheissue.
Ifthoseeffortsfail,restorefromafull-serverbackup.
IMPORTANTThepreferredsolutionforhardwareorupgradefailureistorebuildthelostserverfromareplica.
Formoreinformation,seeRecoveringfromserverlosswithreplication.
7.
6.
CONSIDERATIONSWHENRESTORINGFROMANIDMBACKUPIfyouhaveabackupcreatedwiththeipa-backuputility,youcanrestoreyourIdMserverortheLDAPcontenttothestatetheywereinwhenthebackupwasperformed.
ThefollowingarethekeyconsiderationswhilerestoringfromanIdMbackup:Youcanonlyrestoreabackuponaserverthatmatchestheconfigurationofserverwherethebackupwasoriginallycreated.
Theservermusthave:ThesamehostnameThesameIPaddressThesameversionofIdMsoftwareIfoneIdMserverinamulti-masterenvironmentisrestored,therestoredserverbecomestheonlysourceofinformationforIdM.
Allothermasterserversmustbere-initializedfromtherestoredserver.
Sinceanydatacreatedafterthelastbackupwillbelost,donotusethebackupandrestoresolutionfornormalsystemmaintenance.
Ifaserverislost,RedHatrecommendsrebuildingtheserverbyreinstallingitasareplicainsteadofrestoringfromabackup.
Creatinganewreplicapreservesdatafromthecurrentworkingenvironment.
Formoreinformation,seePreparingforserverlosswithreplication.
ThebackupandrestorefeaturescanonlybemanagedfromthecommandlineandarenotavailableintheIdMwebUI.
TIPRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement44TIPRestoringfromabackuprequiresthesamesoftware(RPM)versionsonthetargethostaswereinstalledwhenthebackupwasperformed.
Duetothis,RedHatrecommendsrestoringfromaVirtualMachinesnapshotratherthanabackup.
Formoreinformation,seeRecoveringfromdatalosswithVMsnapshots.
7.
7.
RESTORINGANIDMSERVERFROMABACKUPThefollowingproceduredescribesrestoringanIdMserver,oritsLDAPdata,fromanIdMbackup.
Figure7.
1.
ReplicationTopologyusedinthisexampleTable7.
1.
ServernamingconventionsusedinthisexampleServerNameFunctionmaster1.
example.
comTheserverthatneedstoberestoredfrombackupcaReplica2.
example.
comACertificateAuthority(CA)replicaconnectedtomaster1.
example.
com.
replica3.
example.
comAreplicaconnectedtocaReplica2.
example.
com.
PrerequisitesAfull-serverordata-onlybackupoftheIdMserverwasgeneratedwiththeipa-backuputility.
SeeCreatingabackup.
Beforeperformingafull-serverrestorefromafull-serverbackup,uninstallIdMfromtheserverandreinstallIdMusingthesameserverconfigurationasbefore.
Procedure1.
Usetheipa-restoreutilitytorestoreafull-serverordata-onlybackup.
Ifthebackupdirectoryisinthedefault/var/lib/ipa/backup/location,enteronlythenameofthedirectory:[root@master1~]#ipa-restoreipa-full-2020-01-14-12-02-32Ifthebackupdirectoryisnotinthedefaultlocation,enteritsfullpath:[root@master1~]#ipa-restore/mybackups/ipa-data-2020-02-01-05-30-00NOTECHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM45NOTETheipa-restoreutilityautomaticallydetectsthetypeofbackupthatthedirectorycontains,andperformsthesametypeofrestorebydefault.
Toperformadata-onlyrestorefromafull-serverbackup,addthe--dataoptiontoipa-restore:[root@master1~]#ipa-restore--dataipa-full-2020-01-14-12-02-322.
EntertheDirectoryManagerpassword.
DirectoryManager(existingmaster)password:3.
Enteryestoconfirmoverwritingcurrentdatawiththebackup.
Preparingrestorefrom/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-14-12-02-32onmaster1.
example.
comPerformingFULLrestorefromFULLbackupTemporarysettingumaskto022Restoringdatawilloverwriteexistinglivedata.
Continuetorestore[no]:yes4.
Theipa-restoreutilitydisablesreplicationonallserversthatareavailable:Eachmasterwillindividuallyneedtobere-initializedorre-createdfromthisone.
ThereplicationagreementsonmastersrunningIPA3.
1orearlierwillneedtobemanuallyre-enabled.
Seethemanpagefordetails.
Disablingallreplication.
Disablingreplicationagreementonmaster1.
example.
comtocaReplica2.
example.
comDisablingCAreplicationagreementonmaster1.
example.
comtocaReplica2.
example.
comDisablingreplicationagreementoncaReplica2.
example.
comtomaster1.
example.
comDisablingreplicationagreementoncaReplica2.
example.
comtoreplica3.
example.
comDisablingCAreplicationagreementoncaReplica2.
example.
comtomaster1.
example.
comDisablingreplicationagreementonreplica3.
example.
comtocaReplica2.
example.
comTheutilitythenstopsIdMservices,restoresthebackup,andrestartstheservices:StoppingIPAservicesSystemwideCAdatabaseupdated.
RestoringfilesSystemwideCAdatabaseupdated.
RestoringfromuserRootinEXAMPLE-COMRestoringfromipacainEXAMPLE-COMRestartingGSS-proxyStartingIPAservicesRestartingSSSDRestartingoddjobdRestoringumaskto18Theipa-restorecommandwassuccessful5.
Re-initializeallreplicasconnectedtotherestoredserver:a.
Listallreplicationtopologysegmentsforthedomainsuffix,takingnoteoftopologysegmentsinvolvingtherestoredserver.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement46[root@master1~]#ipatopologysegment-finddomain2segmentsmatchedSegmentname:master1.
example.
com-to-caReplica2.
example.
comLeftnode:master1.
example.
comRightnode:caReplica2.
example.
comConnectivity:bothSegmentname:caReplica2.
example.
com-to-replica3.
example.
comLeftnode:caReplica2.
example.
comRightnode:replica3.
example.
comConnectivity:bothNumberofentriesreturned2b.
Re-initializethedomainsuffixforalltopologysegmentswiththerestoredserver.
Inthisexample,performare-initializationofcaReplica2withdatafrommaster1.
[root@caReplica2~]#ipa-replica-managere-initialize--from=master1.
example.
comUpdateinprogress,2secondselapsedUpdatesucceededc.
MovingontoCertificateAuthoritydata,listallreplicationtopologysegmentsforthecasuffix.
[root@master1~]#ipatopologysegment-findca1segmentmatchedSegmentname:master1.
example.
com-to-caReplica2.
example.
comLeftnode:master1.
example.
comRightnode:caReplica2.
example.
comConnectivity:bothNumberofentriesreturned1d.
Re-initializeallCAreplicasconnectedtotherestoredserver.
Inthisexample,performacsreplicare-initializationofcaReplica2withdatafrommaster1.
[root@caReplica2~]#ipa-csreplica-managere-initialize--from=master1.
example.
comDirectoryManagerpassword:Updateinprogress,3secondselapsedUpdatesucceeded6.
Continuemovingoutwardthroughthereplicationtopology,re-initializingsuccessivereplicas,untilallservershavebeenupdatedwiththedatafromrestoredservermaster1.
example.
com.
Inthisexample,weonlyhavetore-initializethedomainsuffixonreplica3withthedatafromcaReplica2:CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM47[root@replica3~]#ipa-replica-managere-initialize--from=caReplica2.
example.
comDirectoryManagerpassword:Updateinprogress,3secondselapsedUpdatesucceeded7.
ClearSSSD'scacheoneveryserverinordertoavoidauthenticationproblemsduetoinvaliddata:a.
StoptheSSSDservice:[root@server~]#systemctlstopsssdb.
RemoveallcachedcontentfromSSSD:[root@server~]#sss_cache-Ec.
StarttheSSSDservice:[root@server~]#systemctlstartsssdd.
Reboottheserver.
AdditionalresourcesTheipa-restore(1)manpagealsocoversindetailhowtohandlecomplexreplicationscenariosduringrestoration.
7.
8.
RESTORINGFROMANENCRYPTEDBACKUPTheipa-restoreutilityautomaticallydetectsifanIdMbackupisencrypted,andrestoresitusingtheGPG2rootkeyringandgpg-agentbydefault.
PrerequisitesAGPG-encryptedIdMbackup.
SeeCreatingencryptedIdMbackups.
TheLDAPDirectoryManagerpasswordThePassphraseusedwhencreatingtheGPGkeyProcedure1.
IfyouusedacustomkeyringlocationwhencreatingtheGPG2keys,makesurethatthe$GNUPGHOMEenvironmentvariableissettothatdirectory.
SeeCreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackups.
[root@server~]#echo$GNUPGHOME/root/backup2.
Providetheipa-restoreutilitywiththebackupdirectorylocation.
[root@server~]#ipa-restoreipa-full-2020-01-13-18-30-54RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement48a.
EntertheDirectoryManagerpassword.
DirectoryManager(existingmaster)password:b.
EnterthePassphraseyouusedwhencreatingtheGPGkey.
PleaseenterthepassphrasetounlocktheOpenPGPsecretkey:"IPABackup(IPABackup)"2048-bitRSAkey,IDBF28FFA302EF4557,created2020-01-13.
Passphrase:SecretPassPhrase423.
Re-initializeallreplicasconnectedtotherestoredserver.
SeeRestoringanIdMserverfrombackup.
CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM49
ThetextofandillustrationsinthisdocumentarelicensedbyRedHatunderaCreativeCommonsAttribution–ShareAlike3.
0Unportedlicense("CC-BY-SA").
AnexplanationofCC-BY-SAisavailableathttp://creativecommons.
org/licenses/by-sa/3.
0/.
InaccordancewithCC-BY-SA,ifyoudistributethisdocumentoranadaptationofit,youmustprovidetheURLfortheoriginalversion.
RedHat,asthelicensorofthisdocument,waivestherighttoenforce,andagreesnottoassert,Section4dofCC-BY-SAtothefullestextentpermittedbyapplicablelaw.
RedHat,RedHatEnterpriseLinux,theShadowmanlogo,theRedHatlogo,JBoss,OpenShift,Fedora,theInfinitylogo,andRHCEaretrademarksofRedHat,Inc.
,registeredintheUnitedStatesandothercountries.
LinuxistheregisteredtrademarkofLinusTorvaldsintheUnitedStatesandothercountries.
JavaisaregisteredtrademarkofOracleand/oritsaffiliates.
XFSisatrademarkofSiliconGraphicsInternationalCorp.
oritssubsidiariesintheUnitedStatesand/orothercountries.
MySQLisaregisteredtrademarkofMySQLABintheUnitedStates,theEuropeanUnionandothercountries.
Node.
jsisanofficialtrademarkofJoyent.
RedHatisnotformallyrelatedtoorendorsedbytheofficialJoyentNode.
jsopensourceorcommercialproject.
TheOpenStackWordMarkandOpenStacklogoareeitherregisteredtrademarks/servicemarksortrademarks/servicemarksoftheOpenStackFoundation,intheUnitedStatesandothercountriesandareusedwiththeOpenStackFoundation'spermission.
Wearenotaffiliatedwith,endorsedorsponsoredbytheOpenStackFoundation,ortheOpenStackcommunity.
Allothertrademarksarethepropertyoftheirrespectiveowners.
AbstractThisdocumentdescribestheplanningofIdentityManagementservicesonRedHatEnterpriseLinux8.
Thecurrentversionofthedocumentcontainsonlyselectedpreviewuserstories.
TableofContentsMAKINGOPENSOURCEMOREINCLUSIVEPROVIDINGFEEDBACKONREDHATDOCUMENTATIONCHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL1.
1.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDM1.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTS1.
3.
IDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL:CENTRALVS.
LOCAL1.
4.
IDMTERMINOLOGY1.
5.
ADDITIONALRESOURCESCHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY2.
1.
MULTIPLEREPLICASERVERSASASOLUTIONFORHIGHPERFORMANCEANDDISASTERRECOVERY2.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTS2.
3.
REPLICATIONAGREEMENTS2.
4.
DETERMININGTHEAPPROPRIATENUMBEROFREPLICAS2.
5.
CONNECTINGTHEREPLICASINATOPOLOGY2.
6.
REPLICATOPOLOGYEXAMPLES2.
7.
THEHIDDENREPLICAMODECHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMES3.
1.
DNSSERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVER3.
2.
GUIDELINESFORPLANNINGTHEDNSDOMAINNAMEANDKERBEROSREALMNAMEAdditionalnotesonplanningtheDNSdomainnameandKerberosrealmnameCHAPTER4.
PLANNINGYOURCASERVICES4.
1.
CASERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVER4.
2.
CASUBJECTDN4.
3.
GUIDELINESFORDISTRIBUTIONOFCASERVICESCHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHAD5.
1.
DIRECTINTEGRATIONRecommendations5.
2.
INDIRECTINTEGRATION5.
3.
DECIDINGBETWEENINDIRECTANDDIRECTINTEGRATIONNumberofsystemstobeconnectedtoActiveDirectoryFrequencyofdeployingnewsystemsandtheirtypeActiveDirectoryistherequiredauthenticationproviderCHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD6.
1.
CROSS-FORESTTRUSTSBETWEENIDMANDADAnexternaltrusttoanADdomain6.
2.
TRUSTCONTROLLERSANDTRUSTAGENTS6.
3.
ONE-WAYTRUSTSANDTWO-WAYTRUSTS6.
4.
NON-POSIXEXTERNALGROUPSANDSIDMAPPING6.
5.
SETTINGUPDNS6.
6.
NETBIOSNAMES6.
7.
SUPPORTEDVERSIONSOFWINDOWSSERVER6.
8.
CONFIGURINGADSERVERDISCOVERYANDAFFINITYOptionsforconfiguringLDAPandKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalIdMserversOptionsforconfiguringKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalADserversOptionsforconfiguringembeddedclientsonIdMserversforcommunicationwithlocalADserversover4566891016171717181919202223232324262627272929292930313131323232323333343435353536TableofContents1KerberosandLDAP6.
