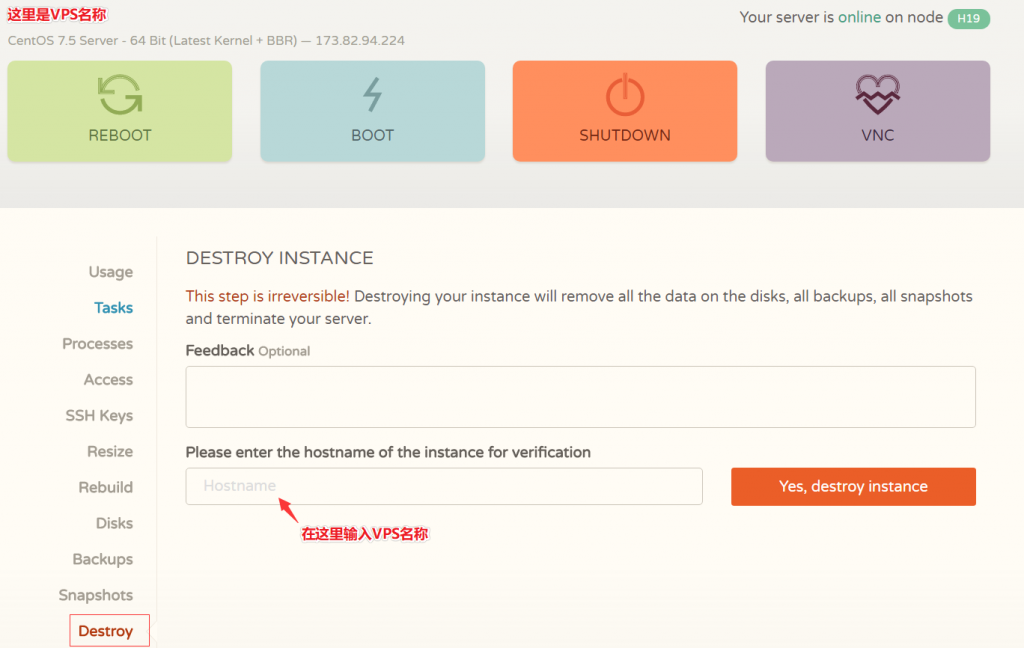
resultantwww.haole008.com
www.haole008.com 时间:2021-04-06 阅读:()
Microstructural,opticalandelectricalpropertiesofCr-dopedZnOShubraSingh,*E.
SenthilKumarandM.
S.
RamachandraRaoDepartmentofPhysicsandMaterialsScienceResearchCentre,IITMadras,Chennai600036,IndiaReceived27September2007;revised6November2007;accepted2January2008Availableonline12January2008UndopedandCr-dopedZnOpolycrystallinesamplesweresynthesizedchemically.
OpticalmeasurementsconrmedthepresenceofCrintheZnOlattice.
Microstructuralstudiesofbulksamplesrevealedanetworkofpetal-likestructuresfoundtobeuniquetoCr-dopedsamples.
ElementalmappingofthesesamplesrevealeduniformdistributionofCrandZnatoms.
Crdopingwasseentosuppresstherecombinationradiationnear385nmandincreasethestabilityofZnOlmsinO2atmosphere.
2008ActaMaterialiaInc.
PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Allrightsreserved.
Keywords:ZnO;Crdoping;Microstructure;Optical;Sol–gelWidebandgapII–VIsemiconductorshavebeenthefocusofinterestofmanyresearchgroupsduringthepastfewyearsduetothepossibilityoftheirapplicationsinlight-emittingdiodes(LEDs)andlaserdiodes.
Thereareavastnumberofbinarycompounds,suchasGaAs,ZnS1ySeyandquaternaryZnxCdyMg1xySealloys,whicharecurrentlyemployedinthedevelopmentofLEDs.
Asaresultoflargereectivemassandlowersta-ticdielectricconstant,thebindingenergyofexcitonsinII–VIsemiconductorsislargecomparedwithsimilarbandgapIII–Vmaterials.
OneofthemostimportantmaterialsinthisfamilyisZnO.
WurtziteZnOhasbeenwidelyusedinopticalapplicationsasithasawidebandgapof3.
4eV.
Itistransparentandhasalargeexcitonbindingenergyof60meV.
