0.014www.gogo.com
www.gogo.com 时间:2021-03-20 阅读:()
RESEARCHOpenAccessIshypoglycemiafearindependentlyassociatedwithhealth-relatedqualityoflifeLizhengShi1*,HuiShao1,YingnanZhao2andNinaAThomas3AbstractObjective:Patientsmayfearthesymptomsandconsequencesassociatedwithhypoglycemia.
Wetestedwhetherfearofhypoglycemiaisindependentlyassociatedwithpoorerhealth-relatedqualityoflife(HRQOL).
Researchdesignandmethods:Datawerecollectedusingdirect-mailsurveyandenrollmentinformationfromadultcommercialhealthplanenrolleeswithtype2diabetesduringa12-monthperiod(12/01/2008to11/30/2009).
HRQOLwasevaluatedbytheEuroQol(EQ)–5Dindexand12-itemShortFormHealthSurveyMentalComponentSummary(SF-12MCS)andPhysicalComponentSummary(SF-12PCS).
FearofhypoglycemiawasassessedusingtheHypoglycemiaFearSurvey(HFS).
Twoordinaryleast-squares(OLS)modelsofHRQOLcontrollingfordemographicsandillnesscharacteristicswerespecified,andOLSregressioncoefficientsandstatisticalinferenceswerecompared.
Model1included1variableofhypoglycemiasymptoms;Model2includedbothhypoglycemiasymptomsandHFSscore.
Results:Of3999patientscontacted,813respondedtothesurvey.
Model1:hypoglycemiasymptomsalonewereassociatedwithworseHRQOL(SF-12MCSandSF-12PCSscoresandEQ-5Dutilityscore;allP10pointsofHFStotalscore,P0.
05).
Model2showedthattheHFSscorewasstillsignificantlyassociatedwithscoresonall3HRQOLoutcomes(eachP0.
05).
Forsulfonylureausers(n=246),Model1showedthatthesymptomatichypoglycemiawasassociatedwithEQ-5DscoresandSF-12MCSscores(eachP1020(8.
6)69(12.
0)EthnicityWhiteNo52(22.
5)161(28.
3)0.
0961Yes179(77.
5)409(71.
8)BlackorAfricanAmericanNo196(84.
9)469(82.
3)0.
3806Yes35(15.
2)101(17.
7)HispanicorLatinoNo209(89.
7)525(92.
3)0.
2360Yes24(10.
3)44(7.
7)MaritalstatusSingle,nevermarried25(10.
7)68(11.
8)0.
6079Married167(71.
4)390(67.
7)Divorced32(13.
7)82(14.
2)Separated2(0.
9)14(2.
4)Widowed8(3.
4)22(3.
8)Annualhouseholdincome,$US100,00063(28.
4)142(25.
9)Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page4of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167Table1Populationcharacteristicsbetweenpatientswhoreportedversusthosewhodidnotreportsymptomsofhypoglycemia(Continued)EducationLessthansecondary9(3.
9)14(2.
5)0.
8425Somesecondary4(1.
7)14(2.
5)Secondaryorequivalent53(22.
8)131(22.
9)Tertiarybutnodegree60(25.
8)166(29.
0)2-yearundergraduatedegree28(12.
0)59(10.
3)>2-yearundergraduatedegree51(21.
9)199(20.
8)Graduateschool28(12.
0)69(12.
1)USRegionNortheast13(5.
5)33(5.
7)0.
2144Midwest29(12.
3)54(9.
3)South181(77.
0)440(76.
1)West12(5.
1)51(8.
8)MoriskyadherenceLow123(52.
8)265(46.
3)0.
3058Relativelylow71(30.
5)186(32.
5)Middle28(12.
0)77(13.
4)Relativelyhigh10(4.
3)36(6.
3)High1(0.
4)9(1.
6)OAD=oralantidiabeticmedication;SU=sulfonylurea.
*Chi-squaretest.
SF-12PCSNoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia0102030405060HFSNoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia010203040*NoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia0.
00.
20.
40.
60.
81.
01.
2*EQ-5DSF-12MCSNoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia0102030405060*Figure1Comparisonofhealth-relatedquality-of-lifescoresandfearofhypoglycemiabetweenpatientswhoreported(n=235)vsthosewhodidnotreport(n=578)symptomsofhypoglycemia.
EQ-5D=EuroQol-5Dscale;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
*P<0.
0001,P=0.
0007byttest.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page5of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167shownanassociationbetweenfearofhypoglycemiaandHRQOL[29,32].
Asignificantassociationwasobservedbetweensymp-tomatichypoglycemiaandEQ-5DandSF-12MCSscoresinModel1,whereasonlytheassociationwithSF-12MCSwassignificantafterincorporatingtheHFSintothemodel.
Incontrast,fearofhypoglycemiademon-stratedasignificantassociationwithall3HRQOLout-comes.
Thisfindingsuggeststhat,statistically,fearofhypoglycemiamaybeamoreimportantpredictorthanhypoglycemiaitselfofpatientwell-beingandhealthstatus.
Multiplefactorsassociatedwithfearofhypoglycemiawereidentified.
Consistentwithourstudy[16]andotherreports[29,31,33],symptomatichypoglycemiahadthestrongest(positive)associationwithfearofhypoglycemia.
Thus,itappearsthatinpatientswithtype2diabetes,ex-periencinganeventofhypoglycemiaincreasesratherthandiminishesfearofsuchanevent.
AnimportantclinicalpracticeimplicationofthisfindingistheneedforTable2InfluencingfactorsofhypoglycemiafearsurveytotalscoresVariable(reference)RegressioncoefficientStandarderrorPvalue95%CILowerUpperHypoglycemia10.
471.
28<0.
00017.
9512.
99Age(<65y)≥65y1.
231.
910.
524.
982.
51Sex(male)Female1.
761.
230.
154.
170.
66Bodymassindex0.
100.
080.
220.
250.
06Familyhistoryofdiabetes0.
581.
370.
673.
272.
10Treatment(SUwithoutinsulin)Non-SUOADwithoutinsulin2.
251.
440.
125.
090.
58AnyOADwithinsulin2.
091.
420.
140.
714.
89Durationofcurrentdiabetesmedication0.
700.
470.
141.
630.
23EthnicityWhite(notwhite)4.
561.
35<0.
00017.
221.
91HispanicorLatino(notHispanicorLatino)4.
742.
130.
030.
568.
92Married(currentlynotmarried)0.
041.
290.
972.
592.
50Householdincomelevel1.
940.
47<0.
00012.
861.
03Education(lessthansecondary)0.
753.
560.
836.
257.
75Region(Northeast)Midwest1.
242.
820.
664.
296.
77South1.
412.
330.
553.
175.
99West0.
213.
140.
955.
966.
37Diabetesduration(y)0.
360.
08<0.
00010.
200.
52Moriskyadherence1.