9.
OPERATIONSPERFORMEDDURINGINDIRECTINTEGRATIONOFIDMTOADCHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM7.
1.
IDMBACKUPTYPES7.
2.
NAMINGCONVENTIONSFORIDMBACKUPFILES7.
3.
CREATINGABACKUP7.
4.
CREATINGENCRYPTEDIDMBACKUPS7.
4.
1.
CreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackups7.
4.
2.
CreatingaGPG2-encryptedIdMbackup7.
5.
WHENTORESTOREFROMANIDMBACKUP7.
6.
CONSIDERATIONSWHENRESTORINGFROMANIDMBACKUP7.
7.
RESTORINGANIDMSERVERFROMABACKUP7.
8.
RESTORINGFROMANENCRYPTEDBACKUP36363939394041414344444548RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement2TableofContents3MAKINGOPENSOURCEMOREINCLUSIVERedHatiscommittedtoreplacingproblematiclanguageinourcode,documentation,andwebproperties.
Wearebeginningwiththesefourterms:master,slave,blacklist,andwhitelist.
Becauseoftheenormityofthisendeavor,thesechangeswillbeimplementedgraduallyoverseveralupcomingreleases.
Formoredetails,seeourCTOChrisWright'smessage.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement4PROVIDINGFEEDBACKONREDHATDOCUMENTATIONWeappreciateyourinputonourdocumentation.
Pleaseletusknowhowwecouldmakeitbetter.
Todoso:Forsimplecommentsonspecificpassages:1.
MakesureyouareviewingthedocumentationintheMulti-pageHTMLformat.
Inaddition,ensureyouseetheFeedbackbuttonintheupperrightcornerofthedocument.
2.
Useyourmousecursortohighlightthepartoftextthatyouwanttocommenton.
3.
ClicktheAddFeedbackpop-upthatappearsbelowthehighlightedtext.
4.
Followthedisplayedinstructions.
Forsubmittingmorecomplexfeedback,createaBugzillaticket:1.
GototheBugzillawebsite.
2.
AstheComponent,useDocumentation.
3.
FillintheDescriptionfieldwithyoursuggestionforimprovement.
Includealinktotherelevantpart(s)ofdocumentation.
4.
ClickSubmitBug.
PROVIDINGFEEDBACKONREDHATDOCUMENTATION5CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHELThefollowingsectionsprovideanoverviewoftheoptionsforidentitymanagement(IdM)andaccesscontrolinRedHatEnterpriseLinux.
Afterreadingthesesections,youwillbeabletoapproachtheplanningstageforyourenvironment.
1.
1.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMThismoduleexplainsthepurposeofIdentityManagement(IdM)inRedHatEnterpriseLinux.
ItalsoprovidesbasicinformationabouttheIdMdomain,includingtheclientandservermachinesthatarepartofthedomain.
ThegoalofIdMinRedHatEnterpriseLinuxIdMinRedHatEnterpriseLinuxprovidesacentralizedandunifiedwaytomanageidentitystores,authentication,policies,andauthorizationpoliciesinaLinux-baseddomain.
IdMsignificantlyreducestheadministrativeoverheadofmanagingdifferentservicesindividuallyandusingdifferenttoolsondifferentmachines.
IdMisoneofthefewcentralizedidentity,policy,andauthorizationsoftwaresolutionsthatsupport:AdvancedfeaturesofLinuxoperatingsystemenvironmentsUnifyinglargegroupsofLinuxmachinesNativeintegrationwithActiveDirectoryIdMcreatesaLinux-basedandLinux-controlleddomain:IdMbuildsonexisting,nativeLinuxtoolsandprotocols.
Ithasitsownprocessesandconfiguration,butitsunderlyingtechnologiesarewell-establishedonLinuxsystemsandtrustedbyLinuxadministrators.
IdMserversandclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxmachines.
IdMclientscanalsobeotherLinuxandUNIXdistributionsiftheysupportstandardprotocols.
WindowsclientcannotbeamemberoftheIdMdomainbutuserloggedintoWindowssystemsmanagedbyActiveDirectory(AD)canconnecttoLinuxclientsoraccessservicesmanagedbyIdM.
ThisisaccomplishedbyestablishingcrossforesttrustbetweenADandIdMdomains.
ManagingidentitiesandpoliciesonmultipleLinuxserversWithoutIdM:Eachserverisadministeredseparately.
Allpasswordsaresavedonthelocalmachines.
TheITadministratormanagesusersoneverymachine,setsauthenticationandauthorizationpoliciesseparately,andmaintainslocalpasswords.
However,moreoftentheusersrelyonothercentralizedsolution,forexampledirectintegrationwithAD.
SystemscanbedirectlyintegratedwithADusingseveraldifferentsolutions:LegacyLinuxtools(notrecommendedtouse)SolutionbasedonSambawinbind(recommendedforspecificusecases)Solutionbasedonathird-partysoftware(usuallyrequirealicensefromanothervendor)SolutionbasedonSSSD(nativeLinuxandrecommendedforthemajorityofusecases)RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement6WithIdM:TheITadministratorcan:Maintaintheidentitiesinonecentralplace:theIdMserverApplypoliciesuniformlytomultiplesofmachinesatthesametimeSetdifferentaccesslevelsforusersbyusinghost-basedaccesscontrol,delegation,andotherrulesCentrallymanageprivilegeescalationrulesDefinehowhomedirectoriesaremountedEnterpriseSSOIncaseofIdMEnterprise,singlesign-on(SSO)isimplementedleveragingtheKerberosprotocol.
ThisprotocolispopularintheinfrastructurelevelandenablesSSOwithservicessuchasSSH,LDAP,NFS,CUPS,orDNS.
Webservicesusingdifferentwebstacks(Apache,EAP,Django,andothers)canalsobeenabledtouseKerberosforSSO.
However,practiceshowsthatusingOpenIDConnectorSAMLbasedonSSOismoreconvenientforwebapplications.
Tobridgethetwolayers,itisrecommendedtodeployanIdentityProvider(IdP)solutionthatwouldbeabletoconvertKerberosauthenticationintoaOpenIDConnectticketorSAMLassertion.
RedHatSSOtechnologybasedontheKeycloakopensourceprojectisanexampleofsuchanIdPWithoutIdM:Userslogintothesystemandarepromptedforapasswordeverysingletimetheyaccessaserviceorapplication.
Thesepasswordsmightbedifferent,andtheusershavetorememberwhichcredentialtouseforwhichapplication.
WithIdm:Afteruserslogintothesystem,theycanaccessmultipleservicesandapplicationswithoutbeingrepeatedlyaskedfortheircredentials.
Thishelpsto:ImproveusabilityReducethesecurityriskofpasswordsbeingwrittendownorstoredinsecurelyBoostuserproductivityManagingamixedLinuxandWindowsenvironmentWithoutIdM:WindowssystemsaremanagedinanADforest,butdevelopment,production,andotherteamshavemanyLinuxsystems.
TheLinuxsystemsareexcludedfromtheADenvironment.
WithIdM:TheITadministratorcan:ManagetheLinuxsystemsusingnativeLinuxtoolsIntegratetheLinuxsystemsintotheenvironmentscentrallymanagedbyActiveDirectory,thuspreservingacentralizeduserstore.
EasilydeploynewLinuxsystemsatscaleorasneeded.
QuicklyreacttobusinessneedsandmakedecisionsrelatedtomanagementoftheLinuxinfrastructurewithoutdependencyonotherteamsavoidingdelays.
ContrastingIdMwithaStandardLDAPDirectoryAstandardLDAPdirectory,suchasRedHatDirectoryServer,isageneral-purposedirectory:itcanbecustomizedtofitabroadrangeofusecases.
Schema:aflexibleschemathatcanbecustomizedforavastarrayofentries,suchasusers,CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL7Schema:aflexibleschemathatcanbecustomizedforavastarrayofentries,suchasusers,machines,networkentities,physicalequipment,orbuildings.
Typicallyusedas:aback-enddirectorytostoredataforotherapplications,suchasbusinessapplicationsthatprovideservicesontheInternet.
IdMhasaspecificpurpose:managinginternal,inside-the-enterpriseidentitiesaswellasauthenticationandauthorizationpoliciesthatrelatetotheseidentities.
Schema:aspecificschemathatdefinesaparticularsetofentriesrelevanttoitspurpose,suchasentriesforuserormachineidentities.
Typicallyusedas:theidentityandauthenticationservertomanageidentitieswithintheboundariesofanenterpriseoraproject.
TheunderlyingdirectoryservertechnologyisthesameforbothRedHatDirectoryServerandIdM.
However,IdMisoptimizedtomanageidentitiesinsidetheenterprise.
Thislimitsitsgeneralextensibility,butalsobringscertainbenefits:simplerconfiguration,betterautomationofresourcemanagement,andincreasedefficiencyinmanagingenterpriseidentities.
AdditionalResourcesIdentityManagementorRedHatDirectoryServer–WhichOneShouldIUseontheRedHatEnterpriseLinuxBlog.
KnowledgeBasearticleaboutStandardprotocols.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8BetaReleaseNotes1.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTSTheIdentityManagement(IdM)domainincludesthefollowingtypesofsystems:IdMserversIdMserversareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsthatrespondtoidentity,authentication,andauthorizationrequestswithinanIdMdomain.
Inmostdeployments,anintegratedcertificateauthority(CA)isalsoinstalledwiththeIdMserver.
IdMserversarethecentralrepositoriesforidentityandpolicyinformation.
IdMserverscanalsohostanyoftheoptionalservicesusedbydomainmembers:Certificateauthority(CA)KeyRecoveryAuthority(KRA)DNSActiveDirectory(AD)trustcontrollerActiveDirectory(AD)trustagentThefirstserverinstalledtocreatethedomainistheIdMmasterormasterserver.
TheIdMmasterisnottobeconfusedwiththemasterCAserver:theycanrunontwodifferentmachines.
IdMclientsIdMclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsenrolledwiththeserversandconfiguredtousetheRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement8IdMclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsenrolledwiththeserversandconfiguredtousetheIdMservicesontheseservers.
ClientsinteractwiththeIdMserverstoaccessservicesprovidedbythem.
Forexample,clientsusetheKerberosprotocoltoperformauthenticationandacquireticketsforenterprisesinglesign-on(SSO),useLDAPtogetidentityandpolicyinfromation,useDNStodetectwheretheserversandservicesarelocatedandhowtoconnecttothem.
IdMserversarealsoembeddedIdMclients.
Asclientsenrolledwiththemselves,theserversprovidethesamefunctionalityasotherclients.
Toprovideservicesforlargenumbersofclients,aswellasforredundancyandavailability,IdMallowsdeploymentonmultipleIdMserversinasingledomain.
Itispossibletodeployupto60servers.
ThisisthemaximumnumberofIdMservers,alsocalledreplicas,thatiscurrentlysupportedintheIdMdomain.
IdMserversprovidedifferentservicesfortheclient.
Notalltheserversneedtoprovideallthepossibleservices.
SomeservercomponentslikeKerberosandLDAParealwaysavailableoneveryserver.
OtherserviceslikeCA,DNS,TrustControllerorVaultareoptional.
Thismeansthatdifferentserversingeneralplaydifferentrolesinthedeployment.
IfyourIdMtopologycontainsanintegratedCA,oneserveralsohastheroleoftheCertificaterevocationlist(CRL)generationmasterandtheCArenewalmaster.
ThisserveristhemasterCA.
WARNINGThemasterCAserveriscriticalforyourIdMdeploymentbecauseitistheonlysysteminthedomainresponsiblefortrackingCAsubsystemcertificatesandkeys,andforgeneratingtheCRL.
FordetailsabouthowtorecoverfromadisasteraffectingyourIdMdeployment,seePerformingdisasterrecoverywithIdentityManagement.
Forredundancyandloadbalancing,administratorscreateadditionalserversbycreatingareplicaofanyexistingserver,eitherthemasterserveroranotherreplica.
Whencreatingareplica,IdMclonestheconfigurationoftheexistingserver.
Areplicashareswiththeinitialserveritscoreconfiguration,includinginternalinformationaboutusers,systems,certificates,andconfiguredpolicies.
NOTEAreplicaandtheserveritwascreatedfromarefunctionallyidenticalexceptfortheroleoftheCRLgenerationmaster.
Therefore,thetermserverandreplicaareusedinterchangeablyheredependingonthecontext.
1.
3.
IDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL:CENTRALVS.
LOCALInRedHatEnterpriseLinux,youcanmanageidentitiesandaccesscontrolpoliciesusingcentralizedtoolsforawholedomainofsystems,orusinglocaltoolsforasinglesystem.
ManagingidentitiesandpoliciesonmultipleRedHatEnterpriseLinuxservers:WithandwithoutIdMWithIdentityManagementIdM,theITadministratorcan:CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL9Maintaintheidentitiesandgroupingmechanismsinonecentralplace:theIdMserverCentrallymanagedifferenttypesofcredentialssuchaspasswords,PKIcertificates,OTPtokens,orSSHkeysApplypoliciesuniformlytomultiplesofmachinesatthesametimeManagePOSIXandotherattributesforexternalActiveDirectoryusersSetdifferentaccesslevelsforusersbyusinghost-basedaccesscontrol,delegation,andotherrulesCentrallymanageprivilegeescalationrules(sudo)andmandatoryaccesscontrol(SELinuxusermapping)MaintaincentralPKIinfrastructureandsecretsstoreDefinehowhomedirectoriesaremountedWithoutIdM:Eachserverisadministeredseparately.
Allpasswordsaresavedonthelocalmachines.
TheITadministratormanagesusersoneverymachine,setsauthenticationandauthorizationpoliciesseparately,andmaintainslocalpasswords.
1.
4.
IDMTERMINOLOGYActiveDirectoryforestAnActiveDirectory(AD)forestisasetofoneormoredomaintreeswhichshareacommonglobalcatalog,directoryschema,logicalstructure,anddirectoryconfiguration.