Apartfromthevariousopti-calandoptoelectronicapplications,ZnOisalsousedwidelyasacosmeticandantibioticmaterial.
However,forthisparticularapplication,therecombinationradia-tionnear385nmisadeterrent.
ToeliminatetheeectofthisrecombinationradiationintheUVregion,itisnec-essarytodopetransitionmetalionsinZnOinordertoenvisagethepossibilityofshiftingtherecombinationwavelengthtohigherwavelengths.
Inlinewiththis,wehavedopedCrinZnO.
VariousgroupshaveperformedmagneticstudiesonCr-dopedZnOsamples[1,2].
First-principlescalculationsbySatoetal.
indicatethattheferromagneticstateofZnO:Crwouldbemorestablethanaspinglassstate[3],anditwouldalsobemoreenergeticallyfavorablethantheferromagnetisminCo-dopedZnO.
Inthiswork,wepresentthestructural,opticalandtransportpropertiesofCr-dopedandundopedZnO.
High-purityZnOandCr2O3wereusedtoprepareZn1xCrxO(x=0.
01)bychemicalprocessing.
Thechemicalingredientswereweighedinstoichiometricpro-portions,dissolvedinabout50mlofdeionizedwaterandstirredcontinuouslyonamagneticstirrer.
Citricacidwasaddedand,tomaketheresultingsolutioncom-pletelytransparent,afewdrops(about3ml)ofHNO3wereadded.
Thetemperatureofthesolutionwasraisedinsmallsteps(5°Cafterevery2h).
Whenagelwasformed,thetemperaturewasfurtherraisedto100°Ctoboiloanywater.
Afterheattreatmentat600°Ctheresultantsubstancerevealedanetwork-likestruc-ture.
Scanningelectronmicroscopy(SEM)studieswereperformedonthissubstance.
Apartofthesamplewassubsequentlygroundintonepowderandthepowderwasthenmadeintodisc-shapedpellets(8mmindiame-terand2mminthickness)byuniaxialpressing.
Inordertodensifythetargets(usedforthinlmgrowth),thediscsweresinteredat1200°Cfor24h.
ForpulsedlaserdepositiongrowthofCr-dopedZnOlms,asolid-state(NdYAG)laser(laseruence2Jcm2,repetitionrate10Hz)wasused.
Thinlmsweregrownonquartzsub-strateatanoxygenpartialpressureof5106mbarandasubstratetemperatureof500°C.
ThephasepurityofZnOandCr-dopedZnOwasstudiedbyX-raydirac-tion(XRD)usingCuKa1radiation(k=1.
5405A).
Thediusereectancespectra(DRS)atnormalincidenceofpowdersamplesweremeasuredwitha1359-6462/$-seefrontmatter2008ActaMaterialiaInc.
PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Allrightsreserved.
doi:10.
1016/j.
scriptamat.
2008.
01.
008*Correspondingauthor.
Tel.
:+914422575910;e-mail:shubra@physics.
iitm.
ac.
inAvailableonlineatwww.
sciencedirect.
comScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869www.
elsevier.
com/locate/scriptamatspectrophotometer(OceanOpticsUSB2000).
Photolu-minescenceofsampleswasmeasuredusingaFluorogspectrophotometer.
Resistivityofsampleswasmeasuredbylinearfourprobetechnique.
Figure1showsXRDpatternsofdopedandundopedZnO.
Theaveragecrys-tallitesize(Debye–Scherrerformula,Dhkl=kk/(bcosh))forCr-dopedZnOsamples(fullwidthhalfmaximum(FWHM)=0.
26°)wasfoundtobe$385nm,whereasitwas703nmforundopedZnO(FWHM=0.
14°).
Asmallportionoftheas-preparedsample,calcinedat600°C,wascharacterizedbySEM.
Figure2apresentstheSEMimagesofbulkCr-dopedZnO.
Intheinsetahoneycomb-likestructurewithfourbranchesateachnodecanbeseen.
Itwasobservedthatthenetworkcon-sistedofpetal-likestructureswithtaperingends,eachhavinganaveragesizeof$5lm.
Eachpetal-likestruc-turehasasubstructureconsistingofaclusteroflongrodsjoinedtogethertoformlargerpetals.
ThisstructurewasobservedonlyforCr-dopedZnOandnotfortheundopedsample(Fig.
2b),preparedusingthesametech-niqueasthedopedsample.