720.
60<0.
00010.
542.
91OAD=oralantidiabeticmedication;SU=sulfonylurea.
Table3Roleofhypoglycemiafearonhealth-relatedqualityoflifeusingalternativemodelsVariableEQ-5D(US)SF-12MCSSF-12PCSβPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforβModel1Hypo0.
0410.
0020.
067to0.
0153.
628<0.
00015.
259to1.
9980.
9740.
2472.
623to0.
675Model2Hypo0.
0140.
3030.
040to0.
0131.
9370.
0223.
591to0.
2830.
5790.
5001.
104to2.
262HFS0.
003<0.
00010.
003to0.
0020.
162<0.
00010.
210to0.
1150.
149<0.
00010.
197to0.
101β=regressioncoefficient;EQ=EuroQol;Hypo=symptomatichypoglycemia;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page6of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167healthcareprofessionalstobecognizantofthefearofhypoglycemiaandtakestepstoaddressthisfearandre-latedbehaviors.
Inthecurrentanalysis,Hispanic/Latinoethnicity,dur-ationofdiabetes,andself-reportedadherencealsoshowedapositiveassociationwithfearofhypoglycemia,whereashouseholdincomeandwhiteraceshowedanegativeassociation.
Thesedatasuggestthatdemo-graphicvariablesmightbehelpfulinpredictingthosepatientsmostlikelytoexperiencefearofhypoglycemia.
Thepositiveassociationbetweendurationofdiabetesandfearofhypoglycemiacouldreflectgreaterinsulinuseinpatientswithalongerdurationofdisease.
Alter-natively,anindependentassociationbetweenthesevari-ableswouldseemtofurtherindicatethatexperiencinghypoglycemiaincreasesfearoftheevent.
Asnocausalitycanbeinferredinthiscross-sectionalanalysis,thepositiverelationshipbetweenself-reportedadherenceandfearofhypoglycemiaisdifficulttointer-pret.
Inapreviousstudy,patientsreportinghypoglycemiasymptomsweremorelikelytoreportbarrierstoadher-ence(eg,botheredbymedicationsideeffects,unabletofollowplans)[4].
Inaddition,datasuggestthatpatientswhohaveexperiencedahypoglycemicepisodearelikelytoinitiatepreventivebehaviorsthatmayincludemodifica-tionoftheirdosingregimen[14,16].
Althoughthesefind-ingsmayseematoddswithoneanother,itisreasonabletoexpectthatpatientsadherenttostrictglycemiccontrolregimenswouldhavemorereasontobefearfulofhypoglycemia.
Additionalstudieswithlongitudinaldatacollectionareneededtofullyunderstandthevariablesthatpredictfearofhypoglycemia.
Predictorsofhypoglycemiainpatientswithtype2dia-betesarebetterunderstood.
Inthecurrentanalysis,morewomenversusmenandmorepatientstreatedwithOADplusinsulinversussulfonylureawithoutinsulinornonsul-fonylureaOADwithoutinsulinreportedhypoglycemia.
Thedifferenceinhypoglycemiawithrespecttodiabetestherapyistobeexpected,giventhatinsulinandinsulinse-cretagoguesarethemostcommoncauseofhypoglycemiainpatientswithtype2diabetes[15].
Theobservationthatmorewomenthanmenreportedhypoglycemicsymptomswasunexpectedbuthasbeenobservedinanotherstudy[29]andcouldpossiblyreflectsex-relateddifferencesinself-reportingofhypoglycemicsymptoms.
Thisanalysishassomelimitations.
Becausethestudywascross-sectional,nocausalrelationshipscanbein-ferredfromthefindings.
Dataonthefrequencyandse-verityofhypoglycemicepisodeswerenotcollectedsotheircontributiontofearofhypoglycemiacouldnotbeassessed.
Also,becausethesurveydesignusedacon-veniencesampleofpatientsthatincludedonlythosewhoweremembersofspecifichealthplans,withvolun-taryparticipation,surveyparticipantsmaynotberepre-sentativeofallpatientswithtype2diabetes.
Thestudyalsoreliedonpatientself-report,andthesurveyhadapatientrecallperiodof6months.
LongitudinalcohortstudiesarewarrantedtofurtherunderstandtheimpactofhypoglycemiaandtotestpotentialinterventionstoaddresstheissueofhypoglycemiafeartoimprovehealthTable4Roleofhypoglycemiafearonhealth-relatedqualityoflifeusingalternativemodels(InsulinSubgroup)VariableEQ-5D(US)SF-12MCSSF-12PCSβPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforβModel1Hypo0.
0010.
960.
058to0.
0552.
5060.
1375.
813to0.
8011.
6680.
3595.
244to1.
908Model2Hypo0.
0290.
3110.
027to0.
0860.
2850.
8633.
534to2.
9650.
3580.
8474.
011to3.
296HFS0.
003<0.
0010.
004to0.
0010.
188<0.
00010.
259to0.
1160.
111<0.
0070.
191to0.
031β=regressioncoefficient;EQ=EuroQol;Hypo=symptomatichypoglycemia;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
Table5Roleofhypoglycemiafearonhealth-relatedqualityoflifeusingalternativemodels(SulfonylureaSubgroup)VariableEQ-5D(US)SF-12MCSSF-12PCSβPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforβModel1Hypo0.
0770.
0010.
123to0.
0316.
531<0.
0019.
606to3.
4561.
8150.
2414.
857to1.
226Model2Hypo0.
0600.
0140.
107to-0.
0135.
3000.
0018.
453to2.
1470.
0560.
9712.
973to3.
084HFS0.
0020.
0140.
004to0.
0000.
1400.
0080.
243to0.
0380.
213<0.
0010.
311to0.
114β=regressioncoefficient;EQ=EuroQol;Hypo=symptomatichypoglycemia;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page7of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167forpatientswithdiabetes.
Inconclusion,inadditiontosymptomatichypoglycemiaitself,fearofhypoglycemiawasindependentlyassociatedwithlowerHRQOL(over-allhealthstatus,mentalhealth,andphysicalhealth)inpatientswithtype2diabetes.
Thereisanunmetneedforpatienteducationprogramsthataddresspatientfearofhypoglycemiaanduseofmedicationswithalowerriskofhypoglycemia.
AdditionalfileAdditionalfile1:TableS1.
1FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel1:EQ-5D(US).
TableS1.
2FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel1:SF-12MCS.
TableS1.
3FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel1:SF-12PCS.
TableS1.
4FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel2:EQ-5D(US).
TableS1.
5FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel2:SF-12MCS.
TableS1.
6FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel2:SF-12PCS.
TableS2.
0HypoglycemiaModel1:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS2.
1HypoglycemiaModel1:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS2.
2HypoglycemiaModel1:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
TableS2.
3HypoglycemiaModel2:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS2.
4HypoglycemiaModel2:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS2.