Theforestrepresentsthesecurityboundarywithinwhichusers,computers,groups,andotherobjectsareaccessible.
Formoreinformation,seetheMicrosoftdocumentonForests.
ActiveDirectoryglobalcatalogTheglobalcatalogisafeatureofActiveDirectory(AD)thatallowsadomaincontrollertoprovideinformationonanyobjectintheforest,regardlessofwhethertheobjectisamemberofthedomaincontroller'sdomain.
Domaincontrollerswiththeglobalcatalogfeatureenabledarereferredtoasglobalcatalogservers.
Theglobalcatalogprovidesasearchablecatalogofallobjectsineverydomaininamulti-domainActiveDirectoryDomainServices(ADDS).
ActiveDirectorysecurityidentifierAsecurityidentifier(SID)isauniqueIDnumberassignedtoanobjectinActiveDirectory,suchasauser,group,orhost.
ItisthefunctionalequivalentofUIDsandGIDsinLinux.
AnsibleplayAnsibleplaysarethebuildingblocksofAnsibleplaybooks.
Thegoalofaplayistomapagroupofhoststosomewell-definedroles,representedbyAnsibletasks.
AnsibleplaybookAnAnsibleplaybookisafilethatcontainsoneormoreAnsibleplays.
Formoreinformation,seetheofficialAnsibledocumentationaboutplaybooks.
AnsibletaskAnsibletasksareunitsofactioninAnsible.
AnAnsibleplaycancontainmultipletasks.
ThegoalofRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement10eachtaskistoexecuteamodule,withveryspecificarguments.
AnAnsibletaskisasetofinstructionstoachieveastatedefined,initsbroadterms,byaspecificAnsibleroleormodule,andfine-tunedbythevariablesofthatroleormodule.
Formoreinformation,seetheofficialAnsibletasksdocumentation.
CertificateAcertificateisanelectronicdocumentusedtoidentifyanindividual,aserver,acompany,orotherentityandtoassociatethatidentitywithapublickey.
Suchasadriver'slicenseorpassport,acertificateprovidesgenerallyrecognizedproofofaperson'sidentity.
Public-keycryptographyusescertificatestoaddresstheproblemofimpersonation.
CertificateAuthorities(CA)inIdMAnentitythatissuesdigitalcertificates.
InRedHatIdentityManagement,theprimaryCAisipa,theIdMCA.
TheipaCAcertificateisoneofthefollowingtypes:Self-signed.
Inthiscase,theipaCAistherootCA.
Externallysigned.
Inthiscase,theipaCAissubordinatedtotheexternalCA.
InIdM,youcanalsocreatemultiplesub-CAs.
Sub-CAsareIdMCAswhosecertificatesareoneofthefollowingtypes:SignedbytheipaCA.
SignedbyanyoftheintermediateCAsbetweenitselfandipaCA.
Thecertificateofasub-CAcannotbeself-signed.
Cross-foresttrustAtrustestablishesanaccessrelationshipbetweentwoKerberosrealms,allowingusersandservicesinonedomaintoaccessresourcesinanotherdomain.
Withacross-foresttrustbetweenanActiveDirectory(AD)forestrootdomainandanIdMdomain,usersfromtheADforestdomainscaninteractwithLinuxmachinesandservicesfromtheIdMdomain.
FromtheperspectiveofAD,IdentityManagementrepresentsaseparateADforestwithasingleADdomain.
Formoreinformation,seeHowthetrustworks.
DNSPTRrecordsDNSpointer(PTR)recordsresolveanIPaddressofahosttoadomainorhostname.
PTRrecordsaretheoppositeofDNSAandAAAArecords,whichresolvehostnamestoIPaddresses.
DNSPTRrecordsenablereverseDNSlookups.
PTRrecordsarestoredontheDNSserver.
DNSSRVrecordsADNSservice(SRV)recorddefinesthehostname,portnumber,transportprotocol,priorityandweightofaserviceavailableinadomain.
YoucanuseSRVrecordstolocateIdMserversandreplicas.
DomainController(DC)Adomaincontroller(DC)isahostthatrespondstosecurityauthenticationrequestswithinadomainandcontrolsaccesstoresourcesinthatdomain.
IdMserversworkasDCsfortheIdMdomain.
ADCauthenticatesusers,storesuseraccountinformationandenforcessecuritypolicyforadomain.
Whenauserlogsintoadomain,theDCauthenticatesandvalidatestheircredentialsandeitherallowsordeniesaccess.
FullyqualifieddomainnameAfullyqualifieddomainname(FQDN)isadomainnamethatspecifiestheexactlocationofahostwithinthehierarchyoftheDomainNameSystem(DNS).
Adevicewiththehostnamemyhostintheparentdomainexample.
comhastheFQDNmyhost.
example.
com.
TheFQDNuniquelydistinguishesthedevicefromanyotherhostscalledmyhostinotherdomains.
CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL11IfyouareinstallinganIdMclientonhostmachine1usingDNSautodiscoveryandyourDNSrecordsarecorrectlyconfigured,theFQDNofmachine1isallyouneed.
Formoreinformation,seeHostnameandDNSrequirementsforIdM.
HiddenreplicaAhiddenreplicaisanIdMreplicathathasallservicesrunningandavailable,butitsserverrolesaredisabled,andclientscannotdiscoverthereplicabecauseithasnoSRVrecordsinDNS.
Hiddenreplicasareprimarilydesignedforservicessuchasbackups,bulkimportingandexporting,oractionsthatrequireshuttingdownIdMservices.
Sincenoclientsuseahiddenreplica,administratorscantemporarilyshutdowntheservicesonthishostwithoutaffectinganyclients.
Formoreinformation,seeThehiddenreplicamode.
IDrangesAnIDrangeisarangeofIDnumbersassignedtotheIdMtopologyoraspecificreplica.
YoucanuseIDrangestospecifythevalidrangeofUIDsandGIDsfornewusers,hostsandgroups.
IDrangesareusedtoavoidIDnumberconflicts.
TherearetwodistincttypesofIDrangesinIdM:IdMIDrangeUsethisIDrangetodefinetheUIDsandGIDsforusersandgroupsinthewholeIdMtopology.
InstallingthefirstIdMmastercreatestheIdMIDrange.
YoucannotmodifytheIdMIDrangeaftercreatingit.
However,youcancreateanadditionalIdMIDrange,forexamplewhentheoriginalonenearsdepletion.
DistributedNumericAssignment(DNA)IDrangeUsethisIDrangetodefinetheUIDsandGIDsareplicauseswhencreatingnewusers.
AddinganewuserorhostentrytoanIdMreplicaforthefirsttimeassignsaDNAIDrangetothatreplica.
AnadministratorcanmodifytheDNAIDrange,butthenewdefinitionmustfitwithinanexistingIdMIDrange.
NotethattheIdMrangeandtheDNArangematch,buttheyarenotinterconnected.
Ifyouchangeonerange,ensureyouchangetheothertomatch.
Formoreinformation,seeIDranges.
IDviewsIDviewsenableyoutospecifynewvaluesforPOSIXuserorgroupattributes,andtodefineonwhichclienthostorhoststhenewvalueswillapply.
Forexample,youcanuseIDviewsto:Definedifferentattributevaluesfordifferentenvironments.
Replaceapreviouslygeneratedattributevaluewithadifferentvalue.
InanIdM-ADtrustsetup,theDefaultTrustViewisanIDviewappliedtoADusersandgroups.
UsingtheDefaultTrustView,youcandefinecustomPOSIXattributesforADusersandgroups,thusoverridingthevaluesdefinedinAD.
Formoreinformation,seeUsinganIDviewtooverrideauserattributevalueonanIdMclient.
IdMCAserverAnIdMserveronwhichtheIdMcertificateauthority(CA)serviceisinstalledandrunning.
Alternativenames:CAserverIdMdeploymentAtermthatreferstotheentiretyofyourIdMinstallation.
YoucandescribeyourIdMdeploymentbyRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement12AtermthatreferstotheentiretyofyourIdMinstallation.
YoucandescribeyourIdMdeploymentbyansweringthefollowingquestions:IsyourIdMdeploymentatestingdeploymentorproductiondeploymentHowmanyIdMserversdoyouhaveDoesyourIdMdeploymentcontainanintegratedCAIfitdoes,istheintegratedCAself-signedorexternallysignedIfitdoes,onwhichserversistheCAroleavailableOnwhichserversistheKRAroleavailableDoesyourIdMdeploymentcontainanintegratedDNSIfitdoes,onwhichserversistheDNSroleavailableIsyourIdMdeploymentinatrustagreementwithanADforestIfitis,onwhichserversistheADtrustcontrollerorADtrustagentroleavailableIdMmasterandreplicasThefirstserverinstalledusingtheipa-server-installcommand,usedtocreatetheIdMdomain,isknownasthemasterserverorIdMmaster.
Administratorscanusetheipa-replica-installcommandtoinstallreplicasinadditiontothemaster.
Bydefault,installingareplicacreatesareplicationagreementwiththeIdMserverfromwhichitwascreated,enablingreceivingandsendingupdatestotherestofIdM.
Thereisnofunctionaldifferencebetweenamasterandareplica.
BotharefullyfunctionalIdMservers.
Alternativenames:master,masterserver,IdMmasterserverIdMmasterCAserverIfyourIdMtopologycontainsanintegratedcertificateauthority(CA),oneserverhastheroleoftheCertificaterevocationlist(CRL)generationmasterandtheCArenewalmaster.
ThisserveristhemasterCAserver.
InadeploymentwithoutintegratedCA,thereisnomasterCAserver.
Alternativenames:masterCAIMPORTANTIdMmasterandmasterCAserveraretwodifferentterms.
Forexample,inthefollowingdeploymentscenario,thefirstserveristheIdMmasterandthereplicaisthemasterCAserver:1.
YouinstallthefirstIdMserverinyourenvironmentwithoutintegratedCA.
2.
Youinstallareplica.
3.
YouinstallaCAonthereplica.
Inthisscenario,thefirstserveristheIdMmasterandthereplicaisthemasterCAserver.
CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL13IdMtopologyAtermthatreferstothestructureofyourIdMsolution,especiallythereplicationagreementsbetweenandwithinindividualdatacentersandclusters.
KerberosauthenticationindicatorsAuthenticationindicatorsareattachedtoKerberosticketsandrepresenttheinitialauthenticationmethodusedtoacquireaticket:otpfortwo-factorauthentication(password+One-TimePassword)radiusforRemoteAuthenticationDial-InUserService(RADIUS)authentication(commonlyfor802.
1xauthentication)pkinitforPublicKeyCryptographyforInitialAuthenticationinKerberos(PKINIT),smartcard,orcertificateauthenticationhardenedforpasswordshardenedagainstbrute-forceattemptsFormoreinformation,seeKerberosauthenticationindicators.
KerberoskeytabWhileapasswordisthedefaultauthenticationmethodforauser,keytabsarethedefaultauthenticationmethodforhostsandservices.
AKerberoskeytabisafilethatcontainsalistofKerberosprincipalsandtheirassociatedencryptionkeys,soaservicecanretrieveitsownKerberoskeyandverifyauser'sidentity.
Forexample,everyIdMclienthasan/etc/krb5.
keytabfilethatstoresinformationaboutthehostprincipal,whichrepresentstheclientmachineintheKerberosrealm.
KerberosprincipalUniqueKerberosprincipalsidentifyeachuser,service,andhostinaKerberosrealm:EntityNamingconventionExampleUsersidentifier@REALMadmin@EXAMPLE.
COMServicesservice/fully-qualified-hostname@REALMhttp/master.
example.
com@EXAMPLE.
COMHostshost/fully-qualified-hostname@REALMhost/client.
example.
com@EXAMPLE.
COMKerberosprotocolKerberosisanetworkauthenticationprotocolthatprovidesstrongauthenticationforclientandserverapplicationsbyusingsecret-keycryptography.
IdMandActiveDirectoryuseKerberosforauthenticatingusers,hostsandservices.
KerberosrealmAKerberosrealmencompassesalltheprincipalsmanagedbyaKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC).
InanIdMdeployment,theKerberosrealmincludesallIdMusers,hosts,andservices.
KerberosticketpoliciesTheKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC)enforcesticketaccesscontrolthroughconnectionpolicies,andmanagesthedurationofKerberosticketsthroughticketlifecyclepolicies.
Forexample,RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement14thedefaultglobalticketlifetimeisoneday,andthedefaultglobalmaximumrenewalageisoneweek.
Formoreinformation,seeIdMKerberosticketpolicytypes.
KeyDistributionCenter(KDC)TheKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC)isaservicethatactsasthecentral,trustedauthoritythatmanagesKerberoscredentialinformation.
TheKDCissuesKerberosticketsandensurestheauthenticityofdataoriginatingfromentitieswithintheIdMnetwork.
Formoreinformation,seeTheroleoftheIdMKDC.
Lightweightsub-CAInIdM,alightweightsub-CAisacertificateauthority(CA)whosecertificateissignedbyanIdMrootCAoroneoftheCAsthataresubordinatetoit.
Alightweightsub-CAissuescertificatesonlyforaspecificpurpose,forexampletosecureaVPNorHTTPconnection.
Formoreinformation,seeRestrictinganapplicationtotrustonlyasubsetofcertificates.
PasswordpolicyApasswordpolicyisasetofconditionsthatthepasswordsofaparticularIdMusergroupmustmeet.
Theconditionscanincludethefollowingparameters:ThelengthofthepasswordThenumberofcharacterclassesusedThemaximumlifetimeofapassword.
Formoreinformation,seeWhatisapasswordpolicy.
POSIXattributesPOSIXattributesareuserattributesformaintainingcompatibilitybetweenoperatingsystems.