ThisresultcanbeexplainedonthebasisofionicfractionofthebondinCr-dopedZnO.
Themorphologyofaparticledependsonthevalueoftheionicfractionofthebond.
Takeshietal.
usedtheconceptoftheelectronegativity(EN)(theratioFigure1.
XRDpatternsofundopedandCr-dopedZnObulksamples.
representstheimpuritypeakcorrespondingtoCr2O3.
Figure2.
(a)SEMimagesofCr-dopedZnOatdierentmagnications.
TheinsetshowsthemicrostructureofCr-dopedZnO.
(b)SEMimageofundopedZnO.
Figure3.
ElementalmappingofCr-dopedZnOsampleheatedat600°Cshowingthepresenceof(a)Crand(b)Znions,respectively.
Figure4.
(a)Diusereectancespectra.
(b)EmissionspectraofundopedandCr-dopedZnObulksamples.
Figure5.
(a)Ramanspectra.
(b)RTresistivityofdopedandundopedthinlmsbeforeandafterannealinginO2.
S.
Singhetal.
/ScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869867ofnegativeiontoelectrondensitiesofelements)toesti-matetheionicfractionofthebond.
TheENofZnis1.
65onthePaulingscale,whilethatofCris1.
66onthesamescale,i.
e.
theionicfractionislow($1),givingrisetolongitudinalstructures[4].
ItwasdemonstratedbyTakeshietal.
thatafurtherincreaseintheelectro-negativityofthedopantelement(foraslowas1at.
%doping)canchangethemicrostructurefromlongitudi-naltospherical.
Theseresultsindicatethatthemorphol-ogyoftheparentcompoundwasalteredbythedopingelement.
ElementalmappingoftheCr-dopedsamplere-vealedauniformdistributionofvariousionsinthesam-ple(Fig.
3).
Figure4aandbshowsthediusereectance(DR)andphotoluminescence(PL)spectraofundopedanddopedsamples.
ThevariationofDRnearthebandedgeforthedopedsamplesascomparedwiththeundopedsampleisanindicationofincorporationofCrionsintheZnOlattice.
Themid-band-gapstatesarisingduetoabsorptionat460and580nmcorrespondtothed–dtransitionbandsofCrions.
Thebroadabsorptionbandaround580nmcorrespondstothe4A24T2tran-sition[5].
However,thereectanceintensitywasfoundtoreduceongrindingthenetwork-likestructureandtheresolutionbetweenthetwotransitionsimproved.
Thiscanbeattributedtotheincreasedabsorptioncausedbytheincreaseinsurfaceareaduetothegrind-ing.
ThePLspectrumshowsthatultraviolet(UV)radi-ationwithawavelengthofabout385nm(therecombinationradiationduetotheexciton[6])issup-pressedforthedopedsample.
ThisindicatesthattheCrdopingincreasesthenonradiativerecombinationprocessandthattheexistenceoftransitionmetalionslikeCrcancontroltheexcitonicrecombinationradiation.
Figure5ashowsthenormalizedRamanspectraofthebulkundopedandCr-dopedcompound.
Thespectrarevealsstandardphononmodesat331,381,407,437and579cm1correspondingtoundopedZnO[7,8].
Themodeat655cm1isattributedtoan(E2L+B1H)combinedphononmode[8].
Forthedopedsampletherewasashifttowardsthelow-frequencyside,whichdependsontheresidualstress,structuraldisorderandcrystaldefectofthesamples.
The579cm1modeseemtomergewithanadditionalmodeat609cm1.
Therea-sonfortheappearanceoftheadditionalmodeisnotclearatpresent,butcanbeattributedtothechangesinducedbythedoping.
Weobservedanincreaseinresistivity(Fig.
5b)forCr-dopedZnOsamplesascom-paredwiththeundopedlmsforaslowas1mol.
%dopedZnO(bothincaseofthinlmandbulk).
ThemobilityoftheundopedZnOthinlmswasfoundtobe145cm2V1s1,whileforCr-dopedZnOlmsitwas90cm2V1s1.
Thiscanbeattributedtothepres-enceoftheCrintheZnO,whichaectsgraingrowth(wellknownasCrpoisoning)anddecreasesthecarriermobility(aswecanseefromtheaboveresults)duetocarrierscatteringatthegrainboundaries[9].