5HypoglycemiaModel2:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
TableS3.
0HypoglycemiaModel1:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS3.
1HypoglycemiaModel1:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS3.
2HypoglycemiaModel1:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
TableS3.
3HypoglycemiaModel2:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS3.
4HypoglycemiaModel2:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS3.
5HypoglycemiaModel2:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
CompetinginterestsTheauthorsdeclarethattheyhavenocompetinginterests.
Authors'contributionsLSistheguarantorofthisarticle.
HSperformeddataanalysis.
YZreviewedtheresultsandimprovedmodelspecifications.
LS,HS,YZ,andNATreviewed,edited,andapprovedthemanuscript.
AcknowledgmentsTheauthorsthankVivianFonseca,MD,forhishelpfuldiscussionsduringthedevelopmentofthisstudy.
Allauthorscontributedtotheconceptanddesignofthestudy;theacquisition,analysis,andinterpretationofdata;developmentofthestatisticalanalysisplan;andreview/editingofthemanuscriptforcontent.
Allauthorshadfullaccesstothedataincludedinthemanuscriptandapprovedthefinalversion.
L.
S.
hasreceivedgrants(toTulane)fromNovartis,Takeda,andGenentechandhasreceivedhonorariaforconsultingfromAstraZeneca.
N.
A.
TisanemployeeofBristol-MyersSquibb.
Y.
Z.
andH.
S.
reportnopotentialconflicts.
ThestudywassponsoredbyAstraZeneca(Wilmington,DE).
MedicalwritingsupportforthepreparationofthismanuscriptwasprovidedbyDeborahM.
Campoli-Richards,BSPharm,RPh,NicoleStrangman,PhD,andJanetE.
Matsuura,PhD,ofCompleteHealthcareCommunications,Inc.
(ChaddsFord,PA),withfundingfromBristol-MeyersSquibbandAstraZeneca.
DatafromthisstudywerepresentedattheInternationalSocietyforPharmacoeconomicsandOutcomesResearch18thAnnualInternationalMeeting,May18–22,2013,NewOrleans,LA.
Authordetails1DepartmentofGlobalHealthSystemsandDevelopment,TulaneUniversitySchoolofPublicHealthandTropicalMedicine,NewOrleans,LA,USA.
2CollegeofPharmacy,XavierUniversityofLouisiana,NewOrleans,LA,USA.
3USHealthServicesResearch,Bristol-MyersSquibb,Princeton,NJ,USA.
Received:5May2014Accepted:6November2014References1.
ZhaoY,CampbellCR,FonsecaV,ShiL:Impactofhypoglycemiaassociatedwithantihyperglycemicmedicationsonvascularrisksinveteranswithtype2diabetes.
DiabetesCare2012,35:1126–1132.
2.
ZoungasS,PatelA,ChalmersJ,DeGalanBE,LiQ,BillotL,WoodwardM,NinomiyaT,NealB,MacMahonS,GrobbeeDE,PascalKengneA,MarreM,HellerS:Severehypoglycemiaandrisksofvasculareventsanddeath.
NEnglJMed2010,363:1410–1418.
3.
HsuPF,SungSH,ChengHM,YehJS,LiuWL,ChanWL,ChenCH,ChouP,ChuangSY:Associationofclinicalsymptomatichypoglycemiawithcardiovasculareventsandtotalmortalityintype2diabetes:anationwidepopulation-basedstudy.
DiabetesCare2013,36:894–900.
4.
AlvarezGuisasolaF,TofePovedanoS,KrishnarajahG,LyuR,MavrosP,YinD:Hypoglycaemicsymptoms,treatmentsatisfaction,adherenceandtheirassociationswithglycaemicgoalinpatientswithtype2diabetesmellitus:findingsfromtheReal-LifeEffectivenessandCarePatternsofDiabetesManagement(RECAP-DM)study.
DiabetesObesMetab2008,10:25–32.
5.
MarrettE,StargardtT,MavrosP,AlexanderCM:Patient-reportedoutcomesinasurveyofpatientstreatedwithoralantihyperglycaemicmedications:associationswithhypoglycaemiaandweightgain.
DiabetesObesMetab2009,11:1138–1144.
6.
PollackMF,PurayidathilFW,BolgeSC,WilliamsSA:Patient-reportedtolerabilityissueswithoralantidiabeticagents:associationswithadherence;treatmentsatisfactionandhealth-relatedqualityoflife.
DiabetesResClinPract2010,87:204–210.
7.
GreenAJ,FoxKM,GrandyS:Self-reportedhypoglycemiaandimpactonqualityoflifeanddepressionamongadultswithtype2diabetesmellitus.
DiabetesResClinPract2012,96:313–318.
8.
WilliamsSA,PollackMF,DiBonaventuraM:Effectsofhypoglycemiaonhealth-relatedqualityoflife,treatmentsatisfactionandhealthcareresourceutilizationinpatientswithtype2diabetesmellitus.
DiabetesResClinPract2011,91:363–370.
9.
InzucchiSE,BergenstalRM,BuseJB,DiamantM,FerranniniE,NauckM,PetersAL,TsapasA,WenderR,MatthewsDR:Managementofhyperglycemiaintype2diabetes:apatient-centeredapproach:positionstatementoftheAmericanDiabetesAssociation(ADA)andtheEuropeanAssociationfortheStudyofDiabetes(EASD).
DiabetesCare2012,35:1364–1379.
10.
BruntonSA:Hypoglycemicpotentialofcurrentandemergingpharmacotherapiesintype2diabetesmellitus.
PostgradMed2012,124:74–83.
11.
CryerPE:Hypoglycemia:stillthelimitingfactorintheglycemicmanagementofdiabetes.
EndocrPract2008,14:750–756.
12.
WildD,vonMaltzahnR,BrohanE,ChristensenT,ClausonP,Gonder-FrederickL:Acriticalreviewoftheliteratureonfearofhypoglycemiaindiabetes:implicationsfordiabetesmanagementandpatienteducation.
PatientEducCouns2007,68:10–15.
13.
PetterssonB,RosenqvistU,DeleskogA,JournathG,WandellP:Self-reportedexperienceofhypoglycemiaamongadultswithtype2diabetesmellitus(Exhype).
DiabetesResClinPract2011,92:19–25.
14.
LeiterLA,YaleJ,ChiassonJ,HarrisS,KleinstiverP,SauriolL:Assessmentoftheimpactoffearofhypoglycemicepisodesonglycemicandhypoglycemiamanagement.
CanJDiabetes2005,29:186–192.
15.
AmielSA,DixonT,MannR,JamesonK:Hypoglycaemiaintype2diabetes.
DiabetMed2008,25:245–254.
16.
WilliamsSA,ShiL,BrennemanSK,JohnsonJC,WegnerJC,FonsecaV:Theburdenofhypoglycemiaonhealthcareutilization,costs,andqualityoflifeamongtype2diabetesmellituspatients.