InaRedHatIdentityManagementenvironment,POSIXattributesforusersinclude:cn,theuser'snameuid,theaccountname(login)uidNumber,ausernumber(UID)gidNumber,theprimarygroupnumber(GID)homeDirectory,theuser'shomedirectoryInaRedHatIdentityManagementenvironment,POSIXattributesforgroupsinclude:cn,thegroup'snamegidNumber,thegroupnumber(GID)Theseattributesidentifyusersandgroupsasseparateentities.
ReplicationagreementAreplicationagreementisanagreementbetweentwoIdMserversinthesameIdMdeployment.
Thereplicationagreementensuresthatthedataandconfigurationiscontinuouslyreplicatedbetweenthetwoservers.
IdMusestwotypesofreplicationagreements:domainreplicationagreements,whichreplicateidentityinformation,andcertificatereplicationagreements,whichreplicatecertificateinformation.
CHAPTER1.
OVERVIEWOFPLANNINGFORIDMANDACCESSCONTROLINRHEL15Formoreinformation,see:ReplicationagreementsDeterminingtheappropriatenumberofreplicasConnectingthereplicasinatopologyReplicatopologyexamplesSmartcardAsmartcardisaremovabledeviceorcardusedtocontrolaccesstoaresource.
Theycanbeplasticcreditcard-sizedcardswithanembeddedintegratedcircuit(IC)chip,smallUSBdevicessuchasaYubikey,orothersimilardevices.
Smartcardscanprovideauthenticationbyallowinguserstoconnectasmartcardtoahostcomputer,andsoftwareonthathostcomputerinteractswithkeymaterialstoredonthesmartcardtoauthenticatetheuser.
SSSDTheSystemSecurityServicesDaemon(SSSD)isasystemservicethatmanagesuserauthenticationanduserauthorizationonaRHELhost.
SSSDoptionallykeepsacacheofuseridentitiesandcredentialsretrievedfromremoteprovidersforofflineauthentication.
Formoreinformation,seeUnderstandingSSSDanditsbenefits.
SSSDbackendAnSSSDbackend,oftenalsocalledadataprovider,isanSSSDchildprocessthatmanagesandcreatestheSSSDcache.
ThisprocesscommunicateswithanLDAPserver,performsdifferentlookupqueriesandstorestheresultsinthecache.
ItalsoperformsonlineauthenticationagainstLDAPorKerberosandappliesaccessandpasswordpolicytotheuserthatisloggingin.
Ticket-grantingticket(TGT)AfterauthenticatingtoaKerberosKeyDistributionCenter(KDC),auserreceivesaticket-grantingticket(TGT),whichisatemporarysetofcredentialsthatcanbeusedtorequestaccessticketstootherservices,suchaswebsitesandemail.
UsingaTGTtorequestfurtheraccessprovidestheuserwithaSingleSign-Onexperience,astheuseronlyneedstoauthenticateonceinordertoaccessmultipleservices.
TGTsarerenewable,andKerberosticketpoliciesdetermineticketrenewallimitsandaccesscontrol.
Formoreinformation,seeManagingKerberosticketpolicies.
AdditionalGlossariesIfyouareunabletofindanIdentityManagementterminthisglossary,seetheDirectoryServerandCertificateSystemglossaries:DirectoryServer11GlossaryCertificateSystem9Glossary1.
5.
ADDITIONALRESOURCESForgeneralinformationonRedHatIdM,seetheRedHatIdentityManagementproductpageontheRedHatCustomerPortal.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement16CHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGYThefollowingsectionsprovideadviceondeterminingtheappropriatereplicatopologyforyourusecase.
2.
1.
MULTIPLEREPLICASERVERSASASOLUTIONFORHIGHPERFORMANCEANDDISASTERRECOVERYContinuousfunctionalityandhighavailabilityofIdentityManagement(IdM)servicesisvitalforuserswhoaccessresources.
Oneofthebuilt-insolutionsforaccomplishingcontinuousfunctionalityandhighavailabilityoftheIdMinfrastructurethroughloadbalancingisthereplicationofthecentraldirectorybycreatingreplicaserversofthemasterserver.
IdMallowsplacingadditionalserversingeographicallydisperseddatacenterstoreflectyourenterpriseorganizationalstructure.
Inthisway,thepathbetweenIdMclientsandthenearestaccessibleserverisshortened.
Inaddition,havingmultipleserversallowsspreadingtheloadandscalingformoreclients.
MaintainingmultipleredundantIdMserversandlettingthemreplicatewitheachotherisalsoacommonbackupmechanismtomitigateorpreventserverloss.
Forexample,ifoneserverfails,theotherserverskeepprovidingservicestothedomain.
Youcanalsorecoverthelostserverbycreatinganewreplicabasedononeoftheremainingservers.
2.
2.
INTRODUCTIONTOIDMSERVERSANDCLIENTSTheIdentityManagement(IdM)domainincludesthefollowingtypesofsystems:IdMserversIdMserversareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsthatrespondtoidentity,authentication,andauthorizationrequestswithinanIdMdomain.
Inmostdeployments,anintegratedcertificateauthority(CA)isalsoinstalledwiththeIdMserver.
IdMserversarethecentralrepositoriesforidentityandpolicyinformation.
IdMserverscanalsohostanyoftheoptionalservicesusedbydomainmembers:Certificateauthority(CA)KeyRecoveryAuthority(KRA)DNSActiveDirectory(AD)trustcontrollerActiveDirectory(AD)trustagentThefirstserverinstalledtocreatethedomainistheIdMmasterormasterserver.
TheIdMmasterisnottobeconfusedwiththemasterCAserver:theycanrunontwodifferentmachines.
IdMclientsIdMclientsareRedHatEnterpriseLinuxsystemsenrolledwiththeserversandconfiguredtousetheIdMservicesontheseservers.
ClientsinteractwiththeIdMserverstoaccessservicesprovidedbythem.
Forexample,clientsusetheKerberosprotocoltoperformauthenticationandacquireticketsforenterprisesinglesign-on(SSO),useLDAPtogetidentityandpolicyinfromation,useDNStodetectwheretheserversandservicesarelocatedandhowtoconnecttothem.
IdMserversarealsoembeddedIdMclients.
Asclientsenrolledwiththemselves,theserversprovideCHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY17IdMserversarealsoembeddedIdMclients.
Asclientsenrolledwiththemselves,theserversprovidethesamefunctionalityasotherclients.
Toprovideservicesforlargenumbersofclients,aswellasforredundancyandavailability,IdMallowsdeploymentonmultipleIdMserversinasingledomain.
Itispossibletodeployupto60servers.
ThisisthemaximumnumberofIdMservers,alsocalledreplicas,thatiscurrentlysupportedintheIdMdomain.
IdMserversprovidedifferentservicesfortheclient.
Notalltheserversneedtoprovideallthepossibleservices.
SomeservercomponentslikeKerberosandLDAParealwaysavailableoneveryserver.
OtherserviceslikeCA,DNS,TrustControllerorVaultareoptional.
Thismeansthatdifferentserversingeneralplaydifferentrolesinthedeployment.
IfyourIdMtopologycontainsanintegratedCA,oneserveralsohastheroleoftheCertificaterevocationlist(CRL)generationmasterandtheCArenewalmaster.
ThisserveristhemasterCA.
WARNINGThemasterCAserveriscriticalforyourIdMdeploymentbecauseitistheonlysysteminthedomainresponsiblefortrackingCAsubsystemcertificatesandkeys,andforgeneratingtheCRL.
FordetailsabouthowtorecoverfromadisasteraffectingyourIdMdeployment,seePerformingdisasterrecoverywithIdentityManagement.
Forredundancyandloadbalancing,administratorscreateadditionalserversbycreatingareplicaofanyexistingserver,eitherthemasterserveroranotherreplica.
Whencreatingareplica,IdMclonestheconfigurationoftheexistingserver.
Areplicashareswiththeinitialserveritscoreconfiguration,includinginternalinformationaboutusers,systems,certificates,andconfiguredpolicies.
NOTEAreplicaandtheserveritwascreatedfromarefunctionallyidenticalexceptfortheroleoftheCRLgenerationmaster.
Therefore,thetermserverandreplicaareusedinterchangeablyheredependingonthecontext.
2.
3.
REPLICATIONAGREEMENTSWhenanadministratorcreatesareplicabasedonanexistingserver,IdentityManagement(IdM)createsareplicationagreementbetweentheinitialserverandthereplica.
Thereplicationagreementensuresthatthedataandconfigurationiscontinuouslyreplicatedbetweenthetwoservers.
Replicationagreementsarealwaysbilateral:thedataisreplicatedfromoneservertotheotheraswellasfromtheotherservertothefirstserver.
IdMusesmulti-masterreplication.
Inmulti-masterreplication,allreplicasjoinedinareplicationagreementreceiveupdates,andarethereforeconsidereddatamasters.
Figure2.
1.
ServerandreplicaagreementsRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement18Figure2.
1.
ServerandreplicaagreementsIdMusestwotypesofreplicationagreements:DomainreplicationagreementsTheseagreementsreplicatetheidentityinformation.
CertificatereplicationagreementsTheseagreementsreplicatethecertificateinformation.
Bothreplicationchannelsareindependent.
Twoserverscanhaveoneorbothtypesofreplicationagreementsconfiguredbetweenthem.
Forexample,whenserverAandserverBhaveonlydomainreplicationagreementconfigured,onlyidentityinformationisreplicatedbetweenthem,notthecertificateinformation.
2.
4.
DETERMININGTHEAPPROPRIATENUMBEROFREPLICASSetupatleasttworeplicasineachdatacenter(notahardrequirement)Adatacentercanbe,forexample,amainofficeorageographicallocation.
SetupasufficientnumberofserverstoserveyourclientsOneIdentityManagement(IdM)servercanprovideservicesto2000-3000clients.
Thisassumestheclientsquerytheserversmultipletimesaday,butnot,forexample,everyminute.
Ifyouexpectmorefrequentqueries,planformoreservers.
Setupamaximumof60replicasinasingleIdMdomainRedHatguaranteestosupportenvironmentswith60replicasorfewer.
2.
5.
CONNECTINGTHEREPLICASINATOPOLOGYConnecteachreplicatoatleasttwootherreplicasConfiguringadditionalreplicationagreementsensuresthatinformationisreplicatednotjustbetweentheinitialreplicaandthemasterserver,butbetweenotherreplicasaswell.
Connectareplicatoamaximumoffourotherreplicas(notahardrequirement)Alargenumberofreplicationagreementsperserverdoesnotaddsignificantbenefits.
Areceivingreplicacanonlybeupdatedbyoneotherreplicaatatimeandmeanwhile,theotherreplicationagreementsareidle.
Morethanfourreplicationagreementsperreplicatypicallymeansawasteofresources.
NOTECHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY19NOTEThisrecommendationappliestobothcertificatereplicationanddomainreplicationagreements.
Therearetwoexceptionstothelimitoffourreplicationagreementsperreplica:Youwantfailoverpathsifcertainreplicasarenotonlineorresponding.
Inlargerdeployments,youwantadditionaldirectlinksbetweenspecificnodes.
Configuringahighnumberofreplicationagreementscanhaveanegativeimpactonoverallperformance:whenmultiplereplicationagreementsinthetopologyaresendingupdates,certainreplicascanexperienceahighcontentiononthechangelogdatabasefilebetweenincomingupdatesandtheoutgoingupdates.
Ifyoudecidetousemorereplicationagreementsperreplica,ensurethatyoudonotexperiencereplicationissuesandlatency.
However,notethatlargedistancesandhighnumbersofintermediatenodescanalsocauselatencyproblems.
ConnectthereplicasinadatacenterwitheachotherThisensuresdomainreplicationwithinthedatacenter.
ConnecteachdatacentertoatleasttwootherdatacentersThisensuresdomainreplicationbetweendatacenters.
ConnectdatacentersusingatleastapairofreplicationagreementsIfdatacentersAandBhaveareplicationagreementfromA1toB1,havingareplicationagreementfromA2toB2ensuresthatifoneoftheserversisdown,thereplicationcancontinuebetweenthetwodatacenters.
2.
6.
REPLICATOPOLOGYEXAMPLESThefiguresbelowshowexamplesofIdentityManagement(IdM)topologiesbasedontheguidelinesforcreatingareliabletopology.
Figure2.
2,"ReplicaTopologyExample1"showsfourdatacenters,eachwithfourservers.
Theserversareconnectedwithreplicationagreements.
Figure2.
2.
ReplicaTopologyExample1RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement20Figure2.
2.
ReplicaTopologyExample1Figure2.
3,"ReplicaTopologyExample2"showsthreedatacenters,eachwithadifferentnumberofservers.
Theserversareconnectedwithreplicationagreements.
Figure2.
3.
ReplicaTopologyExample2CHAPTER2.
PLANNINGTHEREPLICATOPOLOGY212.
7.
THEHIDDENREPLICAMODEBydefault,whenyousetupanewreplica,theinstallerautomaticallycreatesservice(SRV)resourcerecordsinDNS.
Theserecordsenableclientstoauto-discoverthereplicaanditsservices.
AhiddenreplicaisanIdMserverthathasallservicesrunningandavailable.
However,ithasnoSRVrecordsinDNS,andLDAPserverrolesarenotenabled.
Therefore,clientscannotuseservicediscoverytodetectthesehiddenreplicas.
NOTEThehiddenreplicafeatureisavailableinRedHatEnterpriseLinux8.
1andlaterasaTechnologyPreviewand,therefore,notsupported.
Hiddenreplicasareprimarilydesignedfordedicatedservicesthatcanotherwisedisruptclients.
Forexample,afullbackupofIdMrequirestoshutdownallIdMservicesonthemasterorreplica.
Sincenoclientsuseahiddenreplica,administratorscantemporarilyshutdowntheservicesonthishostwithoutaffectinganyclients.
NOTERestoringabackupfromahiddenreplicaonanewhostalwaysresultsinanon-hidden(regular)replica.
Allserverrolesusedinacluster,especiallytheCertificateAuthorityroleiftheintegratedCAisused,mustbeinstalledonthehiddenreplicaforthebackuptobeabletorestorethoseservices.