Thismayleadtoanincreaseinresistivityforbulkaswellasdopedlms.
TEMimagesofas-preparedundopedandCr-dopedZnOthinlms(Fig.
6aandb)alsoshowthattheaverageparticlesizeissmallerinthecaseoftheCr-dopedthinlms.
UndopedandCr-dopedZnOlmswerefurtherannealedinanoxygenatmosphereexsitufor5htoobserveanychangesinresistivity.
Figure5balsoshowsacomparisonofroomtemperatureresistivityvaluesofdopedandundopedthinlmsbeforeandafteranneal-ing.
Theresistivityofundopedlmincreasedconsider-ablyuponannealinginoxygenwhereasCr-dopedthinlmdidnotshowanyconsiderablechange.
Theincreaseinresistivityfortheundopedsampleinanoxygenatmo-spheremaybeattributedtochangesinthepotentialheightatthegrainboundaries[9],whichshowsthatCrdopingimprovesthestabilityofgrainboundariesun-derexposuretotheoxygenatmosphere.
Energy-disper-siveX-rayanalysis(EDX)onsamplesalsoshowedthatboththeundopedandCr-dopedsamplesareoxy-gendecient(EDXonlmsrevealedthepresenceof16.
55%ofoxygenbyweightinundopedZnOand18.
06%ofoxygenbyweightinCr-dopedZnO),andthatitmaynotberesponsibleforsuchalargevariationinelectricalbehaviourbetweenundopedanddopedsam-pleswhenannealedinoxygenatmosphere.
Inthisworktransitionmetal(Cr)wasdopedintotheZnOlatticeandthiswasconrmedbyopticalstudiessuchasPL,aswellasDRSstudies.
BydopingtransitionmetalionsintoZnOmatrix,UVradiationwithawave-lengthshorterthan385nmwasalmosteliminated.
Themicrostructureofthedopedsampleat600°Cexhibitsanetwork-likestructure.
WealsondthatCrdopingin-creasesthestabilityofZnOlmsunderexposuretoanoxygenatmosphere.
[1]BradleyK.
Roberts,AlexandreB.
Pakhomov,Vaithiya-lingamS.
Shutthanandan,KannanM.
Krishnan,J.
Appl.
Phys.
97(2005)10D310.
[2]ZhengwuJin,K.
Hasegawa,T.
Fukumura,Y.
Z.
Yoo,T.
Hasegawab,H.
Koinuma,M.
Kawasaki,PhysicaE10(2001)256–259.
Figure6.
TEMimagesofas-prepared(a)undopedand(b)Cr-dopedZnOthinlms.
868S.
Singhetal.
/ScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869[3]K.
Sato,H.
Katayama-Yoshida,Semicond.
Sci.
Technol.
17(2002)367.
[4]TakeshiSato,HitoshiSuzuki,OsamuKido,MamiKuru-mada,KatsuyaKamitsuji,YukiKimura,HiromichiKawa-saki,SatooKaneko,YoshioSaitod,ChihiroKaito,J.
Cryst.
Growth275(2005)e983–e987.
[5]M.
Jakani,G.
Campet,J.
Claverie,D.
Fichou,J.
Pouli-quen,J.
Kossanyi,J.
SolidStateChem.
56(1985)269–277.
[6]S.
F.
Chichibu,T.
Sota,G.
Cantwell,D.
B.
Eason,C.
W.
Litton,J.
Appl.
Phys.
93(2003)756.
[7]C.
Sudakar,P.
Kharel,G.
Lawes,R.
Suryanarayanan,R.
Naik,V.
M.
Naik,J.
Phys.
:Condens.
Matter19(2007)026212.
[8]J.
D.
Ye,S.
L.
Gu,S.
M.
Zhu,S.
M.
Liu,Y.
D.
Zheng,R.
Zhang,Y.
Shi,Q.
Chen,H.
Q.
Yu,Y.
D.
Ye,Appl.
Phys.
Letts.
88(2006)101905.
[9]K.
Tominaga,T.
Takaoa,A.
Fukushima,T.
Morigab,I.
Nakabayashib,Vacuum66(2002)511–515.
S.
Singhetal.
/ScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869869
SenthilKumarandM.
S.