JDiabetesComplications2012,26:399–406.
17.
MoriskyDE,GreenLW,LevineDM:Concurrentandpredictivevalidityofaself-reportedmeasureofmedicationadherence.
MedCare1986,24:67–74.
18.
CoxDJ,IrvineA,Gonder-FrederickL,NowacekG,ButterfieldJ:Fearofhypoglycemia:quantification,validation,andutilization.
DiabetesCare1987,10:617–621.
19.
MatzaLS,BoyeKS,YurginN:Validationoftwogenericpatient-reportedoutcomemeasuresinpatientswithtype2diabetes.
HealthQualLifeOutcomes2007,5:47.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page8of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/16720.
WhatisEQ-5D[http://www.
euroqol.
org].
21.
WareJJr,KosinskiM,KellerSD:A12-itemshort-formhealthsurvey:constructionofscalesandpreliminarytestsofreliabilityandvalidity.
MedCare1996,34:220–233.
22.
Livingwithdiabetes.
[http://www.
diabetes.
org/living-with-diabetes/treatment-and-care/blood-glucose-control/hypoglycemia-low-blood.
html]23.
SASInstituteInc:SAS/STATUser'sGuide.
Version9.
2.
Cary,NC:SASInstituteInc;2008.
24.
WrobelMP,WystrychowskiG,PsurekA,Szymborska-KajanekA,StrojekK:Associationbetweenhypoglycemiaandthetypeofinsulinindiabeticpatientstreatedwithmultipleinjections:anobservationalstudy.
PolArchMedWewn2014,124:173–179.
25.
PitsillidesAN,AndersonSM,KovatchevB:Hypoglycemiariskandglucosevariabilityindicesderivedfromroutineself-monitoringofbloodglucosearerelatedtolaboratorymeasuresofinsulinsensitivityandepinephrinecounterregulation.
DiabetesTechnolTher2011,13:11–17.
26.
KalraS,DeepakMC,NarangP,SinghV,MaheshwariA:Correlationbetweenmeasuresofhypoglycemiaandglycemicimprovementinsulfonylureatreatedpatientswithtype2diabetesinIndia:resultsfromtheOBSTACLEhypoglycemiastudy.
JPostgradMed2014,60:151–155.
27.
OdawaraM,KadowakiT,NaitoY:IncidenceandpredictorsofhypoglycemiainJapanesepatientswithtype2diabetestreatedbyinsulinglargineandoralantidiabeticdrugsinreal-life:ALOHApost-marketingsurveillancestudysub-analysis.
DiabetolMetabSyndr2014,6:20.
28.
SeaquistER,AndersonJ,ChildsB,CryerP,Dagogo-JackS,FishL,HellerSR,RodriguezH,RosenzweigJ,VigerskyR:Hypoglycemiaanddiabetes:areportofaworkgroupoftheAmericanDiabetesAssociationandTheEndocrineSociety.
DiabetesCare2013,36:1384–1395.
29.
MarrettE,RadicanL,DaviesMJ,ZhangQ:Assessmentofseverityandfrequencyofself-reportedhypoglycemiaonqualityoflifeinpatientswithtype2diabetestreatedwithoralantihyperglycemicagents:asurveystudy.
BMCResNotes2011,4:251.
30.
SheuWH,JiLN,NitiyanantW,BaikSH,YinD,MavrosP,ChanSP:Hypoglycemiaisassociatedwithincreasedworryandlowerqualityoflifeamongpatientswithtype2diabetestreatedwithoralantihyperglycemicagentsintheAsia-Pacificregion.
DiabetesResClinPract2012,96:141–148.
31.
StargardtT,Gonder-FrederickL,KrobotKJ,AlexanderCM:Fearofhypoglycaemia:definingaminimumclinicallyimportantdifferenceinpatientswithtype2diabetes.
HealthQualLifeOutcomes2009,7:91.
32.
SolliO,StavemK,KristiansenIS:Health-relatedqualityoflifeindiabetes:theassociationsofcomplicationswithEQ-5Dscores.
HealthQualLifeOutcomes2010,8:18.
33.
MitchellBD,VietriJ,ZagarA,CurtisB,ReaneyM:Hypoglycaemiceventsinpatientswithtype2diabetesintheUnitedKingdom:associationswithpatient-reportedoutcomesandself-reportedHbA1c.
BMCEndocrDisord2013,13:59.
doi:10.
1186/s12955-014-0167-3Citethisarticleas:Shietal.
:Ishypoglycemiafearindependentlyassociatedwithhealth-relatedqualityoflifeHealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes201412:167.
SubmityournextmanuscripttoBioMedCentralandtakefulladvantageof:ConvenientonlinesubmissionThoroughpeerreviewNospaceconstraintsorcolorgurechargesImmediatepublicationonacceptanceInclusioninPubMed,CAS,ScopusandGoogleScholarResearchwhichisfreelyavailableforredistributionSubmityourmanuscriptatwww.
biomedcentral.
com/submitShietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page9of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167
Wetestedwhetherfearofhypoglycemiaisindependentlyassociatedwithpoorerhealth-relatedqualityoflife(HRQOL).
Researchdesignandmethods:Datawerecollectedusingdirect-mailsurveyandenrollmentinformationfromadultcommercialhealthplanenrolleeswithtype2diabetesduringa12-monthperiod(12/01/2008to11/30/2009).
HRQOLwasevaluatedbytheEuroQol(EQ)–5Dindexand12-itemShortFormHealthSurveyMentalComponentSummary(SF-12MCS)andPhysicalComponentSummary(SF-12PCS).
FearofhypoglycemiawasassessedusingtheHypoglycemiaFearSurvey(HFS).
Twoordinaryleast-squares(OLS)modelsofHRQOLcontrollingfordemographicsandillnesscharacteristicswerespecified,andOLSregressioncoefficientsandstatisticalinferenceswerecompared.
Model1included1variableofhypoglycemiasymptoms;Model2includedbothhypoglycemiasymptomsandHFSscore.
Results:Of3999patientscontacted,813respondedtothesurvey.
Model1:hypoglycemiasymptomsalonewereassociatedwithworseHRQOL(SF-12MCSandSF-12PCSscoresandEQ-5Dutilityscore;allP10pointsofHFStotalscore,P0.
05).
Model2showedthattheHFSscorewasstillsignificantlyassociatedwithscoresonall3HRQOLoutcomes(eachP0.
05).
Forsulfonylureausers(n=246),Model1showedthatthesymptomatichypoglycemiawasassociatedwithEQ-5DscoresandSF-12MCSscores(eachP1020(8.
6)69(12.
0)EthnicityWhiteNo52(22.
5)161(28.
3)0.
0961Yes179(77.
5)409(71.
8)BlackorAfricanAmericanNo196(84.
9)469(82.
3)0.