FormoreinformationoncreatingandworkingwithIdMbackups,seeBackingUpandRestoringIdM.
Otherusecasesincludehigh-loadoperationsontheIdMAPIortheLDAPserver,suchasamassimportorextensivequeries.
Toinstallareplicaashidden,passthe--hidden-replicaparametertotheipa-replica-installcommand.
Forfurtherdetailsaboutinstallingareplica,seeInstallinganIdentityManagementreplica.
Alternatively,youcanchangethestateofanexistingreplica.
Fordetails,seeDemotionandPromotionofHiddenReplicas.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement22CHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMESIdentityManagement(IdM)providesdifferenttypesofDNSconfigurationsintheIdMserver.
Thefollowingsectionsdescribethemandprovideadviceonhowtodeterminewhichisthebestforyourusecase.
3.
1.
DNSSERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVERYoucaninstallanIdentityManagement(IdM)serverwithorwithoutintegratedDNS.
Table3.
1.
ComparingIdMwithintegratedDNSandwithoutintegratedDNSWithintegratedDNSWithoutintegratedDNSOverview:IdMrunsitsownDNSservicefortheIdMdomain.
IdMusesDNSservicesprovidedbyanexternalDNSserver.
Limitations:TheintegratedDNSserverprovidedbyIdMonlysupportsfeaturesrelatedtoIdMdeploymentandmaintenance.
ItdoesnotsupportsomeoftheadvancedDNSfeatures.
Itisnotdesignedtobeusedasageneral-purposeDNSserver.
DNSisnotintegratedwithnativeIdMtools.
Forexample,IdMdoesnotupdatetheDNSrecordsautomaticallyafterachangeinthetopology.
Worksbestfor:BasicusagewithintheIdMdeployment.
WhentheIdMservermanagesDNS,DNSistightlyintegratedwithnativeIdMtools,whichenablesautomatingsomeoftheDNSrecordmanagementtasks.
EnvironmentswhereadvancedDNSfeaturesbeyondthescopeoftheIdMDNSareneeded.
Environmentswithawell-establishedDNSinfrastructurewhereyouwanttokeepusinganexternalDNSserver.
EvenifanIdentityManagementserverisusedasaprimaryDNSserver,otherexternalDNSserverscanstillbeusedassecondaryservers.
Forexample,ifyourenvironmentisalreadyusinganotherDNSserver,suchasaDNSserverintegratedwithActiveDirectory(AD),youcandelegateonlytheIdMprimarydomaintotheDNSintegratedwithIdM.
ItisnotnecessarytomigrateDNSzonestotheIdMDNS.
NOTEIfyouneedtoissuecertificatesforIdMclientswithanIPaddressintheSubjectAlternativeName(SAN)extension,youmustusetheIdMintegratedDNSservice.
3.
2.
GUIDELINESFORPLANNINGTHEDNSDOMAINNAMEANDKERBEROSREALMNAMEWheninstallingthefirstIdentityManagement(IdM)server,theinstallationpromptsforaprimaryDNSnameoftheIdMdomainandKerberosrealmname.
Theguidelinesinthissectioncanhelpyousetthenamescorrectly.
CHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMES23WARNINGYouwillnotbeabletochangetheIdMprimarydomainnameandKerberosrealmnameaftertheserverisalreadyinstalled.
Donotexpecttobeabletomovefromatestingenvironmenttoaproductionenvironmentbychangingthenames,forexamplefromlab.
example.
comtoproduction.
example.
com.
AseparateDNSdomainforservicerecordsEnsurethattheprimaryDNSdomainusedforIdMisnotsharedwithanyothersystem.
ThishelpsavoidconflictsontheDNSlevel.
ProperDNSdomainnamedelegationEnsureyouhavevaliddelegationinthepublicDNStreefortheDNSdomain.
Donotuseadomainnamethatisnotdelegatedtoyou,notevenonaprivatenetwork.
Multi-labelDNSdomainDonotusesingle-labeldomainnames,forexample.
company.
TheIdMdomainmustbecomposedofoneormoresubdomainsandatopleveldomain,forexampleexample.
comorcompany.
example.
com.
AuniqueKerberosrealmnameEnsuretherealmnameisnotinconflictwithanyotherexistingKerberosrealmname,suchasanameusedbyActiveDirectory(AD).
Kerberosrealmnameasanupper-caseversionoftheprimaryDNSnameConsidersettingtherealmnametoanupper-case(EXAMPLE.
COM)versionoftheprimaryDNSdomainname(example.
com).
WARNINGIfyoudonotsettheKerberosrealmnametobetheupper-caseversionoftheprimaryDNSname,youwillnotbeabletouseADtrusts.
AdditionalnotesonplanningtheDNSdomainnameandKerberosrealmnameOneIdMdeploymentalwaysrepresentsoneKerberosrealm.
YoucanjoinIdMclientsfrommultipledistinctDNSdomains(example.
com,example.
net,example.
org)toasingleKerberosrealm(EXAMPLE.
COM).
IdMclientsdonotneedtobeintheprimaryDNSdomain.
Forexample,iftheIdMdomainisidm.
example.
com,theclientscanbeintheclients.
example.
comdomain,butclearmappingmustbeconfiguredbetweentheDNSdomainandtheKerberosrealm.
NOTERedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement24NOTEThestandardmethodtocreatethemappingisusingthe_kerberosTXTDNSrecords.
TheIdMintegratedDNSaddstheserecordsautomatically.
CHAPTER3.
PLANNINGYOURDNSSERVICESANDHOSTNAMES25CHAPTER4.
PLANNINGYOURCASERVICESIdentityManagement(IdM)inRedHatEnterpriseLinuxprovidesdifferenttypesofcertificateauthority(CA)configurations.
Thefollowingsectionsdescribedifferentscenariosandprovideadvicetohelpyoudeterminewhichconfigurationisbestforyourusecase.
4.
1.
CASERVICESAVAILABLEINANIDMSERVERYoucaninstallanIdentityManagement(IdM)serverwithanintegratedIdMcertificateauthority(CA)orwithoutaCA.
Table4.
1.
ComparingIdMwithintegratedCAandwithoutaCAIntegratedCAWithoutaCAOverview:IdMusesitsownpublickeyinfrastructure(PKI)servicewithaCAsigningcertificatetocreateandsignthecertificatesintheIdMdomain.
IftherootCAistheintegratedCA,IdMusesaself-signedCAcertificate.
IftherootCAisanexternalCA,theintegratedIdMCAissubordinatetotheexternalCA.
TheCAcertificateusedbyIdMissignedbytheexternalCA,butallcertificatesfortheIdMdomainareissuedbytheintegratedCertificateSysteminstance.
IntegratedCAisalsoabletoissuecertificatesforusers,hosts,orservices.
TheexternalCAcanbeacorporateCAorathird-partyCA.
IdMdoesnotsetupitsownCA,butusessignedhostcertificatesfromanexternalCA.
InstallingaserverwithoutaCArequiresyoutorequestthefollowingcertificatesfromathird-partyauthority:AnLDAPservercertificateAnApacheservercertificateAPKINITcertificateFullCAcertificatechainoftheCAthatissuedtheLDAPandApacheservercertificatesRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement26Limitations:IftheintegratedCAissubordinatetoanexternalCA,thecertificatesissuedwithintheIdMdomainarepotentiallysubjecttorestrictionssetbytheexternalCAforvariouscertificateattributes,suchas:Thevalidityperiod.
ConstraintsonwhatsubjectnamescanappearoncertificatesissuedbytheIDMCAoritssubordinates.
.
ConstraintsonwhethertheIDMCAcanitself,issuesubordinateCAcertificates,orhow"deep"thechainofsubordinatecertificatescango.
ManagingcertificatesoutsideofIdMcausesalotofadditionalactivities,suchas:Creating,uploading,andrenewingcertificatesisamanualprocess.
ThecertmongerservicedoesnottracktheIPAcertificates(LDAPserver,Apacheserver,andPKINITcertificates)anddoesnotnotifyyouwhenthecertificatesareabouttoexpire.
Theadministratorsmustmanuallysetupnotificationsforexternallyissuedcertificates,orsettrackingrequestsforthosecertificatesiftheywantcertmongertotrackthem.
Worksbestfor:Environmentsthatallowyoutocreateanduseyourowncertificateinfrastructure.
Veryrarecaseswhenrestrictionswithintheinfrastructuredonotallowyoutoinstallcertificateservicesintegratedwiththeserver.
IntegratedCAWithoutaCANOTESwitchingfromtheself-signedCAtoanexternally-signedCA,ortheotherwayaround,aswellaschangingwhichexternalCAissuestheIdMCAcertificate,ispossibleevenaftertheinstallation.
ItisalsopossibletoconfigureanintegratedCAevenafteraninstallationwithoutaCA.
4.
2.
CASUBJECTDNTheCertificateAuthority(CA)subjectdistinguishedname(DN)isthenameoftheCA.
ItmustbegloballyuniqueintheIdentityManagement(IdM)CAinfrastructureandcannotbechangedaftertheinstallation.
IncaseyouneedtheIdMCAtobeexternallysigned,youmightneedtoconsulttheadministratoroftheexternalCAabouttheformyourIdMCASubjectDNshouldtake.
4.
3.
GUIDELINESFORDISTRIBUTIONOFCASERVICESFollowingstepsprovideguidelinesforthedistributionofyourcertificateauthority(CA)services.
InstalltheCAservicesonmorethanoneserverinthetopologyReplicasconfiguredwithoutaCAforwardallcertificateoperationsrequeststotheCAserversinyourtopology.
CHAPTER4.
PLANNINGYOURCASERVICES27WARNINGIfyouloseallserverswithaCA,youwilllosealltheCAconfigurationwithoutanychanceofrecovery.
InsuchcaseyouneedtosetupnewCAandissueandinstallnewcertificates.
MaintainasufficientnumberofCAserverstohandletheCArequestsinyourdeploymentForrecommendationseethefollowingtable:Table4.
2.
GuidelinesforsettingupappropriatenumberofCAserversDescriptionofthedeploymentSuggestednumberofCAserversAdeploymentwithaverylargenumberofcertificatesissuedThreeorfourCAserversAdeploymentwithbandwidthoravailabilityproblemsbetweenmultipleregionsOneCAserverperregion,withaminimumofthreeserverstotalforthedeploymentAllotherdeploymentsTwoCAserversRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement28CHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHADThefollowingsectionsintroducetheoptionsforintegratingRedHatEnterpriseLinuxwithActiveDirectory(AD).
Foranoverviewofdirectintegration,seeSection5.
1,"Directintegration".
Foranoverviewofindirectintegration,seeSection5.
2,"Indirectintegration".
Foradviceonhowtodecidebetweenthem,seeSection5.
3,"Decidingbetweenindirectanddirectintegration".
5.
1.
DIRECTINTEGRATIONIndirectintegration,LinuxsystemsareconnecteddirectlytoActiveDirectory(AD).
Thefollowingtypesofintegrationarepossible:IntegrationwiththeSystemSecurityServicesDaemon(SSSD)SSSDcanconnectaLinuxsystemwithvariousidentityandauthenticationstores:AD,IdentityManagement(IdM),oragenericLDAPorKerberosserver.
NotablerequirementsforintegrationwithSSSD:WhenintegratingwithAD,SSSDworksonlywithinasingleADforestbydefault.
Formulti-forestsetup,configuremanualdomainenumeration.
RemoteADforestsmusttrustthelocalforesttoensurethattheidmap_adplug-inhandlesremoteforestuserscorrectly.
SSSDsupportsbothdirectandindirectintegration.
Italsoenablesswitchingfromoneintegrationapproachtotheotherwithoutsignificantmigrationcosts.
IntegrationwithSambaWinbindTheWinbindcomponentoftheSambasuiteemulatesaWindowsclientonaLinuxsystemandcommunicateswithADservers.
NotablerequirementsforintegrationwithSambaWinbind:DirectintegrationwithWinbindinamulti-forestADsetuprequiresbidirectionaltrusts.
AbidirectionalpathfromthelocaldomainofaLinuxsystemmustexisttothedomainofauserinaremoteADforesttoallowfullinformationabouttheuserfromtheremoteADdomaintobeavailabletotheidmap_adplug-in.
RecommendationsSSSDsatisfiesmostoftheusecasesforADintegrationandprovidesarobustsolutionasagenericgatewaybetweenaclientsystemanddifferenttypesofidentityandauthenticationproviders-AD,IdM,Kerberos,andLDAP.
WinbindisrecommendedfordeploymentonthoseADdomainmemberserversonwhichyouplantodeploySambaFS.
5.
2.
INDIRECTINTEGRATIONInindirectintegration,LinuxsystemsarefirstconnectedtoacentralserverwhichisthenconnectedtoCHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHAD29Inindirectintegration,LinuxsystemsarefirstconnectedtoacentralserverwhichisthenconnectedtoActiveDirectory(AD).
IndirectintegrationenablestheadministratortomanageLinuxsystemsandpoliciescentrally,whileusersfromADcantransparentlyaccessLinuxsystemsandservices.
Integrationbasedoncross-foresttrustwithADTheIdentityManagement(IdM)serveractsasthecentralservertocontrolLinuxsystems.
Across-realmKerberostrustwithADisestablished,enablingusersfromADtologontoaccessLinuxsystemsandresources.
IdMpresentsitselftoADasaseparateforestandtakesadvantageoftheforest-leveltrustssupportedbyAD.
Whenusingatrust:ADuserscanaccessIdMresources.
IdMserversandclientscanresolvetheidentitiesofADusersandgroups.
ADusersandgroupsaccessIdMundertheconditionsdefinedbyIdM,suchashost-basedaccesscontrol.
ADusersandgroupscontinuebeingmanagedontheADside.
IntegrationbasedonsynchronizationThisapproachisbasedontheWinSynctool.
AWinSyncreplicationagreementsynchronizesuseraccountsfromADtoIdM.