RamachandraRaoDepartmentofPhysicsandMaterialsScienceResearchCentre,IITMadras,Chennai600036,IndiaReceived27September2007;revised6November2007;accepted2January2008Availableonline12January2008UndopedandCr-dopedZnOpolycrystallinesamplesweresynthesizedchemically.
OpticalmeasurementsconrmedthepresenceofCrintheZnOlattice.
Microstructuralstudiesofbulksamplesrevealedanetworkofpetal-likestructuresfoundtobeuniquetoCr-dopedsamples.
ElementalmappingofthesesamplesrevealeduniformdistributionofCrandZnatoms.
Crdopingwasseentosuppresstherecombinationradiationnear385nmandincreasethestabilityofZnOlmsinO2atmosphere.
2008ActaMaterialiaInc.
PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Allrightsreserved.
Keywords:ZnO;Crdoping;Microstructure;Optical;Sol–gelWidebandgapII–VIsemiconductorshavebeenthefocusofinterestofmanyresearchgroupsduringthepastfewyearsduetothepossibilityoftheirapplicationsinlight-emittingdiodes(LEDs)andlaserdiodes.
Thereareavastnumberofbinarycompounds,suchasGaAs,ZnS1ySeyandquaternaryZnxCdyMg1xySealloys,whicharecurrentlyemployedinthedevelopmentofLEDs.
Asaresultoflargereectivemassandlowersta-ticdielectricconstant,thebindingenergyofexcitonsinII–VIsemiconductorsislargecomparedwithsimilarbandgapIII–Vmaterials.
OneofthemostimportantmaterialsinthisfamilyisZnO.
WurtziteZnOhasbeenwidelyusedinopticalapplicationsasithasawidebandgapof3.
4eV.
Itistransparentandhasalargeexcitonbindingenergyof60meV.
Apartfromthevariousopti-calandoptoelectronicapplications,ZnOisalsousedwidelyasacosmeticandantibioticmaterial.
However,forthisparticularapplication,therecombinationradia-tionnear385nmisadeterrent.
ToeliminatetheeectofthisrecombinationradiationintheUVregion,itisnec-essarytodopetransitionmetalionsinZnOinordertoenvisagethepossibilityofshiftingtherecombinationwavelengthtohigherwavelengths.
Inlinewiththis,wehavedopedCrinZnO.
VariousgroupshaveperformedmagneticstudiesonCr-dopedZnOsamples[1,2].
First-principlescalculationsbySatoetal.
indicatethattheferromagneticstateofZnO:Crwouldbemorestablethanaspinglassstate[3],anditwouldalsobemoreenergeticallyfavorablethantheferromagnetisminCo-dopedZnO.
Inthiswork,wepresentthestructural,opticalandtransportpropertiesofCr-dopedandundopedZnO.
High-purityZnOandCr2O3wereusedtoprepareZn1xCrxO(x=0.
01)bychemicalprocessing.
Thechemicalingredientswereweighedinstoichiometricpro-portions,dissolvedinabout50mlofdeionizedwaterandstirredcontinuouslyonamagneticstirrer.
Citricacidwasaddedand,tomaketheresultingsolutioncom-pletelytransparent,afewdrops(about3ml)ofHNO3wereadded.
Thetemperatureofthesolutionwasraisedinsmallsteps(5°Cafterevery2h).
Whenagelwasformed,thetemperaturewasfurtherraisedto100°Ctoboiloanywater.
Afterheattreatmentat600°Ctheresultantsubstancerevealedanetwork-likestruc-ture.
Scanningelectronmicroscopy(SEM)studieswereperformedonthissubstance.
Apartofthesamplewassubsequentlygroundintonepowderandthepowderwasthenmadeintodisc-shapedpellets(8mmindiame-terand2mminthickness)byuniaxialpressing.
Inordertodensifythetargets(usedforthinlmgrowth),thediscsweresinteredat1200°Cfor24h.
ForpulsedlaserdepositiongrowthofCr-dopedZnOlms,asolid-state(NdYAG)laser(laseruence2Jcm2,repetitionrate10Hz)wasused.
Thinlmsweregrownonquartzsub-strateatanoxygenpartialpressureof5106mbarandasubstratetemperatureof500°C.
ThephasepurityofZnOandCr-dopedZnOwasstudiedbyX-raydirac-tion(XRD)usingCuKa1radiation(k=1.
5405A).