3806Yes35(15.
2)101(17.
7)HispanicorLatinoNo209(89.
7)525(92.
3)0.
2360Yes24(10.
3)44(7.
7)MaritalstatusSingle,nevermarried25(10.
7)68(11.
8)0.
6079Married167(71.
4)390(67.
7)Divorced32(13.
7)82(14.
2)Separated2(0.
9)14(2.
4)Widowed8(3.
4)22(3.
8)Annualhouseholdincome,$US100,00063(28.
4)142(25.
9)Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page4of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167Table1Populationcharacteristicsbetweenpatientswhoreportedversusthosewhodidnotreportsymptomsofhypoglycemia(Continued)EducationLessthansecondary9(3.
9)14(2.
5)0.
8425Somesecondary4(1.
7)14(2.
5)Secondaryorequivalent53(22.
8)131(22.
9)Tertiarybutnodegree60(25.
8)166(29.
0)2-yearundergraduatedegree28(12.
0)59(10.
3)>2-yearundergraduatedegree51(21.
9)199(20.
8)Graduateschool28(12.
0)69(12.
1)USRegionNortheast13(5.
5)33(5.
7)0.
2144Midwest29(12.
3)54(9.
3)South181(77.
0)440(76.
1)West12(5.
1)51(8.
8)MoriskyadherenceLow123(52.
8)265(46.
3)0.
3058Relativelylow71(30.
5)186(32.
5)Middle28(12.
0)77(13.
4)Relativelyhigh10(4.
3)36(6.
3)High1(0.
4)9(1.
6)OAD=oralantidiabeticmedication;SU=sulfonylurea.
*Chi-squaretest.
SF-12PCSNoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia0102030405060HFSNoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia010203040*NoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia0.
00.
20.
40.
60.
81.
01.
2*EQ-5DSF-12MCSNoHypoglycemiaHypoglycemia0102030405060*Figure1Comparisonofhealth-relatedquality-of-lifescoresandfearofhypoglycemiabetweenpatientswhoreported(n=235)vsthosewhodidnotreport(n=578)symptomsofhypoglycemia.
EQ-5D=EuroQol-5Dscale;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
*P<0.
0001,P=0.
0007byttest.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page5of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167shownanassociationbetweenfearofhypoglycemiaandHRQOL[29,32].
Asignificantassociationwasobservedbetweensymp-tomatichypoglycemiaandEQ-5DandSF-12MCSscoresinModel1,whereasonlytheassociationwithSF-12MCSwassignificantafterincorporatingtheHFSintothemodel.
Incontrast,fearofhypoglycemiademon-stratedasignificantassociationwithall3HRQOLout-comes.
Thisfindingsuggeststhat,statistically,fearofhypoglycemiamaybeamoreimportantpredictorthanhypoglycemiaitselfofpatientwell-beingandhealthstatus.
Multiplefactorsassociatedwithfearofhypoglycemiawereidentified.
Consistentwithourstudy[16]andotherreports[29,31,33],symptomatichypoglycemiahadthestrongest(positive)associationwithfearofhypoglycemia.
Thus,itappearsthatinpatientswithtype2diabetes,ex-periencinganeventofhypoglycemiaincreasesratherthandiminishesfearofsuchanevent.
AnimportantclinicalpracticeimplicationofthisfindingistheneedforTable2InfluencingfactorsofhypoglycemiafearsurveytotalscoresVariable(reference)RegressioncoefficientStandarderrorPvalue95%CILowerUpperHypoglycemia10.
471.
28<0.
00017.
9512.
99Age(<65y)≥65y1.
231.
910.
524.
982.
51Sex(male)Female1.
761.
230.
154.
170.
66Bodymassindex0.
100.
080.
220.
250.
06Familyhistoryofdiabetes0.
581.
370.
673.
272.
10Treatment(SUwithoutinsulin)Non-SUOADwithoutinsulin2.
251.
440.
125.
090.
58AnyOADwithinsulin2.
091.
420.
140.
714.
89Durationofcurrentdiabetesmedication0.
700.
470.
141.
630.
23EthnicityWhite(notwhite)4.
561.
35<0.
00017.
221.
91HispanicorLatino(notHispanicorLatino)4.
742.
130.
030.
568.
92Married(currentlynotmarried)0.
041.
290.
972.
592.
50Householdincomelevel1.
940.
47<0.
00012.
861.
03Education(lessthansecondary)0.
753.
560.
836.
257.
75Region(Northeast)Midwest1.
242.
820.
664.
296.
77South1.
412.
330.
553.
175.
99West0.
213.
140.
955.
966.
37Diabetesduration(y)0.
360.
08<0.
00010.
200.
52Moriskyadherence1.
720.
60<0.
00010.
542.
91OAD=oralantidiabeticmedication;SU=sulfonylurea.
Table3Roleofhypoglycemiafearonhealth-relatedqualityoflifeusingalternativemodelsVariableEQ-5D(US)SF-12MCSSF-12PCSβPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforβModel1Hypo0.
0410.
0020.
067to0.
0153.
628<0.
00015.
259to1.
9980.
9740.
2472.
623to0.
675Model2Hypo0.
0140.
3030.
040to0.
0131.
9370.
0223.
591to0.
2830.
5790.
5001.
104to2.
262HFS0.
003<0.
00010.
003to0.
0020.
162<0.
00010.
210to0.
1150.
149<0.
00010.
197to0.
101β=regressioncoefficient;EQ=EuroQol;Hypo=symptomatichypoglycemia;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page6of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167healthcareprofessionalstobecognizantofthefearofhypoglycemiaandtakestepstoaddressthisfearandre-latedbehaviors.
Inthecurrentanalysis,Hispanic/Latinoethnicity,dur-ationofdiabetes,andself-reportedadherencealsoshowedapositiveassociationwithfearofhypoglycemia,whereashouseholdincomeandwhiteraceshowedanegativeassociation.
Thesedatasuggestthatdemo-graphicvariablesmightbehelpfulinpredictingthosepatientsmostlikelytoexperiencefearofhypoglycemia.
Thepositiveassociationbetweendurationofdiabetesandfearofhypoglycemiacouldreflectgreaterinsulinuseinpatientswithalongerdurationofdisease.
Alter-natively,anindependentassociationbetweenthesevari-ableswouldseemtofurtherindicatethatexperiencinghypoglycemiaincreasesfearoftheevent.
Asnocausalitycanbeinferredinthiscross-sectionalanalysis,thepositiverelationshipbetweenself-reportedadherenceandfearofhypoglycemiaisdifficulttointer-pret.
Inapreviousstudy,patientsreportinghypoglycemiasymptomsweremorelikelytoreportbarrierstoadher-ence(eg,botheredbymedicationsideeffects,unabletofollowplans)[4].