WARNINGWinSyncisnolongeractivelydevelopedinRedHatEnterpriseLinux8.
Thepreferredsolutionforindirectintegrationiscross-foresttrust.
Thelimitationsofintegrationbasedonsynchronizationinclude:GroupsarenotsynchronizedfromIdMtoAD.
UsersareduplicatedinADandIdM.
WinSyncsupportsonlyasingleADdomain.
OnlyonedomaincontrollerinADcanbeusedtosynchronizedatatooneinstanceofIdM.
Userpasswordsmustbesynchronized,whichrequiresthePassSynccomponenttobeinstalledonalldomaincontrollersintheADdomain.
Afterconfiguringthesynchronization,allADusersmustmanuallychangepasswordsbeforePassSynccansynchronizethem.
5.
3.
DECIDINGBETWEENINDIRECTANDDIRECTINTEGRATIONTheguidelinesinthissectioncanhelpdecidewhichtypeofintegrationfitsyourusecase.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement30NumberofsystemstobeconnectedtoActiveDirectoryConnectinglessthan30-50systems(notahardlimit)Ifyouconnectlessthan30-50systems,considerdirectintegration.
Indirectintegrationmightintroduceunnecessaryoverhead.
Connectingmorethan30-50systems(notahardlimit)Ifyouconnectmorethan30-50systems,considerindirectintegrationwithIdentityManagement.
Withthisapproach,youcanbenefitfromthecentralizedmanagementforLinuxsystems.
ManagingasmallnumberofLinuxsystems,butexpectingthenumbertogrowrapidlyInthisscenario,considerindirectintegrationtoavoidhavingtomigratetheenvironmentlater.
FrequencyofdeployingnewsystemsandtheirtypeDeployingbaremetalsystemsonanirregularbasisIfyoudeploynewsystemsrarelyandtheyareusuallybaremetalsystems,considerdirectintegration.
Insuchcases,directintegrationisusuallysimplestandeasiest.
DeployingvirtualsystemsfrequentlyIfyoudeploynewsystemsoftenandtheyareusuallyvirtualsystemsprovisionedondemand,considerindirectintegration.
Withindirectintegration,youcanuseacentralservertomanagethenewsystemsdynamicallyandintegratewithorchestrationtools,suchasRedHatSatellite.
ActiveDirectoryistherequiredauthenticationproviderDoyourinternalpoliciesstatethatallusersmustauthenticateagainstActiveDirectoryYoucanchooseeitherdirectorindirectintegration.
IfyouuseindirectintegrationwithatrustbetweenIdentityManagementandActiveDirectory,theusersthataccessLinuxsystemsauthenticateagainstActiveDirectory.
PoliciesthatexistinActiveDirectoryareexecutedandenforcedduringauthentication.
CHAPTER5.
PLANNINGINTEGRATIONWITHAD31CHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDADActiveDirectory(AD)andIdentityManagement(IdM)aretwoalternativeenvironmentsmanagingavarietyofcoreservices,suchasKerberos,LDAP,DNS,andcertificateservices.
Across-foresttrustrelationshiptransparentlyintegratesthesetwodiverseenvironmentsbyenablingallcoreservicestointeractseamlessly.
Thefollowingsectionsprovideadviceonhowtoplananddesignacross-foresttrustdeployment.
6.
1.
CROSS-FORESTTRUSTSBETWEENIDMANDADInapureActiveDirectory(AD)environment,across-foresttrustconnectstwoseparateADforestrootdomains.
Whenyoucreateacross-foresttrustbetweenADandIdM,theIdMdomainpresentsitselftoADasaseparateforestwithasingledomain.
AtrustrelationshipisthenestablishedbetweentheADforestrootdomainandtheIdMdomain.
Asaresult,usersfromtheADforestcanaccesstheresourcesintheIdMdomain.
IdMcanestablishatrustwithoneADforestormultipleunrelatedforests.
NOTETwoseparateKerberosrealmscanbeconnectedinacross-realmtrust.
However,aKerberosrealmonlyconcernsauthentication,nototherservicesandprotocolsinvolvedinidentityandauthorizationoperations.
Therefore,establishingaKerberoscross-realmtrustisnotenoughtoenableusersfromonerealmtoaccessresourcesinanotherrealm.
AnexternaltrusttoanADdomainAnexternaltrustisatrustrelationshipbetweenIdMandanActiveDirectorydomain.
WhileaforesttrustalwaysrequiresestablishingatrustbetweenIdMandtherootdomainofanActiveDirectoryforest,anexternaltrustcanbeestablishedfromIdMtoanydomainwithinaforest.
6.
2.
TRUSTCONTROLLERSANDTRUSTAGENTSIdentityManagement(IdM)providesthefollowingtypesofIdMserversthatsupporttrusttoActiveDirectory(AD):TrustagentsIdMserversthatcanperformidentitylookupsagainstADdomaincontrollers.
TrustcontrollersTrustagentsthatalsoruntheSambasuite.
ADdomaincontrollerscontacttrustcontrollerswhenestablishingandverifyingthetrusttoAD.
Thefirsttrustcontrolleriscreatedwhenyouconfigurethetrust.
Trustcontrollersrunmorenetwork-facingservicesthantrustagents,andthuspresentagreaterattacksurfaceforpotentialintruders.
Inadditiontotrustagentsandcontrollers,theIdMdomaincanalsoincludestandardIdMservers.
However,theseserversdonotcommunicatewithAD.
Therefore,clientsthatcommunicatewiththestandardserverscannotresolveADusersandgroupsorauthenticateandauthorizeADusers.
Table6.
1.
ComparingthecapabilitiessupportedbytrustcontrollersandtrustagentsRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement32CapabilityTrustagentTrustcontrollerResolveADusersandgroupsYesYesEnrollIdMclientsthatrunservicesaccessiblebyusersfromtrustedADforestsYesYesManagethetrust(forexample,addtrustagreements)NoYesWhenplanningthedeploymentoftrustcontrollersandtrustagents,considertheseguidelines:ConfigureatleasttwotrustcontrollersperIdMdeployment.
Configureatleasttwotrustcontrollersineachdatacenter.
Ifyoueverwanttocreateadditionaltrustcontrollersorifanexistingtrustcontrollerfails,createanewtrustcontrollerbypromotingatrustagentorastandardserver.
Todothis,usetheipa-adtrust-installutilityontheIdMserver.
IMPORTANTYoucannotdowngradeanexistingtrustcontrollertoatrustagent.
6.
3.
ONE-WAYTRUSTSANDTWO-WAYTRUSTSInonewaytrusts,IdentityManagement(IdM)trustsActiveDirectory(AD)butADdoesnottrustIdM.
ADuserscanaccessresourcesintheIdMdomainbutusersfromIdMcannotaccessresourceswithintheADdomain.
TheIdMserverconnectstoADusingaspecialaccount,andreadsidentityinformationthatisthendeliveredtoIdMclientsoverLDAP.
Intwowaytrusts,IdMuserscanauthenticatetoAD,andADuserscanauthenticatetoIdM.
ADuserscanauthenticatetoandaccessresourcesintheIdMdomainasintheonewaytrustcase.
IdMuserscanauthenticatebutcannotaccessmostoftheresourcesinAD.
TheycanonlyaccessthoseKerberizedservicesinADforeststhatdonotrequireanyaccesscontrolcheck.
TobeabletograntaccesstotheADresources,IdMneedstoimplementtheGlobalCatalogservice.
ThisservicedoesnotyetexistinthecurrentversionoftheIdMserver.
Becauseofthat,atwo-waytrustbetweenIdMandADisnearlyfunctionallyequivalenttoaone-waytrustbetweenIdMandAD.
6.
4.
NON-POSIXEXTERNALGROUPSANDSIDMAPPINGIdentityManagement(IdM)usesLDAPformanaginggroups.
ActiveDirectory(AD)entriesarenotsynchronizedorcopiedovertoIdM,whichmeansthatADusersandgroupshavenoLDAPobjectsintheLDAPserver,sotheycannotbedirectlyusedtoexpressgroupmembershipintheIdMLDAP.
Forthisreason,administratorsinIdMneedtocreatenon-POSIXexternalgroups,referencedasnormalIdMLDAPobjectstosignifygroupmembershipforADusersandgroupsinIdM.
SecurityIDs(SIDs)fornon-POSIXexternalgroupsareprocessedbySSSD,whichmapstheSIDsofgroupsinActiveDirectorytoPOSIXgroupsinIdM.
InActiveDirectory,SIDsareassociatedwithusernames.
WhenanADusernameisusedtoaccessIdMresources,SSSDusestheuser'sSIDtobuildupafullgroupmembershipinformationfortheuserintheIdMdomain.
CHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD336.
5.
SETTINGUPDNSTheseguidelinescanhelpyouachievetherightDNSconfigurationforestablishingacross-foresttrustbetweenIdentityManagement(IdM)andActiveDirectory(AD).
UniqueprimaryDNSdomainsEnsurebothADandIdMhavetheirownuniqueprimaryDNSdomainsconfigured.
Forexample:ad.
example.
comforADandidm.
example.
comforIdMexample.
comforADandidm.
example.
comforIdMThemostconvenientmanagementsolutionisanenvironmentwhereeachDNSdomainismanagedbyintegratedDNSservers,butyoucanalsouseanyotherstandard-compliantDNSserver.
NooverlapbetweenIdMandADDNSDomainsSystemsjoinedtoIdMcanbedistributedovermultipleDNSdomains.
EnsuretheDNSdomainsthatcontainIdMclientsdonotoverlapwithDNSdomainsthatcontainsystemsjoinedtoAD.
ProperSRVrecordsEnsuretheprimaryIdMDNSdomainhasproperSRVrecordstosupportADtrusts.
ForotherDNSdomainsthatarepartofthesameIdMrealm,theSRVrecordsdonothavetobeconfiguredwhenthetrusttoADisestablished.
ThereasonisthatADdomaincontrollersdonotuseSRVrecordstodiscoverKerberoskeydistributioncenters(KDCs)butratherbasetheKDCdiscoveryonnamesuffixroutinginformationforthetrust.
DNSrecordsresolvablefromallDNSdomainsinthetrustEnsureallmachinescanresolveDNSrecordsfromallDNSdomainsinvolvedinthetrustrelationship:WhenconfiguringtheIdMDNS,followtheinstructionsdescribedinInstallinganIdMserverwithanexternalCA.
IfyouareusingIdMwithoutintegratedDNS,followtheinstructionsdescribedinInstallinganIdMserverwithoutintegratedDNS.
Kerberosrealmnamesasupper-caseversionsofprimaryDNSdomainnamesEnsureKerberosrealmnamesarethesameastheprimaryDNSdomainnames,withalllettersuppercase.
Forexample,ifthedomainnamesaread.
example.
comforADandidm.
example.
comforIdM,theKerberosrealmnamesmustbeAD.
EXAMPLE.
COMandIDM.
EXAMPLE.
COM.
6.
6.
NETBIOSNAMESTheNetBIOSnameisusuallythefar-leftcomponentofthedomainname.
Forexample:Inthedomainnamelinux.
example.
com,theNetBIOSnameislinux.
Inthedomainnameexample.
com,theNetBIOSnameisexample.
DifferentNetBIOSnamesfortheIdentityManagement(IdM)andActiveDirectory(AD)domainsEnsuretheIdMandADdomainshavedifferentNetBIOSnames.
TheNetBIOSnameiscriticalforidentifyingtheADdomain.
IftheIdMdomainiswithinasubdomainoftheADDNS,theNetBIOSnameisalsocriticalforidentifyingtheIdMdomainandservices.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement34CharacterlimitforNetBIOSnamesThemaximumlengthofaNetBIOSnameis15characters.
6.
7.
SUPPORTEDVERSIONSOFWINDOWSSERVERYoucanestablishatrustrelationshipwithActiveDirectory(AD)foreststhatusethefollowingforestanddomainfunctionallevels:Forestfunctionallevelrange:WindowsServer2008—WindowsServer2016Domainfunctionallevelrange:WindowsServer2008—WindowsServer2016IdentityManagement(IdM)supportsthefollowingoperatingsystems:WindowsServer2008WindowsServer2008R2WindowsServer2012WindowsServer2012R2WindowsServer2016WindowsServer20196.
8.
CONFIGURINGADSERVERDISCOVERYANDAFFINITYServerdiscoveryandaffinityconfigurationaffectswhichActiveDirectory(AD)serversanIdentityManagement(IdM)clientcommunicateswith.
Thissectionprovidesanoverviewofhowdiscoveryandaffinityworkinanenvironmentwithacross-foresttrustbetweenIdMandAD.
Configuringclientstopreferserversinthesamegeographicallocationhelpspreventtimelagsandotherproblemsthatoccurwhenclientscontactserversfromanother,remotedatacenter.
Tomakesureclientscommunicatewithlocalservers,youmustensurethat:ClientscommunicatewithlocalIdMserversoverLDAPandoverKerberosClientscommunicatewithlocalADserversoverKerberosEmbeddedclientsonIdMserverscommunicatewithlocalADserversoverLDAPandoverKerberosOptionsforconfiguringLDAPandKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalIdMserversWhenusingIdMwithintegratedDNSBydefault,clientsuseautomaticservicelookupbasedontheDNSrecords.
Inthissetup,youcanalsousetheDNSlocationsfeaturetoconfigureDNS-basedservicediscovery.
Tooverridetheautomaticlookup,youcandisabletheDNSdiscoveryinoneofthefollowingways:DuringtheIdMclientinstallationbyprovidingfailoverparametersfromthecommandlineAftertheclientinstallationbymodifyingtheSystemSecurityServicesDaemon(SSSD)configurationCHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD35WhenusingIdMwithoutintegratedDNSYoumustexplicitlyconfigureclientsinoneofthefollowingways:DuringtheIdMclientinstallationbyprovidingfailoverparametersfromthecommandlineAftertheclientinstallationbymodifyingtheSSSDconfigurationOptionsforconfiguringKerberosontheIdMclientforcommunicationwithlocalADserversIdMclientsareunabletoautomaticallydiscoverwhichADserverstocommunicatewith.