Thediusereectancespectra(DRS)atnormalincidenceofpowdersamplesweremeasuredwitha1359-6462/$-seefrontmatter2008ActaMaterialiaInc.
PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Allrightsreserved.
doi:10.
1016/j.
scriptamat.
2008.
01.
008*Correspondingauthor.
Tel.
:+914422575910;e-mail:shubra@physics.
iitm.
ac.
inAvailableonlineatwww.
sciencedirect.
comScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869www.
elsevier.
com/locate/scriptamatspectrophotometer(OceanOpticsUSB2000).
Photolu-minescenceofsampleswasmeasuredusingaFluorogspectrophotometer.
Resistivityofsampleswasmeasuredbylinearfourprobetechnique.
Figure1showsXRDpatternsofdopedandundopedZnO.
Theaveragecrys-tallitesize(Debye–Scherrerformula,Dhkl=kk/(bcosh))forCr-dopedZnOsamples(fullwidthhalfmaximum(FWHM)=0.
26°)wasfoundtobe$385nm,whereasitwas703nmforundopedZnO(FWHM=0.
14°).
Asmallportionoftheas-preparedsample,calcinedat600°C,wascharacterizedbySEM.
Figure2apresentstheSEMimagesofbulkCr-dopedZnO.
Intheinsetahoneycomb-likestructurewithfourbranchesateachnodecanbeseen.
Itwasobservedthatthenetworkcon-sistedofpetal-likestructureswithtaperingends,eachhavinganaveragesizeof$5lm.
Eachpetal-likestruc-turehasasubstructureconsistingofaclusteroflongrodsjoinedtogethertoformlargerpetals.
ThisstructurewasobservedonlyforCr-dopedZnOandnotfortheundopedsample(Fig.
2b),preparedusingthesametech-niqueasthedopedsample.
ThisresultcanbeexplainedonthebasisofionicfractionofthebondinCr-dopedZnO.
Themorphologyofaparticledependsonthevalueoftheionicfractionofthebond.
Takeshietal.
usedtheconceptoftheelectronegativity(EN)(theratioFigure1.
XRDpatternsofundopedandCr-dopedZnObulksamples.
representstheimpuritypeakcorrespondingtoCr2O3.
Figure2.
(a)SEMimagesofCr-dopedZnOatdierentmagnications.
TheinsetshowsthemicrostructureofCr-dopedZnO.
(b)SEMimageofundopedZnO.
Figure3.
ElementalmappingofCr-dopedZnOsampleheatedat600°Cshowingthepresenceof(a)Crand(b)Znions,respectively.
Figure4.
(a)Diusereectancespectra.
(b)EmissionspectraofundopedandCr-dopedZnObulksamples.
Figure5.
(a)Ramanspectra.
(b)RTresistivityofdopedandundopedthinlmsbeforeandafterannealinginO2.
S.
Singhetal.
/ScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869867ofnegativeiontoelectrondensitiesofelements)toesti-matetheionicfractionofthebond.
TheENofZnis1.
65onthePaulingscale,whilethatofCris1.
66onthesamescale,i.
e.
theionicfractionislow($1),givingrisetolongitudinalstructures[4].
ItwasdemonstratedbyTakeshietal.
thatafurtherincreaseintheelectro-negativityofthedopantelement(foraslowas1at.
%doping)canchangethemicrostructurefromlongitudi-naltospherical.
Theseresultsindicatethatthemorphol-ogyoftheparentcompoundwasalteredbythedopingelement.
ElementalmappingoftheCr-dopedsamplere-vealedauniformdistributionofvariousionsinthesam-ple(Fig.
3).
Figure4aandbshowsthediusereectance(DR)andphotoluminescence(PL)spectraofundopedanddopedsamples.
ThevariationofDRnearthebandedgeforthedopedsamplesascomparedwiththeundopedsampleisanindicationofincorporationofCrionsintheZnOlattice.
Themid-band-gapstatesarisingduetoabsorptionat460and580nmcorrespondtothed–dtransitionbandsofCrions.
Thebroadabsorptionbandaround580nmcorrespondstothe4A24T2tran-sition[5].
However,thereectanceintensitywasfoundtoreduceongrindingthenetwork-likestructureandtheresolutionbetweenthetwotransitionsimproved.
Thiscanbeattributedtotheincreasedabsorptioncausedbytheincreaseinsurfaceareaduetothegrind-ing.