Inaddition,datasuggestthatpatientswhohaveexperiencedahypoglycemicepisodearelikelytoinitiatepreventivebehaviorsthatmayincludemodifica-tionoftheirdosingregimen[14,16].
Althoughthesefind-ingsmayseematoddswithoneanother,itisreasonabletoexpectthatpatientsadherenttostrictglycemiccontrolregimenswouldhavemorereasontobefearfulofhypoglycemia.
Additionalstudieswithlongitudinaldatacollectionareneededtofullyunderstandthevariablesthatpredictfearofhypoglycemia.
Predictorsofhypoglycemiainpatientswithtype2dia-betesarebetterunderstood.
Inthecurrentanalysis,morewomenversusmenandmorepatientstreatedwithOADplusinsulinversussulfonylureawithoutinsulinornonsul-fonylureaOADwithoutinsulinreportedhypoglycemia.
Thedifferenceinhypoglycemiawithrespecttodiabetestherapyistobeexpected,giventhatinsulinandinsulinse-cretagoguesarethemostcommoncauseofhypoglycemiainpatientswithtype2diabetes[15].
Theobservationthatmorewomenthanmenreportedhypoglycemicsymptomswasunexpectedbuthasbeenobservedinanotherstudy[29]andcouldpossiblyreflectsex-relateddifferencesinself-reportingofhypoglycemicsymptoms.
Thisanalysishassomelimitations.
Becausethestudywascross-sectional,nocausalrelationshipscanbein-ferredfromthefindings.
Dataonthefrequencyandse-verityofhypoglycemicepisodeswerenotcollectedsotheircontributiontofearofhypoglycemiacouldnotbeassessed.
Also,becausethesurveydesignusedacon-veniencesampleofpatientsthatincludedonlythosewhoweremembersofspecifichealthplans,withvolun-taryparticipation,surveyparticipantsmaynotberepre-sentativeofallpatientswithtype2diabetes.
Thestudyalsoreliedonpatientself-report,andthesurveyhadapatientrecallperiodof6months.
LongitudinalcohortstudiesarewarrantedtofurtherunderstandtheimpactofhypoglycemiaandtotestpotentialinterventionstoaddresstheissueofhypoglycemiafeartoimprovehealthTable4Roleofhypoglycemiafearonhealth-relatedqualityoflifeusingalternativemodels(InsulinSubgroup)VariableEQ-5D(US)SF-12MCSSF-12PCSβPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforβModel1Hypo0.
0010.
960.
058to0.
0552.
5060.
1375.
813to0.
8011.
6680.
3595.
244to1.
908Model2Hypo0.
0290.
3110.
027to0.
0860.
2850.
8633.
534to2.
9650.
3580.
8474.
011to3.
296HFS0.
003<0.
0010.
004to0.
0010.
188<0.
00010.
259to0.
1160.
111<0.
0070.
191to0.
031β=regressioncoefficient;EQ=EuroQol;Hypo=symptomatichypoglycemia;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
Table5Roleofhypoglycemiafearonhealth-relatedqualityoflifeusingalternativemodels(SulfonylureaSubgroup)VariableEQ-5D(US)SF-12MCSSF-12PCSβPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforββPvalue95%CIforβModel1Hypo0.
0770.
0010.
123to0.
0316.
531<0.
0019.
606to3.
4561.
8150.
2414.
857to1.
226Model2Hypo0.
0600.
0140.
107to-0.
0135.
3000.
0018.
453to2.
1470.
0560.
9712.
973to3.
084HFS0.
0020.
0140.
004to0.
0000.
1400.
0080.
243to0.
0380.
213<0.
0010.
311to0.
114β=regressioncoefficient;EQ=EuroQol;Hypo=symptomatichypoglycemia;HFS=HypoglycemiaFearSurvey;MCS=MentalComponentSummary;PCS=PhysicalComponentSummary;SF-12=12-itemShortFormHealthSurvey.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page7of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167forpatientswithdiabetes.
Inconclusion,inadditiontosymptomatichypoglycemiaitself,fearofhypoglycemiawasindependentlyassociatedwithlowerHRQOL(over-allhealthstatus,mentalhealth,andphysicalhealth)inpatientswithtype2diabetes.
Thereisanunmetneedforpatienteducationprogramsthataddresspatientfearofhypoglycemiaanduseofmedicationswithalowerriskofhypoglycemia.
AdditionalfileAdditionalfile1:TableS1.
1FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel1:EQ-5D(US).
TableS1.
2FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel1:SF-12MCS.
TableS1.
3FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel1:SF-12PCS.
TableS1.
4FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel2:EQ-5D(US).
TableS1.
5FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel2:SF-12MCS.
TableS1.
6FullySpecifiedHypoglycemiaModel2:SF-12PCS.
TableS2.
0HypoglycemiaModel1:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS2.
1HypoglycemiaModel1:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS2.
2HypoglycemiaModel1:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
TableS2.
3HypoglycemiaModel2:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS2.
4HypoglycemiaModel2:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS2.
5HypoglycemiaModel2:InsulinSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
TableS3.
0HypoglycemiaModel1:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS3.
1HypoglycemiaModel1:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS3.
2HypoglycemiaModel1:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
TableS3.
3HypoglycemiaModel2:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbyEQ-5D(US).
TableS3.
4HypoglycemiaModel2:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12MCS.
TableS3.
5HypoglycemiaModel2:SulfonylureaSubgroupMeasuredbySF-12PCS.
CompetinginterestsTheauthorsdeclarethattheyhavenocompetinginterests.
Authors'contributionsLSistheguarantorofthisarticle.
HSperformeddataanalysis.
YZreviewedtheresultsandimprovedmodelspecifications.
LS,HS,YZ,andNATreviewed,edited,andapprovedthemanuscript.
AcknowledgmentsTheauthorsthankVivianFonseca,MD,forhishelpfuldiscussionsduringthedevelopmentofthisstudy.
Allauthorscontributedtotheconceptanddesignofthestudy;theacquisition,analysis,andinterpretationofdata;developmentofthestatisticalanalysisplan;andreview/editingofthemanuscriptforcontent.
Allauthorshadfullaccesstothedataincludedinthemanuscriptandapprovedthefinalversion.
L.
S.
hasreceivedgrants(toTulane)fromNovartis,Takeda,andGenentechandhasreceivedhonorariaforconsultingfromAstraZeneca.
N.
A.
TisanemployeeofBristol-MyersSquibb.
Y.
Z.
andH.
S.
reportnopotentialconflicts.
ThestudywassponsoredbyAstraZeneca(Wilmington,DE).
MedicalwritingsupportforthepreparationofthismanuscriptwasprovidedbyDeborahM.
Campoli-Richards,BSPharm,RPh,NicoleStrangman,PhD,andJanetE.
Matsuura,PhD,ofCompleteHealthcareCommunications,Inc.
(ChaddsFord,PA),withfundingfromBristol-MeyersSquibbandAstraZeneca.