TospecifytheADserversmanually,modifythekrb5.
conffile:AddtheADrealminformationExplicitlylisttheADserverstocommunicatewithForexample:[realms]AD.
EXAMPLE.
COM={kdc=server1.
ad.
example.
comkdc=server2.
ad.
example.
com}OptionsforconfiguringembeddedclientsonIdMserversforcommunicationwithlocalADserversoverKerberosandLDAPTheembeddedclientonanIdMserverworksalsoasaclientoftheADserver.
ItcanautomaticallydiscoverandusetheappropriateADsite.
Whentheembeddedclientperformsthediscovery,itmightfirstdiscoveranADserverinaremotelocation.
Iftheattempttocontacttheremoteservertakestoolong,theclientmightstoptheoperationwithoutestablishingtheconnection.
Usethedns_resolver_timeoutoptioninthesssd.
conffileontheclienttoincreasetheamountoftimeforwhichtheclientwaitsforareplyfromtheDNSresolver.
Seethesssd.
conf(5)manpagefordetails.
OncetheembeddedclienthasbeenconfiguredtocommunicatewiththelocalADservers,theSSSDrememberstheADsitetheembeddedclientbelongsto.
Thankstothis,SSSDnormallysendsanLDAPpingdirectlytoalocaldomaincontrollertorefreshitssiteinformation.
Ifthesitenolongerexistsortheclienthasmeanwhilebeenassignedtoadifferentsite,SSSDstartsqueryingforSRVrecordsintheforestandgoesthroughawholeprocessofautodiscovery.
Usingtrusteddomainsectionsinsssd.
conf,youcanalsoexplicitlyoverridesomeoftheinformationthatisdiscoveredautomaticallybydefault.
6.
9.
OPERATIONSPERFORMEDDURINGINDIRECTINTEGRATIONOFIDMTOADTable6.
2,"OperationsperformedfromanIdMtrustcontrollertowardsADdomaincontrollers"showswhichoperationsandrequestsareperformedduringthecreationofanIdentityManagement(IdM)toActiveDirectory(AD)trustfromtheIdMtrustcontrollertowardsADdomaincontrollers.
Table6.
2.
OperationsperformedfromanIdMtrustcontrollertowardsADdomaincontrollersRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement36OperationProtocolusedPurposeDNSresolutionagainsttheADDNSresolversconfiguredonanIdMtrustcontrollerDNSTodiscovertheIPaddressesofADdomaincontrollersRequeststoUDP/UDP6port389onanADDCConnectionlessLDAP(CLDAP)ToperformADDCdiscoveryRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports389and3268onanADDCLDAPToqueryADuserandgroupinformationRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports389and3268onanADDCDCERPCandSMBTosetupandsupportcross-foresttrusttoADRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports135,139,445onanADDCDCERPCandSMBTosetupandsupportcross-foresttrusttoADRequeststodynamicallyopenedportsonanADDCasdirectedbytheActiveDirectorydomaincontroller,likelyintherangeof49152-65535(TCP/TCP6)DCERPCandSMBTorespondtorequestsbyDCERPCEnd-pointmapper(port135TCP/TCP6)Requeststoports88(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),464(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),and749(TCP/TCP6)onanADDCKerberosToobtainaKerberosticket;changeaKerberospassword;administerKerberosremotelyTable6.
3,"OperationsperformedfromanADdomaincontrollertowardsIdMtrustcontrollers"showswhichoperationsandrequestsareperformedduringthecreationofanIdMtoADtrustfromtheADdomaincontrollertowardsIdMtrustcontrollers.
Table6.
3.
OperationsperformedfromanADdomaincontrollertowardsIdMtrustcontrollersOperationProtocolusedPurposeDNSresolutionagainsttheIdMDNSresolversconfiguredonanADdomaincontrollerDNSTodiscovertheIPaddressesofIdMtrustcontrollersRequeststoUDP/UDP6port389onanIdMtrustcontrollerCLDAPToperformIdMtrustcontrollerdiscoveryRequeststoTCP/TCP6ports135,139,445onanIdMtrustcontrollerDCERPCandSMBToverifythecross-foresttrusttoADCHAPTER6.
PLANNINGACROSS-FORESTTRUSTBETWEENIDMANDAD37RequeststodynamicallyopenedportsonanIdMtrustcontrollerasdirectedbytheIdMtrustcontroller,likelyintherangeof49152-65535(TCP/TCP6)DCERPCandSMBTorespondtorequestsbyDCERPCEnd-pointmapper(port135TCP/TCP6)Requeststoports88(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),464(TCP/TCP6andUDP/UDP6),and749(TCP/TCP6)onanIdMtrustcontrollerKerberosToobtainaKerberosticket;changeaKerberospassword;administerKerberosremotelyOperationProtocolusedPurposeRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement38CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDMRedHatEnterpriseLinuxIdentityManagementprovidesasolutiontomanuallybackupandrestoretheIdMsystem.
Thismaybenecessaryafteradatalossevent.
Duringbackup,thesystemcreatesadirectorycontaininginformationonyourIdMsetupandstoresit.
Duringrestore,youcanusethisbackupdirectorytobringyouroriginalIdMsetupback.
NOTETheIdMbackupandrestorefeaturesaredesignedtohelppreventdataloss.
Tomitigatetheimpactoflosingaserver,andensurecontinuedoperationbyprovidingalternativeserverstoclients,ensureyouhaveareplicatopologyaccordingtoMitigatingserverlosswithreplication.
7.
1.
IDMBACKUPTYPESIdMprovidestwotypesofbackups:afull-serverbackup,andadata-onlybackup.
BackuptypeBackupcontentsPerformedOnlineorOfflineSuitableforFull-serverbackupAllserverconfigurationfilesrelatedtoIdMLDAPdatainLDAPDataInterchangeFormat(LDIF)Offlineonly.
IdMservicesmustbetemporarilystopped.
RebuildinganIdMdeploymentfromscratchData-onlybackupLDAPdatainLDAPDataInterchangeFormat(LDIF)ReplicationChangelogOnlineorOffline.
RestoringIdMdatatoastateinthepast7.
2.
NAMINGCONVENTIONSFORIDMBACKUPFILESBydefault,IdMstoresbackupsinthe/var/lib/ipa/backup/directory,andthenamingconventionsforthesesubdirectoriesare:Full-serverbackup:ipa-full-YEAR-MM-DD-HH-MM-SSinGMTtimeData-onlybackup:ipa-data-YEAR-MM-DD-HH-MM-SSinGMTtimeNOTEUninstallinganIdMserverdoesnotautomaticallyremoveanybackupfiles.
CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM397.
3.
CREATINGABACKUPThissectiondescribeshowtocreateafull-serveranddata-onlybackupinofflineandonlinemodesusingtheipa-backupcommand.
IMPORTANTBydefault,ipa-backuprunsinofflinemode,whichwillstopallIdMservices.
Theserviceswillstartautomaticallyafterthebackupisfinished.
Afull-serverbackupmustalwaysrunwithIdMservicesoffline,butadata-onlybackupmaybeperformedwithservicesonline.
Bydefault,backupsarecreatedonthefilesystemcontainingthe/var/lib/ipa/backup/directory.
WerecommendcreatingbackupsregularlyonafilesystemseparatefromtheproductionfilesystemusedbyIdM,andarchivingthebackupstoafixedmedium(tapeoropticalstorage,forexample).
Considerperformingbackupsonhiddenreplicas.
IdMservicescanbeshutdownonhiddenreplicaswithoutaffectingIdMclients.
StartingwithRHEL8.
3.
0,theipa-backuputilitychecksifalloftheservicesusedinyourIdMcluster,suchasaCertificateAuthority(CA),DomainNameSystem(DNS),andKeyRecoveryAgent(KRA),areinstalledontheserverwhereyouarerunningthebackup.
Iftheserverdoesnothavealltheseservicesinstalled,theipa-backuputilityexitswithawarning,becausebackupstakenonthathostwouldnotbesufficientforafullclusterrestoration.
Forexample,ifyourIdMdeploymentusesanintegratedCertificateAuthority(CA),abackuprunonanon-CAreplicawillnotcaptureCAdata.
RedHatrecommendsverifyingthatthereplicawhereyouperformanipa-backuphasalloftheIdMservicesusedintheclusterinstalled.
YoucanbypasstheIdMserverrolecheckwiththeipa-backup--disable-role-checkcommand,buttheresultingbackupwillnotcontainallthedatanecessarytorestoreIdMfully.
Examplesofusingtheipa-backupcommandTocreateafull-serverbackupinofflinemode,usetheipa-backuputilitywithoutadditionaloptions.
[root@server~]#ipa-backupPreparingbackuponserver.
example.
comStoppingIPAservicesBackingupipacainEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupuserRootinEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupEXAMPLE-COMBackingupfilesStartingIPAserviceBackedupto/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-14-11-26-06Theipa-backupcommandwassuccessfulTocreateanofflinedata-onlybackup,specifythe--dataoption.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--dataRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement40Tocreateafull-serverbackupthatincludesIdMlogfiles,usethe--logsoption.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--logsTocreateadata-onlybackupwhileIdMservicesarerunning,specifyboth--dataand--onlineoptions.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--data--onlineNOTEIfthebackupfailsduetoinsufficientspaceinthe/tmpdirectory,usetheTMPDIRenvironmentvariabletochangethedestinationfortemporaryfilescreatedbythebackupprocess:[root@server~]#TMPDIR=/new/locationipa-backupFormoredetails,seeipa-backupCommandFailstoFinish.
VerificationStepsThebackupdirectorycontainsanarchivewiththebackup.
[root@server~]#ls/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-14-11-26-06headeripa-full.
tar7.
4.
CREATINGENCRYPTEDIDMBACKUPSYoucancreateencryptedbackupsusingGNUPrivacyGuard(GPG)encryption.
TocreateencryptedIdMbackups,youwillfirstneedtocreateaGPG2key.
7.
4.
1.
CreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackupsThefollowingproceduredescribeshowtogenerateaGPG2keyfortheipa-backuputility.
Procedure1.
Installandconfigurethepinentryutility.
[root@server~]#dnfinstallpinentry[root@server~]#mkdir~/.
gnupg-m700[root@server~]#echo"pinentry-program/usr/bin/pinentry-curses">>~/.
gnupg/gpg-agent.
conf2.
Createakey-inputfileusedforgeneratingaGPGkeypairwithyourpreferreddetails.
Forexample:[root@server~]#cat>key-inputb.
Confirmthecorrectpassphrasebyenteringitagain.
Pleasere-enterthispassphrasePassphrase:SecretPassphrase42c.
ThenewGPG2keyisnowcreated.
gpg:keybox'/root/backup/pubring.
kbx'createdgpg:Generatingastandardkeygpg:/root/backup/trustdb.
gpg:trustdbcreatedgpg:keyBF28FFA302EF4557markedasultimatelytrustedgpg:directory'/root/backup/openpgp-revocs.
d'createdgpg:revocationcertificatestoredas'/root/backup/openpgp-revocs.
d/8F6FCF10C80359D5A05AED67BF28FFA302EF4557.
rev'gpg:FinishedcreatingstandardkeyVerificationStepsRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement42VerificationStepsListtheGPGkeysontheserver.
[root@server~]#gpg2--list-secret-keysgpg:checkingthetrustdbgpg:marginalsneeded:3completesneeded:1trustmodel:pgpgpg:depth:0valid:1signed:0trust:0-,0q,0n,0m,0f,1u/root/backup/pubring.
kbxsecrsa20482020-01-13[SCEA]8F6FCF10C80359D5A05AED67BF28FFA302EF4557uid[ultimate]IPABackup(IPABackup)AdditionalresourcesFormoreinformationonGPGencryptionanditsuses,seetheGNUPrivacyGuardwebsite.
7.
4.
2.
CreatingaGPG2-encryptedIdMbackupThefollowingprocedurecreatesanIdMbackupandencryptsitusingaGPG2key.
PrerequisitesYouhavecreatedaGPG2key.
SeeCreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackups.
ProcedureCreateaGPG-encryptedbackupbyspecifyingthe--gpgoption.
[root@server~]#ipa-backup--gpgPreparingbackuponserver.
example.
comStoppingIPAservicesBackingupipacainEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupuserRootinEXAMPLE-COMtoLDIFBackingupEXAMPLE-COMBackingupfilesStartingIPAserviceEncrypting/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-13-14-38-00/ipa-full.
tarBackedupto/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-13-14-38-00Theipa-backupcommandwassuccessfulVerificationStepsEnsurethatthebackupdirectorycontainsanencryptedarchivewitha.
gpgfileextension.
[root@server~]#ls/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-13-14-38-00headeripa-full.
tar.
gpgAdditionalresourcesForgeneralinformationoncreatingabackup,seeCreatingabackup.
CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM437.
5.
WHENTORESTOREFROMANIDMBACKUPYoucanrespondtoseveraldisasterscenariosbyrestoringfromanIdMbackup:UndesirablechangesweremadetotheLDAPcontent:Entriesweremodifiedordeleted,replicationcarriedoutthosechangesthroughoutthedeployment,andyouwanttorevertthosechanges.
Restoringadata-onlybackupreturnstheLDAPentriestothepreviousstatewithoutaffectingtheIdMconfigurationitself.
TotalInfrastructureLoss,orlossofallCAinstances:IfadisasterdamagesallCertificateAuthorityreplicas,thedeploymenthaslosttheabilitytorebuilditselfbydeployingadditionalservers.
Inthissituation,restoreabackupofaCAReplicaandbuildnewreplicasfromit.
Anupgradeonanisolatedserverfailed:Theoperatingsystemremainsfunctional,buttheIdMdataiscorrupted,whichiswhyyouwanttorestoretheIdMsystemtoaknowngoodstate.
RedHatrecommendsworkingwithTechnicalSupportinordertodiagnoseandtroubleshoottheissue.