ThePLspectrumshowsthatultraviolet(UV)radi-ationwithawavelengthofabout385nm(therecombinationradiationduetotheexciton[6])issup-pressedforthedopedsample.
ThisindicatesthattheCrdopingincreasesthenonradiativerecombinationprocessandthattheexistenceoftransitionmetalionslikeCrcancontroltheexcitonicrecombinationradiation.
Figure5ashowsthenormalizedRamanspectraofthebulkundopedandCr-dopedcompound.
Thespectrarevealsstandardphononmodesat331,381,407,437and579cm1correspondingtoundopedZnO[7,8].
Themodeat655cm1isattributedtoan(E2L+B1H)combinedphononmode[8].
Forthedopedsampletherewasashifttowardsthelow-frequencyside,whichdependsontheresidualstress,structuraldisorderandcrystaldefectofthesamples.
The579cm1modeseemtomergewithanadditionalmodeat609cm1.
Therea-sonfortheappearanceoftheadditionalmodeisnotclearatpresent,butcanbeattributedtothechangesinducedbythedoping.
Weobservedanincreaseinresistivity(Fig.
5b)forCr-dopedZnOsamplesascom-paredwiththeundopedlmsforaslowas1mol.
%dopedZnO(bothincaseofthinlmandbulk).
ThemobilityoftheundopedZnOthinlmswasfoundtobe145cm2V1s1,whileforCr-dopedZnOlmsitwas90cm2V1s1.
Thiscanbeattributedtothepres-enceoftheCrintheZnO,whichaectsgraingrowth(wellknownasCrpoisoning)anddecreasesthecarriermobility(aswecanseefromtheaboveresults)duetocarrierscatteringatthegrainboundaries[9].
Thismayleadtoanincreaseinresistivityforbulkaswellasdopedlms.
TEMimagesofas-preparedundopedandCr-dopedZnOthinlms(Fig.
6aandb)alsoshowthattheaverageparticlesizeissmallerinthecaseoftheCr-dopedthinlms.
UndopedandCr-dopedZnOlmswerefurtherannealedinanoxygenatmosphereexsitufor5htoobserveanychangesinresistivity.
Figure5balsoshowsacomparisonofroomtemperatureresistivityvaluesofdopedandundopedthinlmsbeforeandafteranneal-ing.
Theresistivityofundopedlmincreasedconsider-ablyuponannealinginoxygenwhereasCr-dopedthinlmdidnotshowanyconsiderablechange.
Theincreaseinresistivityfortheundopedsampleinanoxygenatmo-spheremaybeattributedtochangesinthepotentialheightatthegrainboundaries[9],whichshowsthatCrdopingimprovesthestabilityofgrainboundariesun-derexposuretotheoxygenatmosphere.
Energy-disper-siveX-rayanalysis(EDX)onsamplesalsoshowedthatboththeundopedandCr-dopedsamplesareoxy-gendecient(EDXonlmsrevealedthepresenceof16.
55%ofoxygenbyweightinundopedZnOand18.
06%ofoxygenbyweightinCr-dopedZnO),andthatitmaynotberesponsibleforsuchalargevariationinelectricalbehaviourbetweenundopedanddopedsam-pleswhenannealedinoxygenatmosphere.
Inthisworktransitionmetal(Cr)wasdopedintotheZnOlatticeandthiswasconrmedbyopticalstudiessuchasPL,aswellasDRSstudies.
BydopingtransitionmetalionsintoZnOmatrix,UVradiationwithawave-lengthshorterthan385nmwasalmosteliminated.
Themicrostructureofthedopedsampleat600°Cexhibitsanetwork-likestructure.
WealsondthatCrdopingin-creasesthestabilityofZnOlmsunderexposuretoanoxygenatmosphere.
[1]BradleyK.
Roberts,AlexandreB.
Pakhomov,Vaithiya-lingamS.
Shutthanandan,KannanM.
Krishnan,J.
Appl.
Phys.
97(2005)10D310.
[2]ZhengwuJin,K.
Hasegawa,T.
Fukumura,Y.
Z.
Yoo,T.
Hasegawab,H.
Koinuma,M.
Kawasaki,PhysicaE10(2001)256–259.
Figure6.
TEMimagesofas-prepared(a)undopedand(b)Cr-dopedZnOthinlms.
868S.