DatafromthisstudywerepresentedattheInternationalSocietyforPharmacoeconomicsandOutcomesResearch18thAnnualInternationalMeeting,May18–22,2013,NewOrleans,LA.
Authordetails1DepartmentofGlobalHealthSystemsandDevelopment,TulaneUniversitySchoolofPublicHealthandTropicalMedicine,NewOrleans,LA,USA.
2CollegeofPharmacy,XavierUniversityofLouisiana,NewOrleans,LA,USA.
3USHealthServicesResearch,Bristol-MyersSquibb,Princeton,NJ,USA.
Received:5May2014Accepted:6November2014References1.
ZhaoY,CampbellCR,FonsecaV,ShiL:Impactofhypoglycemiaassociatedwithantihyperglycemicmedicationsonvascularrisksinveteranswithtype2diabetes.
DiabetesCare2012,35:1126–1132.
2.
ZoungasS,PatelA,ChalmersJ,DeGalanBE,LiQ,BillotL,WoodwardM,NinomiyaT,NealB,MacMahonS,GrobbeeDE,PascalKengneA,MarreM,HellerS:Severehypoglycemiaandrisksofvasculareventsanddeath.
NEnglJMed2010,363:1410–1418.
3.
HsuPF,SungSH,ChengHM,YehJS,LiuWL,ChanWL,ChenCH,ChouP,ChuangSY:Associationofclinicalsymptomatichypoglycemiawithcardiovasculareventsandtotalmortalityintype2diabetes:anationwidepopulation-basedstudy.
DiabetesCare2013,36:894–900.
4.
AlvarezGuisasolaF,TofePovedanoS,KrishnarajahG,LyuR,MavrosP,YinD:Hypoglycaemicsymptoms,treatmentsatisfaction,adherenceandtheirassociationswithglycaemicgoalinpatientswithtype2diabetesmellitus:findingsfromtheReal-LifeEffectivenessandCarePatternsofDiabetesManagement(RECAP-DM)study.
DiabetesObesMetab2008,10:25–32.
5.
MarrettE,StargardtT,MavrosP,AlexanderCM:Patient-reportedoutcomesinasurveyofpatientstreatedwithoralantihyperglycaemicmedications:associationswithhypoglycaemiaandweightgain.
DiabetesObesMetab2009,11:1138–1144.
6.
PollackMF,PurayidathilFW,BolgeSC,WilliamsSA:Patient-reportedtolerabilityissueswithoralantidiabeticagents:associationswithadherence;treatmentsatisfactionandhealth-relatedqualityoflife.
DiabetesResClinPract2010,87:204–210.
7.
GreenAJ,FoxKM,GrandyS:Self-reportedhypoglycemiaandimpactonqualityoflifeanddepressionamongadultswithtype2diabetesmellitus.
DiabetesResClinPract2012,96:313–318.
8.
WilliamsSA,PollackMF,DiBonaventuraM:Effectsofhypoglycemiaonhealth-relatedqualityoflife,treatmentsatisfactionandhealthcareresourceutilizationinpatientswithtype2diabetesmellitus.
DiabetesResClinPract2011,91:363–370.
9.
InzucchiSE,BergenstalRM,BuseJB,DiamantM,FerranniniE,NauckM,PetersAL,TsapasA,WenderR,MatthewsDR:Managementofhyperglycemiaintype2diabetes:apatient-centeredapproach:positionstatementoftheAmericanDiabetesAssociation(ADA)andtheEuropeanAssociationfortheStudyofDiabetes(EASD).
DiabetesCare2012,35:1364–1379.
10.
BruntonSA:Hypoglycemicpotentialofcurrentandemergingpharmacotherapiesintype2diabetesmellitus.
PostgradMed2012,124:74–83.
11.
CryerPE:Hypoglycemia:stillthelimitingfactorintheglycemicmanagementofdiabetes.
EndocrPract2008,14:750–756.
12.
WildD,vonMaltzahnR,BrohanE,ChristensenT,ClausonP,Gonder-FrederickL:Acriticalreviewoftheliteratureonfearofhypoglycemiaindiabetes:implicationsfordiabetesmanagementandpatienteducation.
PatientEducCouns2007,68:10–15.
13.
PetterssonB,RosenqvistU,DeleskogA,JournathG,WandellP:Self-reportedexperienceofhypoglycemiaamongadultswithtype2diabetesmellitus(Exhype).
DiabetesResClinPract2011,92:19–25.
14.
LeiterLA,YaleJ,ChiassonJ,HarrisS,KleinstiverP,SauriolL:Assessmentoftheimpactoffearofhypoglycemicepisodesonglycemicandhypoglycemiamanagement.
CanJDiabetes2005,29:186–192.
15.
AmielSA,DixonT,MannR,JamesonK:Hypoglycaemiaintype2diabetes.
DiabetMed2008,25:245–254.
16.
WilliamsSA,ShiL,BrennemanSK,JohnsonJC,WegnerJC,FonsecaV:Theburdenofhypoglycemiaonhealthcareutilization,costs,andqualityoflifeamongtype2diabetesmellituspatients.
JDiabetesComplications2012,26:399–406.
17.
MoriskyDE,GreenLW,LevineDM:Concurrentandpredictivevalidityofaself-reportedmeasureofmedicationadherence.
MedCare1986,24:67–74.
18.
CoxDJ,IrvineA,Gonder-FrederickL,NowacekG,ButterfieldJ:Fearofhypoglycemia:quantification,validation,andutilization.
DiabetesCare1987,10:617–621.
19.
MatzaLS,BoyeKS,YurginN:Validationoftwogenericpatient-reportedoutcomemeasuresinpatientswithtype2diabetes.
HealthQualLifeOutcomes2007,5:47.
Shietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page8of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/16720.
WhatisEQ-5D[http://www.
euroqol.
org].
21.
WareJJr,KosinskiM,KellerSD:A12-itemshort-formhealthsurvey:constructionofscalesandpreliminarytestsofreliabilityandvalidity.
MedCare1996,34:220–233.
22.
Livingwithdiabetes.
[http://www.
diabetes.
org/living-with-diabetes/treatment-and-care/blood-glucose-control/hypoglycemia-low-blood.
html]23.
SASInstituteInc:SAS/STATUser'sGuide.
Version9.
2.
Cary,NC:SASInstituteInc;2008.
24.
WrobelMP,WystrychowskiG,PsurekA,Szymborska-KajanekA,StrojekK:Associationbetweenhypoglycemiaandthetypeofinsulinindiabeticpatientstreatedwithmultipleinjections:anobservationalstudy.
PolArchMedWewn2014,124:173–179.
25.
PitsillidesAN,AndersonSM,KovatchevB:Hypoglycemiariskandglucosevariabilityindicesderivedfromroutineself-monitoringofbloodglucosearerelatedtolaboratorymeasuresofinsulinsensitivityandepinephrinecounterregulation.