Ifthoseeffortsfail,restorefromafull-serverbackup.
IMPORTANTThepreferredsolutionforhardwareorupgradefailureistorebuildthelostserverfromareplica.
Formoreinformation,seeRecoveringfromserverlosswithreplication.
7.
6.
CONSIDERATIONSWHENRESTORINGFROMANIDMBACKUPIfyouhaveabackupcreatedwiththeipa-backuputility,youcanrestoreyourIdMserverortheLDAPcontenttothestatetheywereinwhenthebackupwasperformed.
ThefollowingarethekeyconsiderationswhilerestoringfromanIdMbackup:Youcanonlyrestoreabackuponaserverthatmatchestheconfigurationofserverwherethebackupwasoriginallycreated.
Theservermusthave:ThesamehostnameThesameIPaddressThesameversionofIdMsoftwareIfoneIdMserverinamulti-masterenvironmentisrestored,therestoredserverbecomestheonlysourceofinformationforIdM.
Allothermasterserversmustbere-initializedfromtherestoredserver.
Sinceanydatacreatedafterthelastbackupwillbelost,donotusethebackupandrestoresolutionfornormalsystemmaintenance.
Ifaserverislost,RedHatrecommendsrebuildingtheserverbyreinstallingitasareplicainsteadofrestoringfromabackup.
Creatinganewreplicapreservesdatafromthecurrentworkingenvironment.
Formoreinformation,seePreparingforserverlosswithreplication.
ThebackupandrestorefeaturescanonlybemanagedfromthecommandlineandarenotavailableintheIdMwebUI.
TIPRedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement44TIPRestoringfromabackuprequiresthesamesoftware(RPM)versionsonthetargethostaswereinstalledwhenthebackupwasperformed.
Duetothis,RedHatrecommendsrestoringfromaVirtualMachinesnapshotratherthanabackup.
Formoreinformation,seeRecoveringfromdatalosswithVMsnapshots.
7.
7.
RESTORINGANIDMSERVERFROMABACKUPThefollowingproceduredescribesrestoringanIdMserver,oritsLDAPdata,fromanIdMbackup.
Figure7.
1.
ReplicationTopologyusedinthisexampleTable7.
1.
ServernamingconventionsusedinthisexampleServerNameFunctionmaster1.
example.
comTheserverthatneedstoberestoredfrombackupcaReplica2.
example.
comACertificateAuthority(CA)replicaconnectedtomaster1.
example.
com.
replica3.
example.
comAreplicaconnectedtocaReplica2.
example.
com.
PrerequisitesAfull-serverordata-onlybackupoftheIdMserverwasgeneratedwiththeipa-backuputility.
SeeCreatingabackup.
Beforeperformingafull-serverrestorefromafull-serverbackup,uninstallIdMfromtheserverandreinstallIdMusingthesameserverconfigurationasbefore.
Procedure1.
Usetheipa-restoreutilitytorestoreafull-serverordata-onlybackup.
Ifthebackupdirectoryisinthedefault/var/lib/ipa/backup/location,enteronlythenameofthedirectory:[root@master1~]#ipa-restoreipa-full-2020-01-14-12-02-32Ifthebackupdirectoryisnotinthedefaultlocation,enteritsfullpath:[root@master1~]#ipa-restore/mybackups/ipa-data-2020-02-01-05-30-00NOTECHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM45NOTETheipa-restoreutilityautomaticallydetectsthetypeofbackupthatthedirectorycontains,andperformsthesametypeofrestorebydefault.
Toperformadata-onlyrestorefromafull-serverbackup,addthe--dataoptiontoipa-restore:[root@master1~]#ipa-restore--dataipa-full-2020-01-14-12-02-322.
EntertheDirectoryManagerpassword.
DirectoryManager(existingmaster)password:3.
Enteryestoconfirmoverwritingcurrentdatawiththebackup.
Preparingrestorefrom/var/lib/ipa/backup/ipa-full-2020-01-14-12-02-32onmaster1.
example.
comPerformingFULLrestorefromFULLbackupTemporarysettingumaskto022Restoringdatawilloverwriteexistinglivedata.
Continuetorestore[no]:yes4.
Theipa-restoreutilitydisablesreplicationonallserversthatareavailable:Eachmasterwillindividuallyneedtobere-initializedorre-createdfromthisone.
ThereplicationagreementsonmastersrunningIPA3.
1orearlierwillneedtobemanuallyre-enabled.
Seethemanpagefordetails.
Disablingallreplication.
Disablingreplicationagreementonmaster1.
example.
comtocaReplica2.
example.
comDisablingCAreplicationagreementonmaster1.
example.
comtocaReplica2.
example.
comDisablingreplicationagreementoncaReplica2.
example.
comtomaster1.
example.
comDisablingreplicationagreementoncaReplica2.
example.
comtoreplica3.
example.
comDisablingCAreplicationagreementoncaReplica2.
example.
comtomaster1.
example.
comDisablingreplicationagreementonreplica3.
example.
comtocaReplica2.
example.
comTheutilitythenstopsIdMservices,restoresthebackup,andrestartstheservices:StoppingIPAservicesSystemwideCAdatabaseupdated.
RestoringfilesSystemwideCAdatabaseupdated.
RestoringfromuserRootinEXAMPLE-COMRestoringfromipacainEXAMPLE-COMRestartingGSS-proxyStartingIPAservicesRestartingSSSDRestartingoddjobdRestoringumaskto18Theipa-restorecommandwassuccessful5.
Re-initializeallreplicasconnectedtotherestoredserver:a.
Listallreplicationtopologysegmentsforthedomainsuffix,takingnoteoftopologysegmentsinvolvingtherestoredserver.
RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement46[root@master1~]#ipatopologysegment-finddomain2segmentsmatchedSegmentname:master1.
example.
com-to-caReplica2.
example.
comLeftnode:master1.
example.
comRightnode:caReplica2.
example.
comConnectivity:bothSegmentname:caReplica2.
example.
com-to-replica3.
example.
comLeftnode:caReplica2.
example.
comRightnode:replica3.
example.
comConnectivity:bothNumberofentriesreturned2b.
Re-initializethedomainsuffixforalltopologysegmentswiththerestoredserver.
Inthisexample,performare-initializationofcaReplica2withdatafrommaster1.
[root@caReplica2~]#ipa-replica-managere-initialize--from=master1.
example.
comUpdateinprogress,2secondselapsedUpdatesucceededc.
MovingontoCertificateAuthoritydata,listallreplicationtopologysegmentsforthecasuffix.
[root@master1~]#ipatopologysegment-findca1segmentmatchedSegmentname:master1.
example.
com-to-caReplica2.
example.
comLeftnode:master1.
example.
comRightnode:caReplica2.
example.
comConnectivity:bothNumberofentriesreturned1d.
Re-initializeallCAreplicasconnectedtotherestoredserver.
Inthisexample,performacsreplicare-initializationofcaReplica2withdatafrommaster1.
[root@caReplica2~]#ipa-csreplica-managere-initialize--from=master1.
example.
comDirectoryManagerpassword:Updateinprogress,3secondselapsedUpdatesucceeded6.
Continuemovingoutwardthroughthereplicationtopology,re-initializingsuccessivereplicas,untilallservershavebeenupdatedwiththedatafromrestoredservermaster1.
example.
com.
Inthisexample,weonlyhavetore-initializethedomainsuffixonreplica3withthedatafromcaReplica2:CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM47[root@replica3~]#ipa-replica-managere-initialize--from=caReplica2.
example.
comDirectoryManagerpassword:Updateinprogress,3secondselapsedUpdatesucceeded7.
ClearSSSD'scacheoneveryserverinordertoavoidauthenticationproblemsduetoinvaliddata:a.
StoptheSSSDservice:[root@server~]#systemctlstopsssdb.
RemoveallcachedcontentfromSSSD:[root@server~]#sss_cache-Ec.
StarttheSSSDservice:[root@server~]#systemctlstartsssdd.
Reboottheserver.
AdditionalresourcesTheipa-restore(1)manpagealsocoversindetailhowtohandlecomplexreplicationscenariosduringrestoration.
7.
8.
RESTORINGFROMANENCRYPTEDBACKUPTheipa-restoreutilityautomaticallydetectsifanIdMbackupisencrypted,andrestoresitusingtheGPG2rootkeyringandgpg-agentbydefault.
PrerequisitesAGPG-encryptedIdMbackup.
SeeCreatingencryptedIdMbackups.
TheLDAPDirectoryManagerpasswordThePassphraseusedwhencreatingtheGPGkeyProcedure1.
IfyouusedacustomkeyringlocationwhencreatingtheGPG2keys,makesurethatthe$GNUPGHOMEenvironmentvariableissettothatdirectory.
SeeCreatingaGPG2keyforencryptingIdMbackups.
[root@server~]#echo$GNUPGHOME/root/backup2.
Providetheipa-restoreutilitywiththebackupdirectorylocation.
[root@server~]#ipa-restoreipa-full-2020-01-13-18-30-54RedHatEnterpriseLinux8PlanningIdentityManagement48a.
EntertheDirectoryManagerpassword.
DirectoryManager(existingmaster)password:b.
EnterthePassphraseyouusedwhencreatingtheGPGkey.
PleaseenterthepassphrasetounlocktheOpenPGPsecretkey:"IPABackup(IPABackup)"2048-bitRSAkey,IDBF28FFA302EF4557,created2020-01-13.
Passphrase:SecretPassPhrase423.
Re-initializeallreplicasconnectedtotherestoredserver.
SeeRestoringanIdMserverfrombackup.
CHAPTER7.
BACKINGUPANDRESTORINGIDM49
- simplertrustview相关文档
- 978-1-4799-6065-1/15/$31.00
- ssstrustview
- Cordestrustview
- ,"网络安全扫描"
- 解析trustview
- verifytrustview
极光KVM美国美国洛杉矶元/极光kvmCN7月促销,美国CN2 GIA大带宽vps,洛杉矶联通CUVIP,14元/月起
极光KVM怎么样?极光KVM本月主打产品:美西CN2双向,1H1G100M,189/年!在美西CN2资源“一兆难求”的大环境下,CN2+大带宽 是很多用户的福音,也是商家实力的象征。目前,极光KVM在7月份的促销,7月促销,美国CN2 GIA大带宽vps,洛杉矶联通cuvip,14元/月起;香港CN2+BGP仅19元/月起,这次补货,机会,不要错过了。点击进入:极光KVM官方网站地址极光KVM七月...
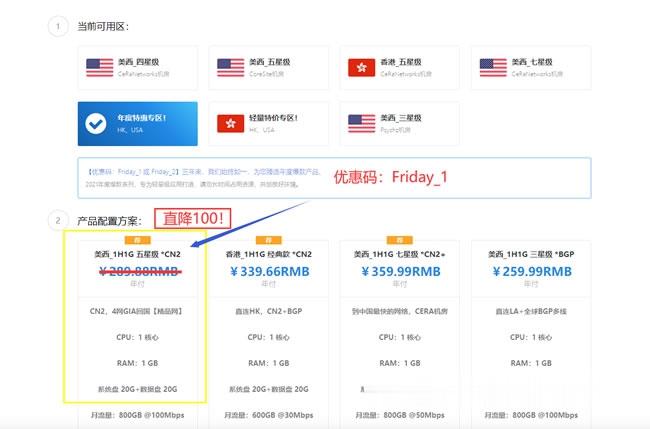
LiCloud:香港CMI/香港CN2+BGP服务器,30Mbps,$39.99/月;香港KVM VPS仅$6.99/月
licloud怎么样?licloud目前提供香港cmi服务器及香港CN2+BGP服务器/E3-1230v2/16GB内存/240GB SSD硬盘/不限流量/30Mbps带宽,$39.99/月。licloud 成立於2021年,是香港LiCloud Limited(CR No.3013909)旗下的品牌,主要提供香港kvm vps,分为精简网络和高级网络A、高级网络B,现在精简网络和高级网络A。现在...

阿里云年中活动最后一周 - ECS共享型N4 2G1M年付59元
以前我们在参与到云服务商促销活动的时候周期基本是一周时间,而如今我们会看到无论是云服务商还是电商活动基本上周期都要有超过一个月,所以我们有一些网友习惯在活动结束之前看看商家是不是有最后的促销活动吸引力的,比如有看到阿里云年中活动最后一周,如果我们有需要云服务器的可以看看。在前面的文章中(阿里云新人福利选择共享性N4云服务器年79.86元且送2月数据库),(LAOZUO.ORG)有提到阿里云今年的云...
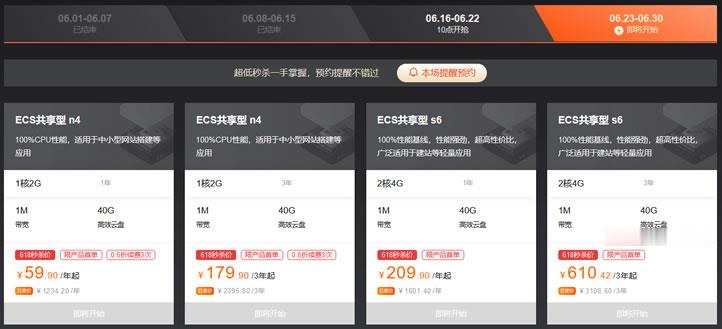
trustview为你推荐
-
火影忍者644火影忍者420到现在644中间讲了什么啊? 太多了看不完==谁来大体说一下桌面背景图片淡雅桌面壁纸的壁纸美化316不锈钢和304哪个好304和316不锈钢区别哪个好输入法哪个好用输入法那个软件好苹果手机助手哪个好最新版iphone助手 PP助手好用吗?dnf魔枪士转职哪个好dnf平民魔枪士转什么好雅思和托福哪个好考托福和雅思哪个好考 急。。。。。云盘哪个好免费的网盘哪个实用?云盘哪个好免费的网盘哪个好用啊?考生个人空间登录如何找回 自考考生个人空间的密码?