Singhetal.
/ScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869[3]K.
Sato,H.
Katayama-Yoshida,Semicond.
Sci.
Technol.
17(2002)367.
[4]TakeshiSato,HitoshiSuzuki,OsamuKido,MamiKuru-mada,KatsuyaKamitsuji,YukiKimura,HiromichiKawa-saki,SatooKaneko,YoshioSaitod,ChihiroKaito,J.
Cryst.
Growth275(2005)e983–e987.
[5]M.
Jakani,G.
Campet,J.
Claverie,D.
Fichou,J.
Pouli-quen,J.
Kossanyi,J.
SolidStateChem.
56(1985)269–277.
[6]S.
F.
Chichibu,T.
Sota,G.
Cantwell,D.
B.
Eason,C.
W.
Litton,J.
Appl.
Phys.
93(2003)756.
[7]C.
Sudakar,P.
Kharel,G.
Lawes,R.
Suryanarayanan,R.
Naik,V.
M.
Naik,J.
Phys.
:Condens.
Matter19(2007)026212.
[8]J.
D.
Ye,S.
L.
Gu,S.
M.
Zhu,S.
M.
Liu,Y.
D.
Zheng,R.
Zhang,Y.
Shi,Q.
Chen,H.
Q.
Yu,Y.
D.
Ye,Appl.
Phys.
Letts.
88(2006)101905.
[9]K.
Tominaga,T.
Takaoa,A.
Fukushima,T.
Morigab,I.
Nakabayashib,Vacuum66(2002)511–515.
S.
Singhetal.
/ScriptaMaterialia58(2008)866–869869
- resultantwww.haole008.com相关文档
- equivalentwww.haole008.com
- icalwww.haole008.com
- varyingwww.haole008.com
- recognizedwww.haole008.com
- Sourceswww.haole008.com
- PAwww.haole008.com
CloudCone(20美元/年)大硬盘VPS云服务器,KVM虚拟架构,1核心1G内存1Gbps带宽
近日CloudCone商家对旗下的大硬盘VPS云服务器进行了少量库存补货,也是悄悄推送了一批便宜VPS云服务器产品,此前较受欢迎的特价20美元/年、1核心1G内存1Gbps带宽的VPS云服务器也有少量库存,有需要美国便宜大硬盘VPS云服务器的朋友可以关注一下。CloudCone怎么样?CloudCone服务器好不好?CloudCone值不值得购买?CloudCone是一家成立于2017年的美国服务...
Letbox(35美元/年),美国洛杉矶VPS终身7折
Letbox 云服务商在前面的文章中其实也有多次介绍,这个服务商其实也算是比较老牌的海外服务商,几年前我也一直有使用过他们家的VPS主机,早年那时候低至年付15-35美元左右的VPS算式比较稀缺的。后来由于服务商确实比较多,而且也没有太多的网站需要用到,所以就没有续费,最近这个服务商好像有点活动就躁动的发布希望引起他人注意。这不有看到所谓的家中有喜事,应该是团队中有生宝宝了,所以也有借此来发布一些...
RAKsmart秒杀服务器$30/月,洛杉矶/圣何塞/香港/日本站群特价
RAKsmart发布了9月份优惠促销活动,从9月1日~9月30日期间,爆款美国服务器每日限量抢购最低$30.62-$46/月起,洛杉矶/圣何塞/香港/日本站群大量补货特价销售,美国1-10Gbps大带宽不限流量服务器低价热卖等。RAKsmart是一家华人运营的国外主机商,提供的产品包括独立服务器租用和VPS等,可选数据中心包括美国加州圣何塞、洛杉矶、中国香港、韩国、日本、荷兰等国家和地区数据中心(...

www.haole008.com为你推荐
-
云爆发什么是蒸汽云爆炸?要具备那些条件?mathplayerjavascript 如何判断document.body.innerHTML是否为空同ip网站查询我的两个网站在同一个IP下,没被百度收录,用同IP站点查询工具查询时也找不到我的网站,是何原因?地陷裂口山崩地裂的意思嘀动网动网和爱动网各自的优势是什么?丑福晋谁有好看的言情小说介绍下广告法新广告法哪些广告词不能用,广告违禁词大全yinrentangweichentang产品功效好不好?xvideos..comxvideos 怎么下载汴京清谈汴京还被称为什么?