DiabetesTechnolTher2011,13:11–17.
26.
KalraS,DeepakMC,NarangP,SinghV,MaheshwariA:Correlationbetweenmeasuresofhypoglycemiaandglycemicimprovementinsulfonylureatreatedpatientswithtype2diabetesinIndia:resultsfromtheOBSTACLEhypoglycemiastudy.
JPostgradMed2014,60:151–155.
27.
OdawaraM,KadowakiT,NaitoY:IncidenceandpredictorsofhypoglycemiainJapanesepatientswithtype2diabetestreatedbyinsulinglargineandoralantidiabeticdrugsinreal-life:ALOHApost-marketingsurveillancestudysub-analysis.
DiabetolMetabSyndr2014,6:20.
28.
SeaquistER,AndersonJ,ChildsB,CryerP,Dagogo-JackS,FishL,HellerSR,RodriguezH,RosenzweigJ,VigerskyR:Hypoglycemiaanddiabetes:areportofaworkgroupoftheAmericanDiabetesAssociationandTheEndocrineSociety.
DiabetesCare2013,36:1384–1395.
29.
MarrettE,RadicanL,DaviesMJ,ZhangQ:Assessmentofseverityandfrequencyofself-reportedhypoglycemiaonqualityoflifeinpatientswithtype2diabetestreatedwithoralantihyperglycemicagents:asurveystudy.
BMCResNotes2011,4:251.
30.
SheuWH,JiLN,NitiyanantW,BaikSH,YinD,MavrosP,ChanSP:Hypoglycemiaisassociatedwithincreasedworryandlowerqualityoflifeamongpatientswithtype2diabetestreatedwithoralantihyperglycemicagentsintheAsia-Pacificregion.
DiabetesResClinPract2012,96:141–148.
31.
StargardtT,Gonder-FrederickL,KrobotKJ,AlexanderCM:Fearofhypoglycaemia:definingaminimumclinicallyimportantdifferenceinpatientswithtype2diabetes.
HealthQualLifeOutcomes2009,7:91.
32.
SolliO,StavemK,KristiansenIS:Health-relatedqualityoflifeindiabetes:theassociationsofcomplicationswithEQ-5Dscores.
HealthQualLifeOutcomes2010,8:18.
33.
MitchellBD,VietriJ,ZagarA,CurtisB,ReaneyM:Hypoglycaemiceventsinpatientswithtype2diabetesintheUnitedKingdom:associationswithpatient-reportedoutcomesandself-reportedHbA1c.
BMCEndocrDisord2013,13:59.
doi:10.
1186/s12955-014-0167-3Citethisarticleas:Shietal.
:Ishypoglycemiafearindependentlyassociatedwithhealth-relatedqualityoflifeHealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes201412:167.
SubmityournextmanuscripttoBioMedCentralandtakefulladvantageof:ConvenientonlinesubmissionThoroughpeerreviewNospaceconstraintsorcolorgurechargesImmediatepublicationonacceptanceInclusioninPubMed,CAS,ScopusandGoogleScholarResearchwhichisfreelyavailableforredistributionSubmityourmanuscriptatwww.
biomedcentral.
com/submitShietal.
HealthandQualityofLifeOutcomes2014,12:167Page9of9http://www.
hqlo.
com/content/12/1/167
- 0.014www.gogo.com相关文档
- 服务www.gogo.com
- fieldwww.gogo.com
- sunwww.gogo.com
- 中国www.gogo.com
- 创业www.gogo.com
- broadwww.gogo.com
TMThosting夏季促销:VPS月付7折,年付65折,独立服务器95折,西雅图机房
TMThosting发布了一个2021 Summer Sale活动,针对西雅图VPS主机提供月付7折优惠码,年付65折优惠码,独立服务器提供95折优惠码,本轮促销活动到7月25日。这是一家成立于2018年的国外主机商,主要提供VPS和独立服务器租用业务,数据中心包括美国西雅图和达拉斯,其中VPS基于KVM架构,都有提供免费的DDoS保护,支持选择Windows或者Linux操作系统。Budget ...

酷锐云香港(19元/月) ,美国1核2G 19元/月,日本独立物理机,
酷锐云是一家2019年开业的国人主机商家,商家为企业运营,主要销售主VPS服务器,提供挂机宝和云服务器,机房有美国CERA、中国香港安畅和电信,CERA为CN2 GIA线路,提供单机10G+天机盾防御,提供美国原生IP,支持媒体流解锁,商家的套餐价格非常美丽,CERA机房月付20元起,香港安畅机房10M带宽月付25元,有需要的朋友可以入手试试。酷锐云自开业以来一直有着良好的产品稳定性及服务态度,支...

半月湾hmbcloud升级500Mbps带宽,原生VPS,$4.99/月
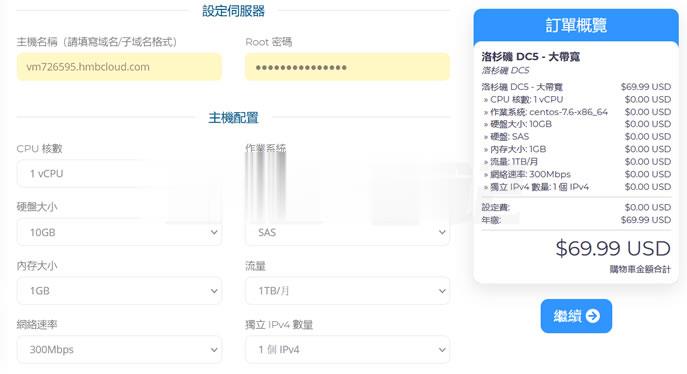
关于半月湾HMBCloud商家之前也有几篇那文章介绍过这个商家的产品,对于他们家的其他产品我都没有多加留意,而是对他们家的DC5机房很多人还是比较喜欢的,这个比我们有些比较熟悉的某商家DC6 DC9机房限时,而且半月湾HMBCloud商家是相对便宜的。关于半月湾DC5机房的方案选择和介绍:1、半月湾三网洛杉矶DC5 CN2 GIA同款DC6 DC9 1G内存 1TB流量 月$4.992、亲测选择半...
www.gogo.com为你推荐
-
工信部约谈电信我在工信部投诉了电信,什么时候才能回复?杨紫别祝我生日快乐一个人过生日的伤感说说有什么钟神发战旗TV ID:新年快乐丶未央不见是哪个主播5xoy.com求个如月群真汉化版下载地址www.baitu.com谁有免费的动漫网站?www.544qq.COM跪求:天时达T092怎么下载QQwww.5any.com重庆哪里有不是全日制的大学?广告法新修订的《广告法》有哪些内容网页源代码网页源代码是什么,具体讲一下?b.faloo.com那有能看完整小说的在线阅读手机网站(我看得都是有删节的,内容勉强连贯)